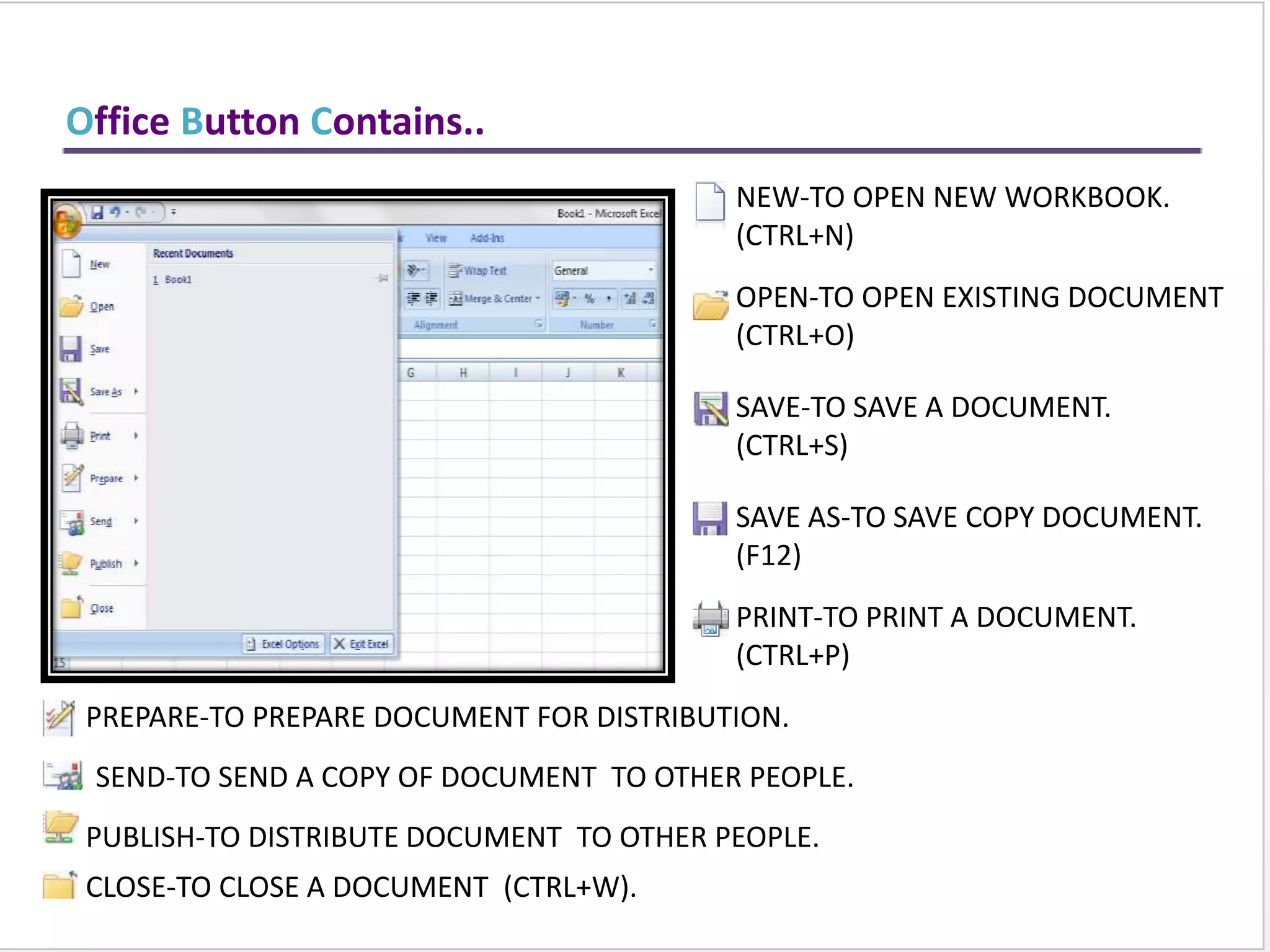
