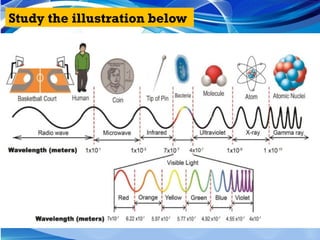
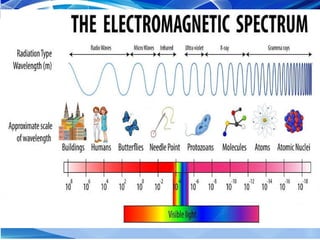
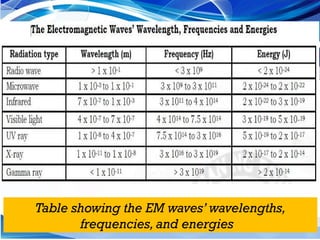
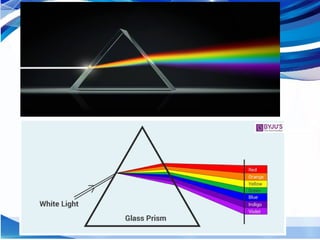
The document discusses electromagnetic waves, explaining their formation, speed, and relationship between wavelength, frequency, and energy. It outlines various types of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, detailing their properties and uses. Additionally, it highlights the work of pioneering scientists like James Clerk Maxwell and Heinrich Hertz in understanding and discovering these waves.