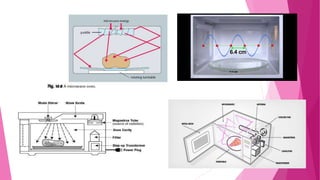
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths between radio waves and infrared radiation. They are used for communication, radar, and heating food in microwave ovens. Percy Spencer is credited with inventing the microwave oven in 1946 after discovering that microwaves can cause molecules like water and fat to vibrate, generating heat. Microwaves work by channeling energy directly into food molecules to heat them by radiation in a similar way to how the sun heats surfaces.