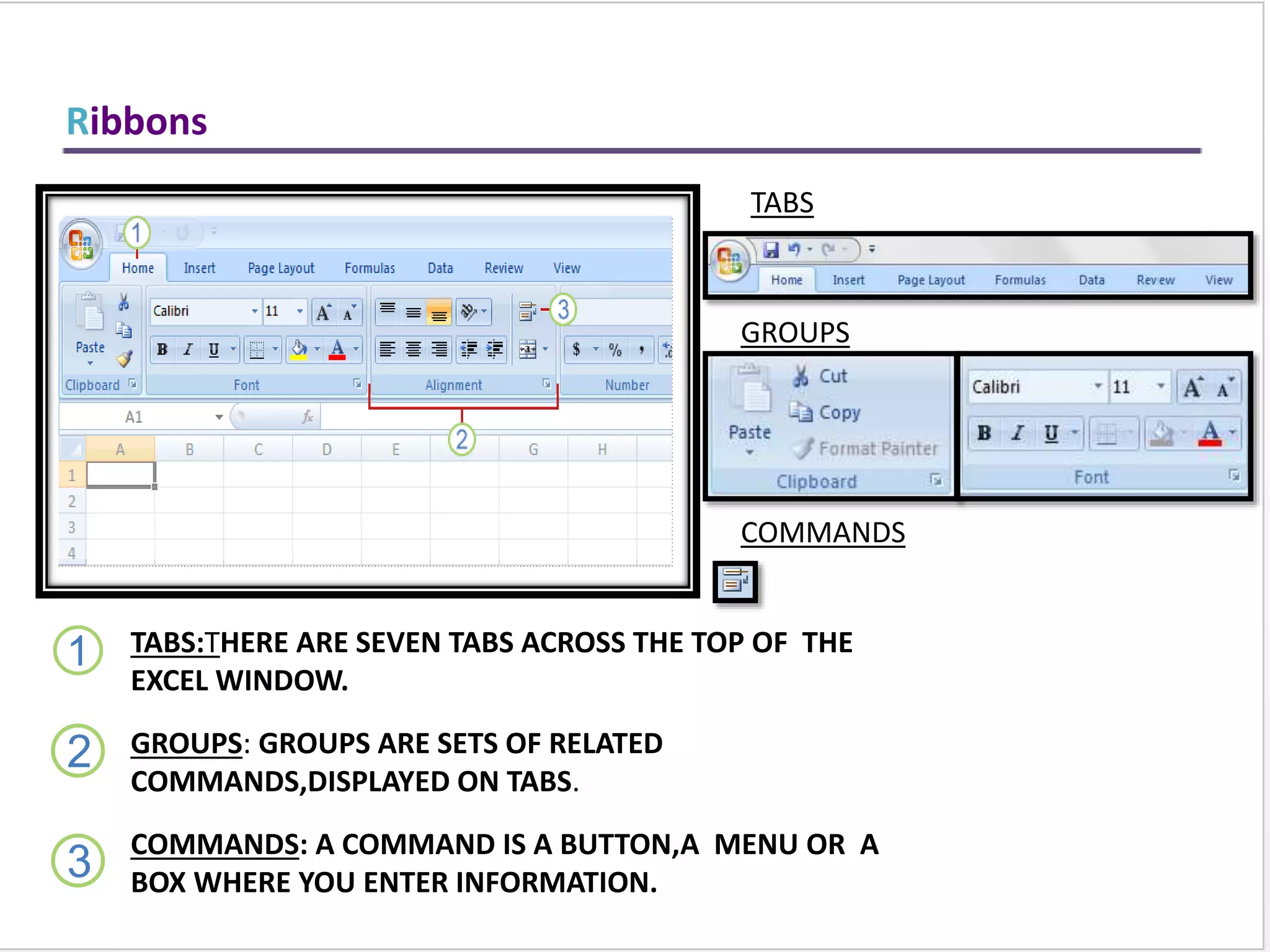
