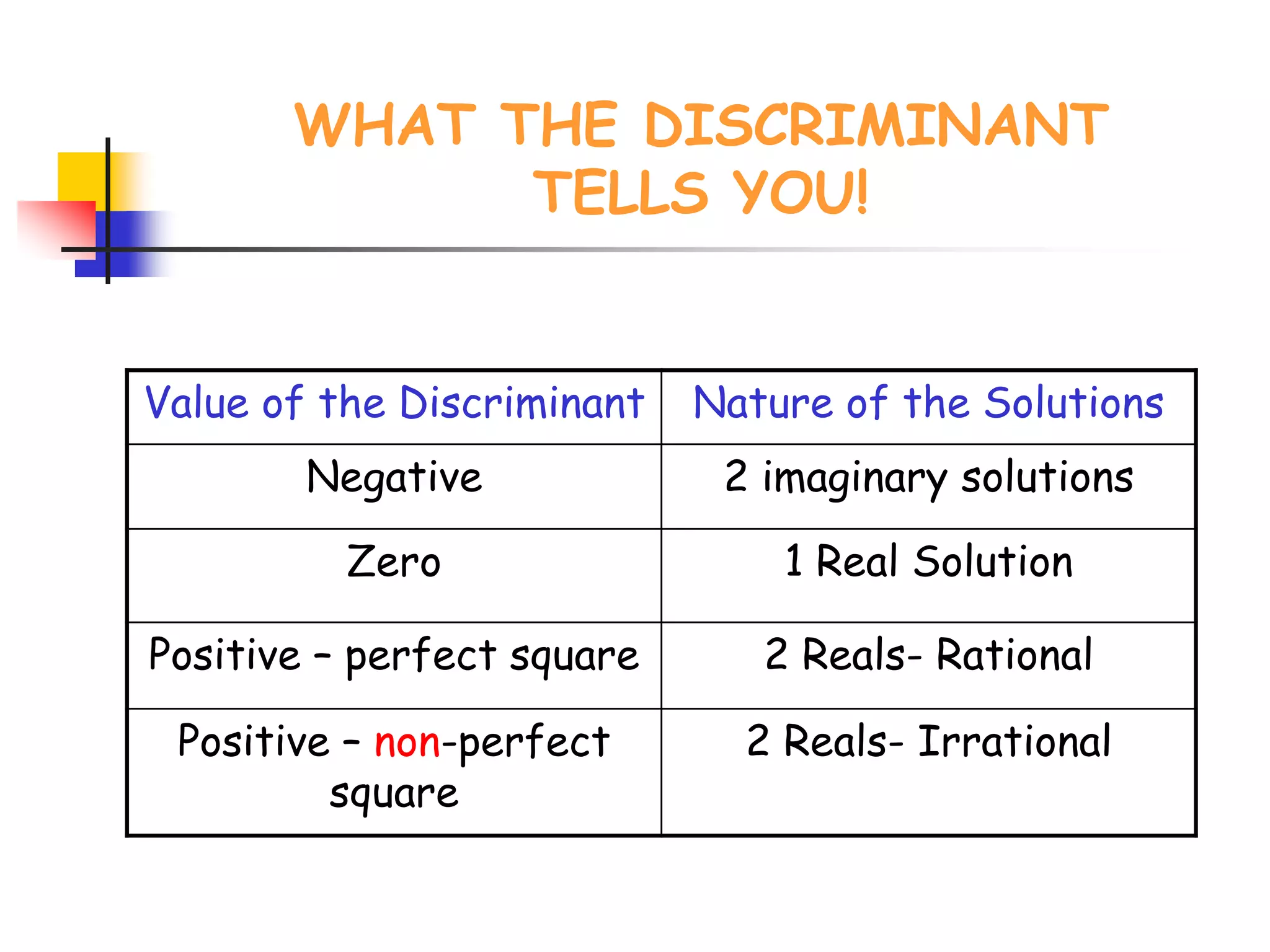
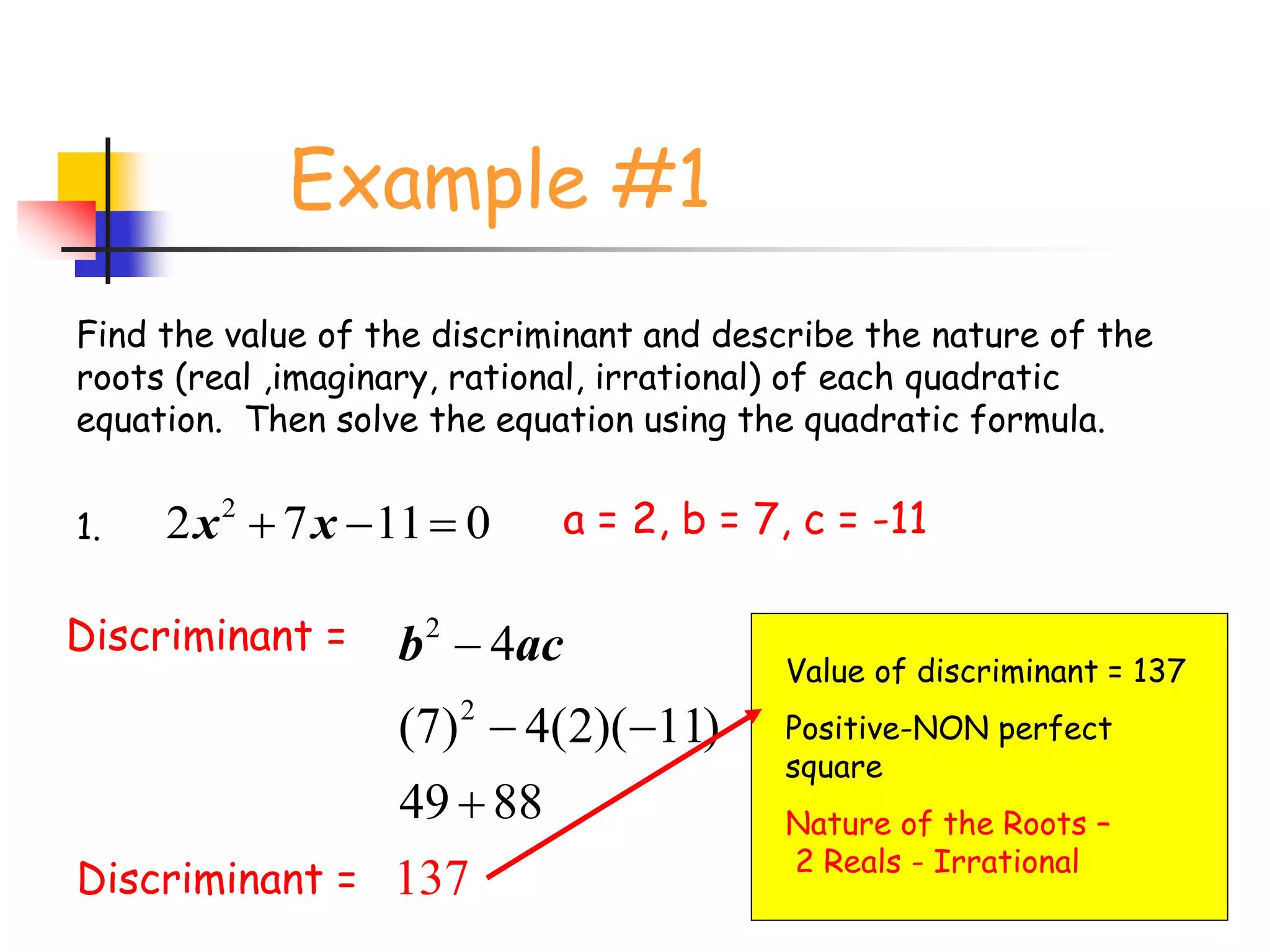
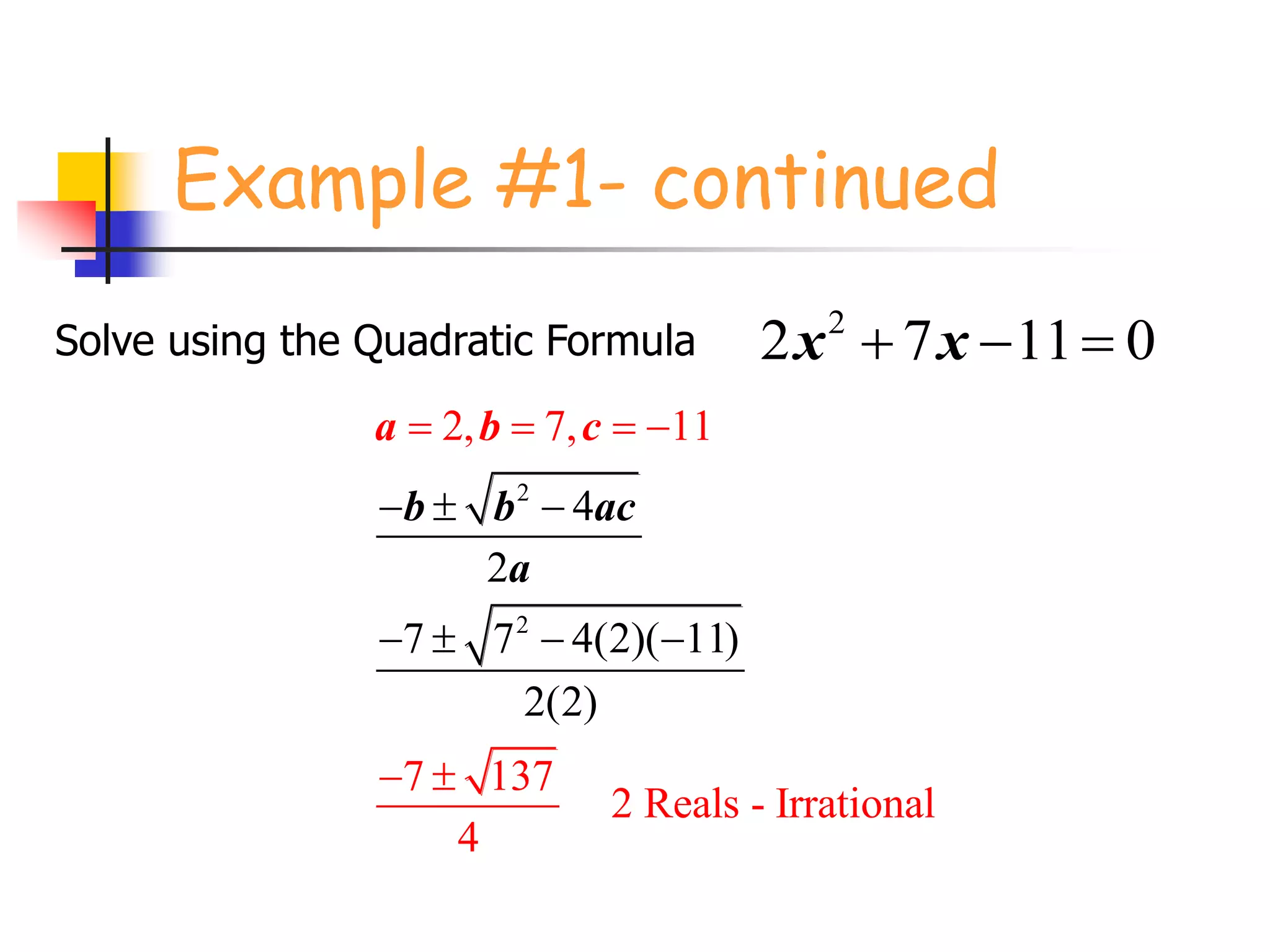
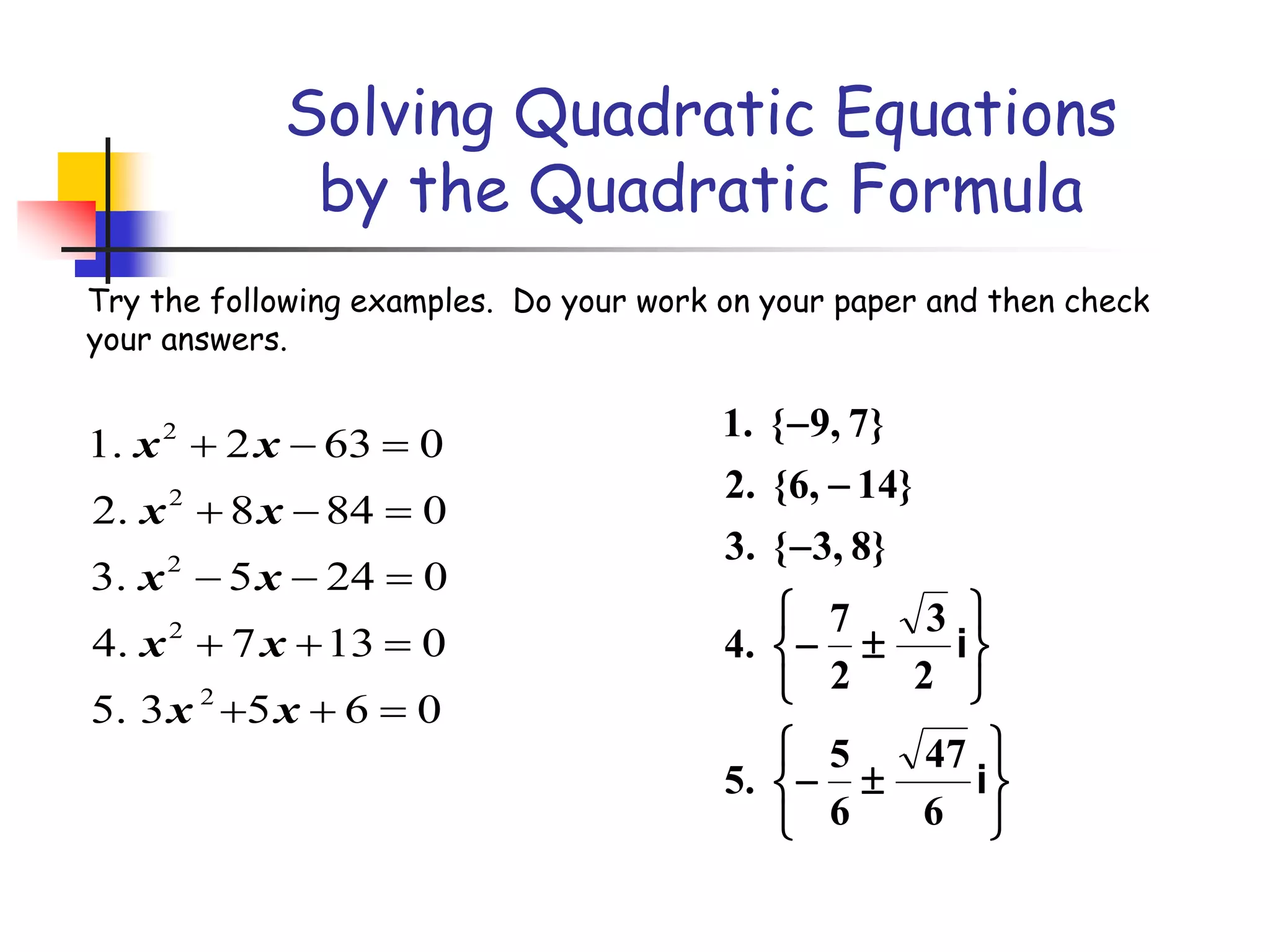
This document provides instruction on solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. It explains that the quadratic formula can be used to solve any quadratic equation, even those that cannot be factored. It defines the discriminant (b^2 - 4ac) as an important part of the formula, as the sign of the discriminant determines the number and type of roots. A negative discriminant means there are two complex roots, zero means there is one real root, and a positive discriminant means there are two real roots that can be rational or irrational depending on whether the discriminant is a perfect or non-perfect square. An example problem demonstrates finding the discriminant, describing the roots, and solving a quadratic equation using the formula. Practice