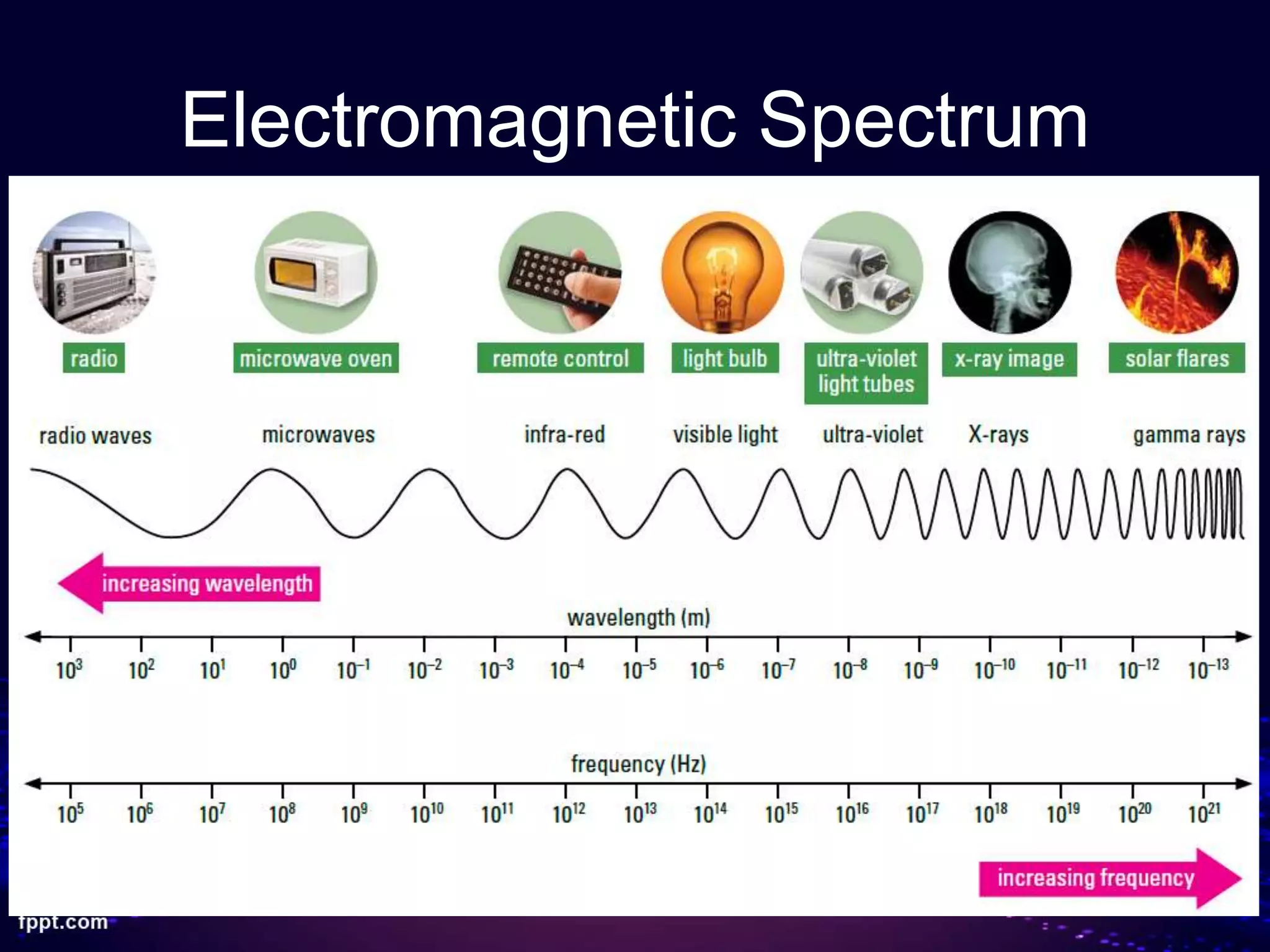
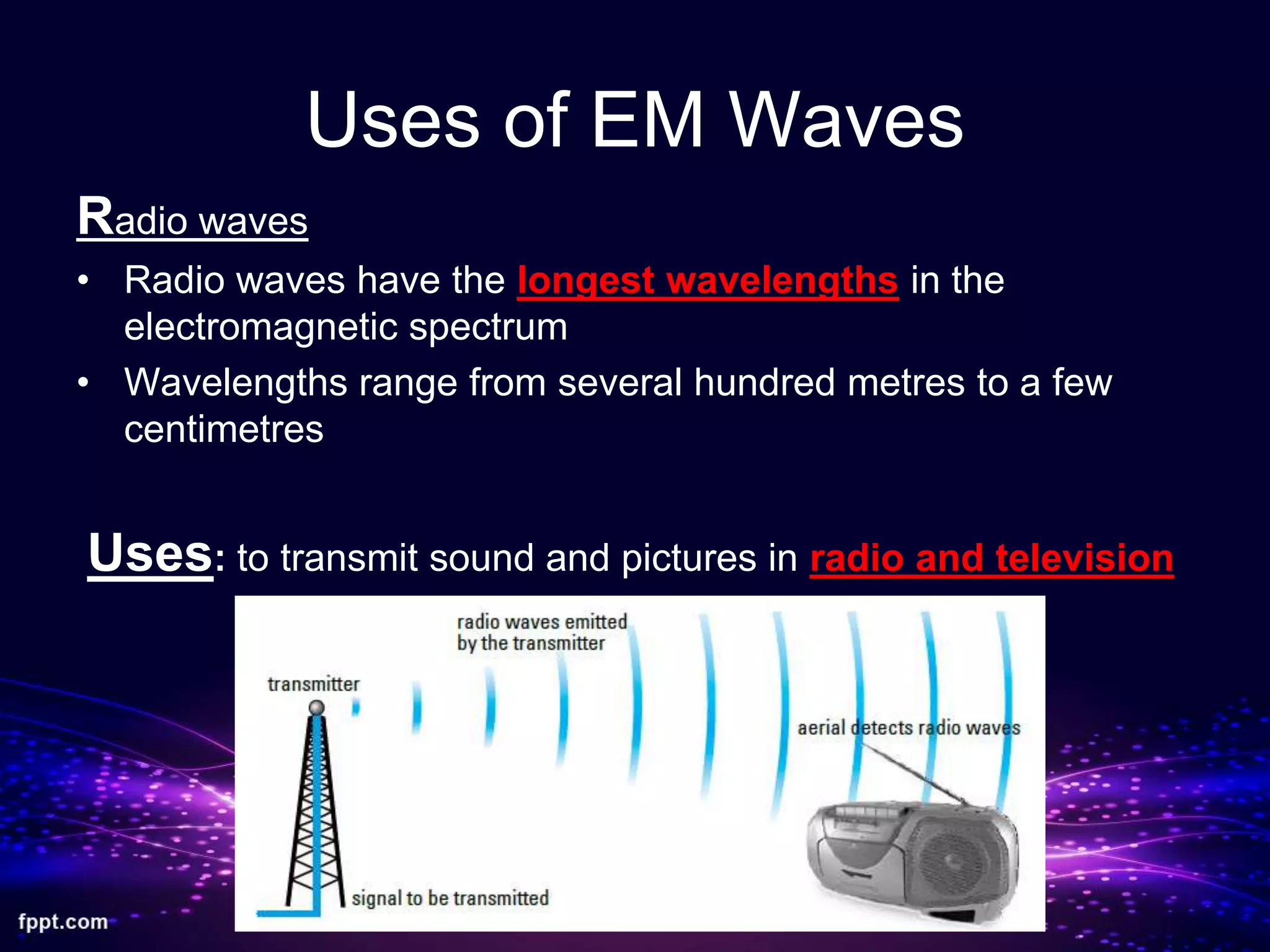
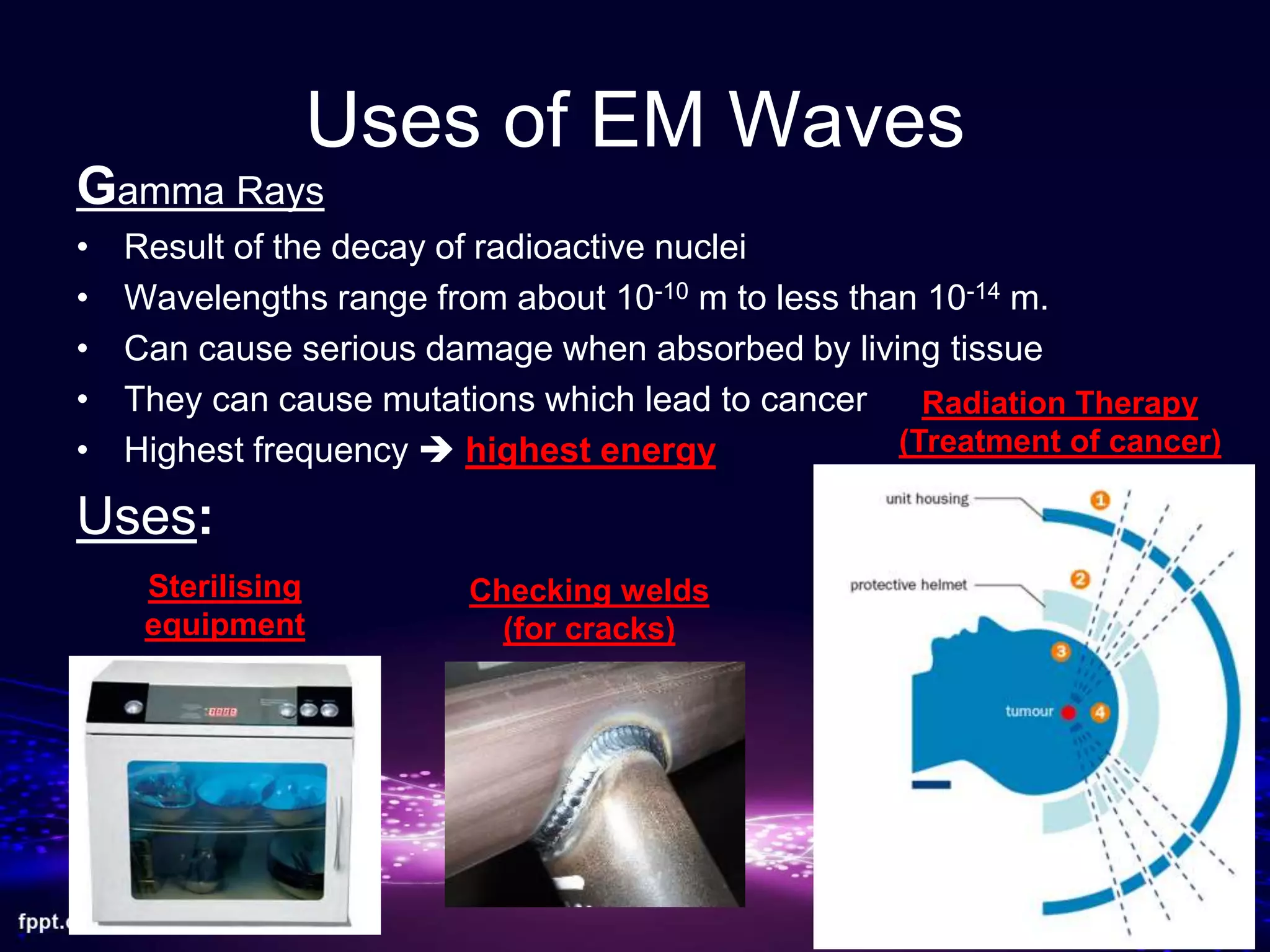
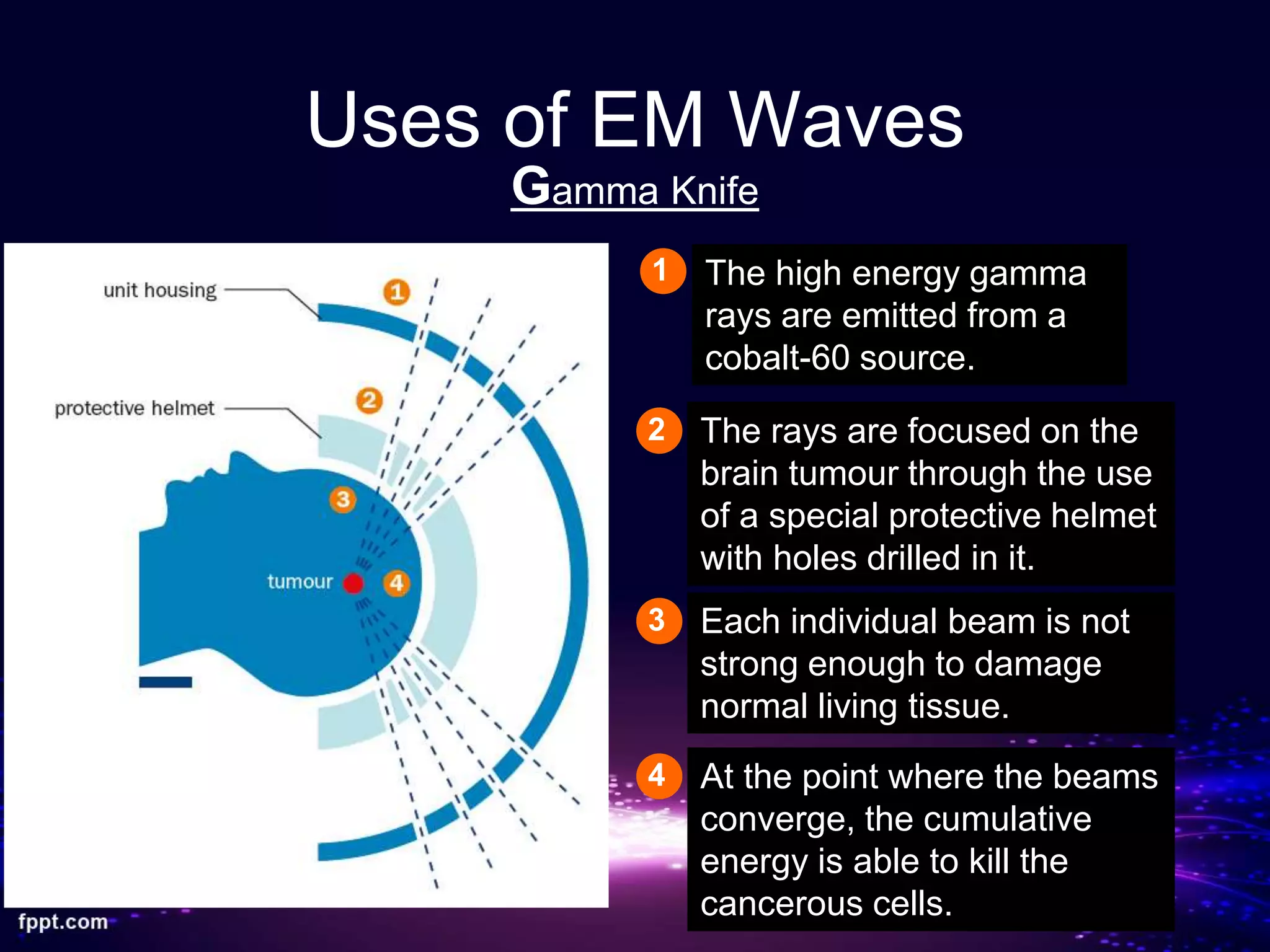
This document discusses electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum. It begins by stating that electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that all travel at the same speed in a vacuum, about 3.0 x 108 m/s. It then describes the main components of the electromagnetic spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays. Examples are given for the uses of radio waves, microwaves, infrared, light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The document also discusses how electromagnetic waves can cause heating effects and ionization when absorbed, potentially damaging living cells.