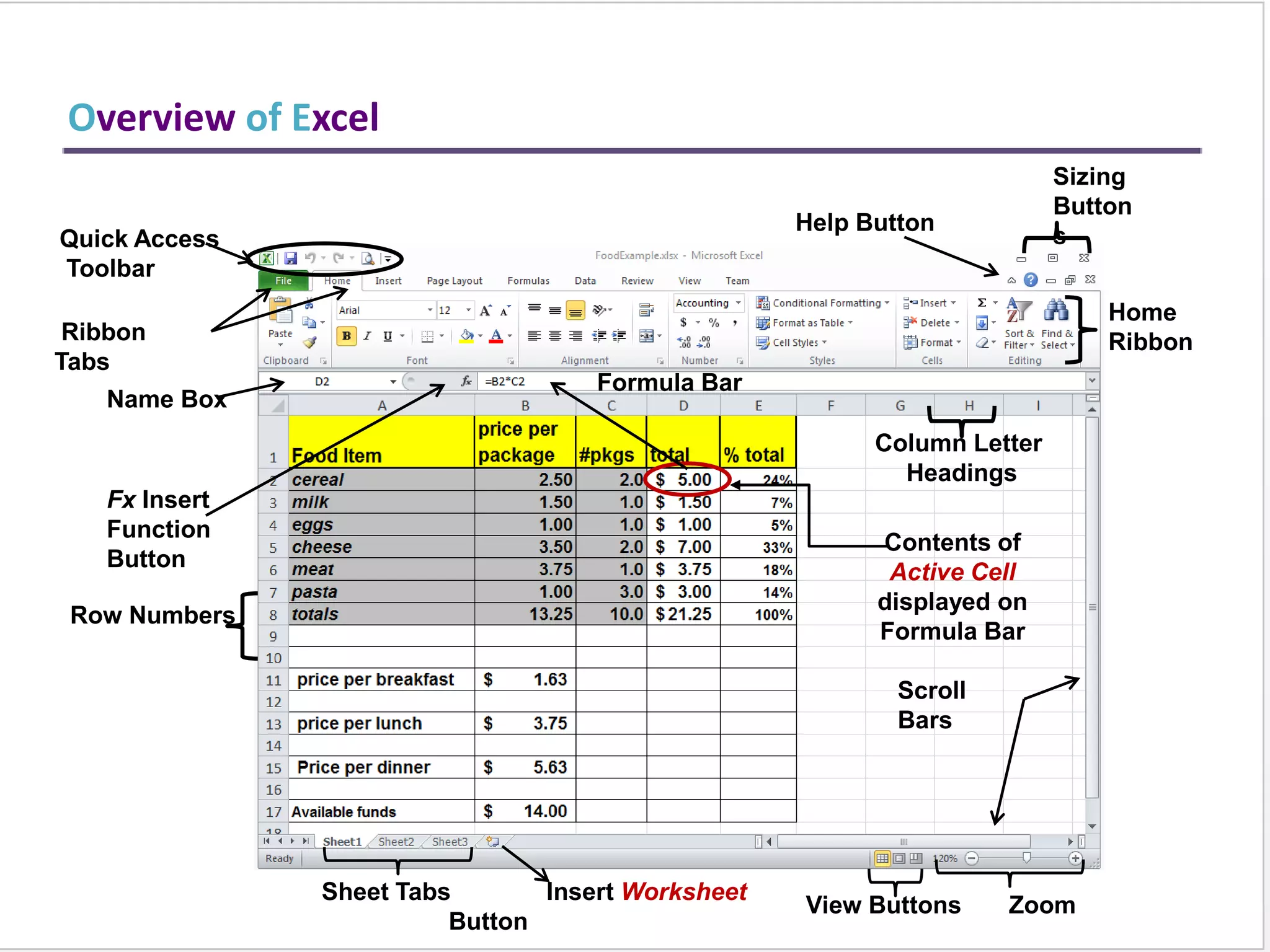
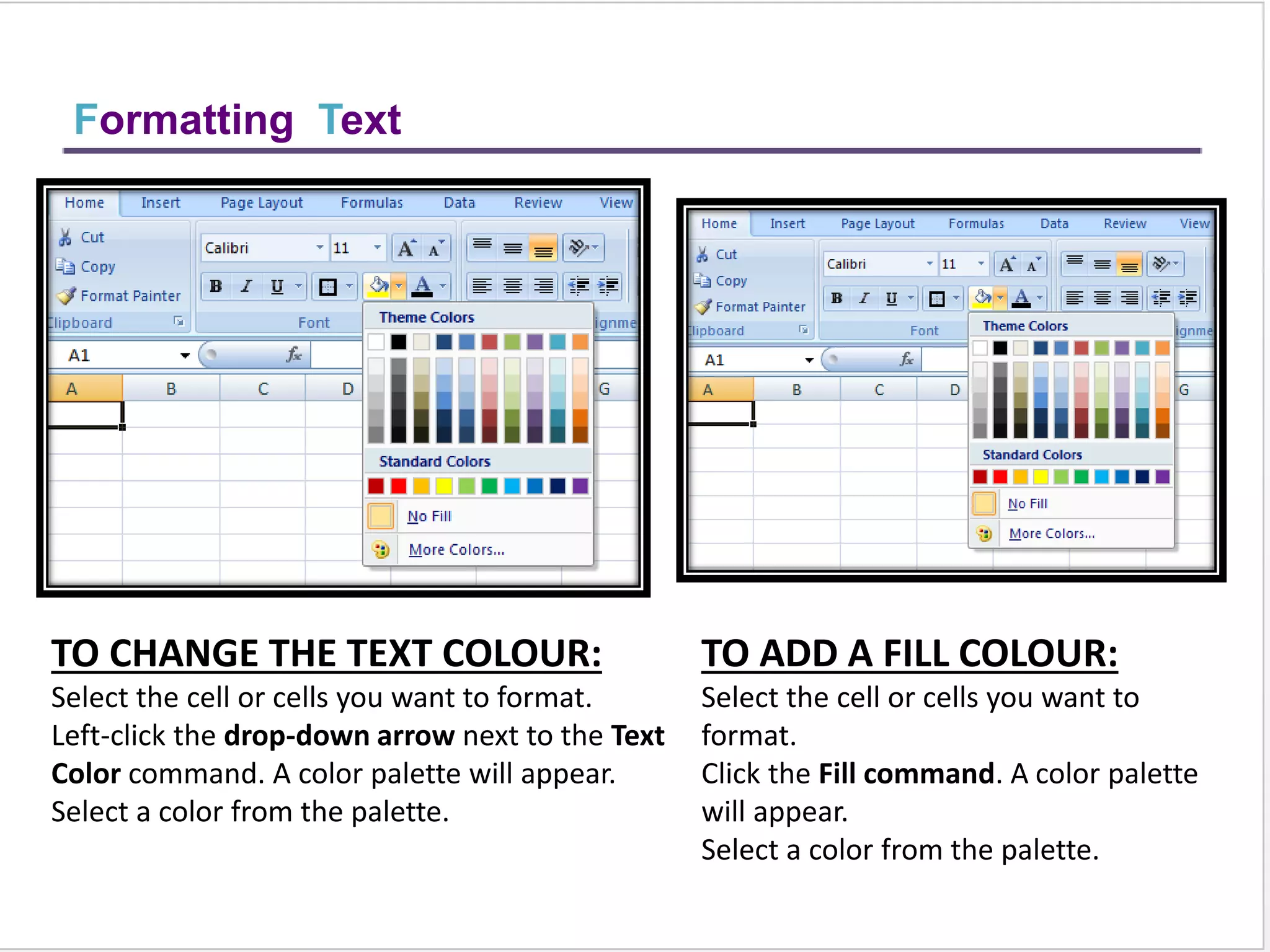
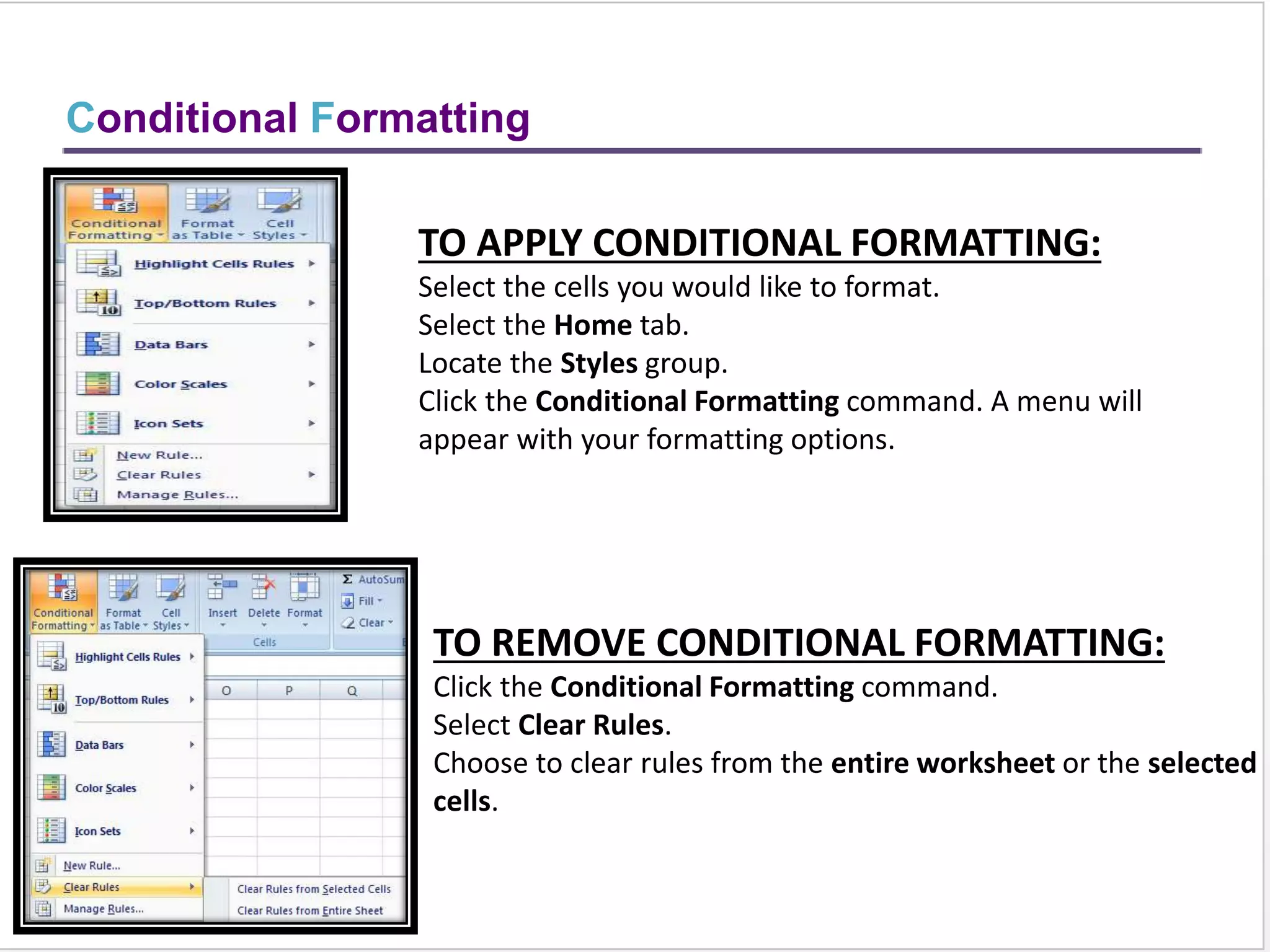
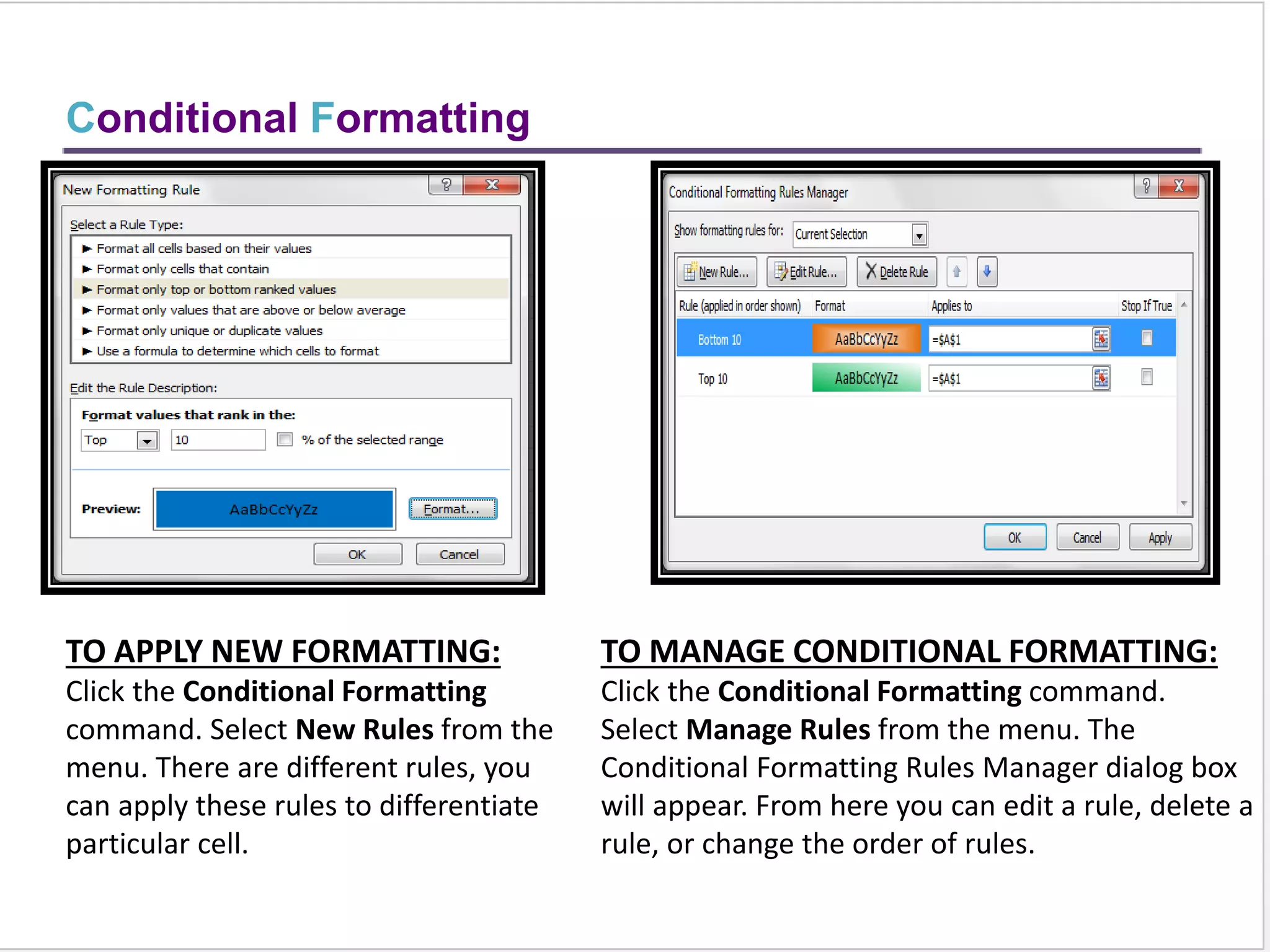
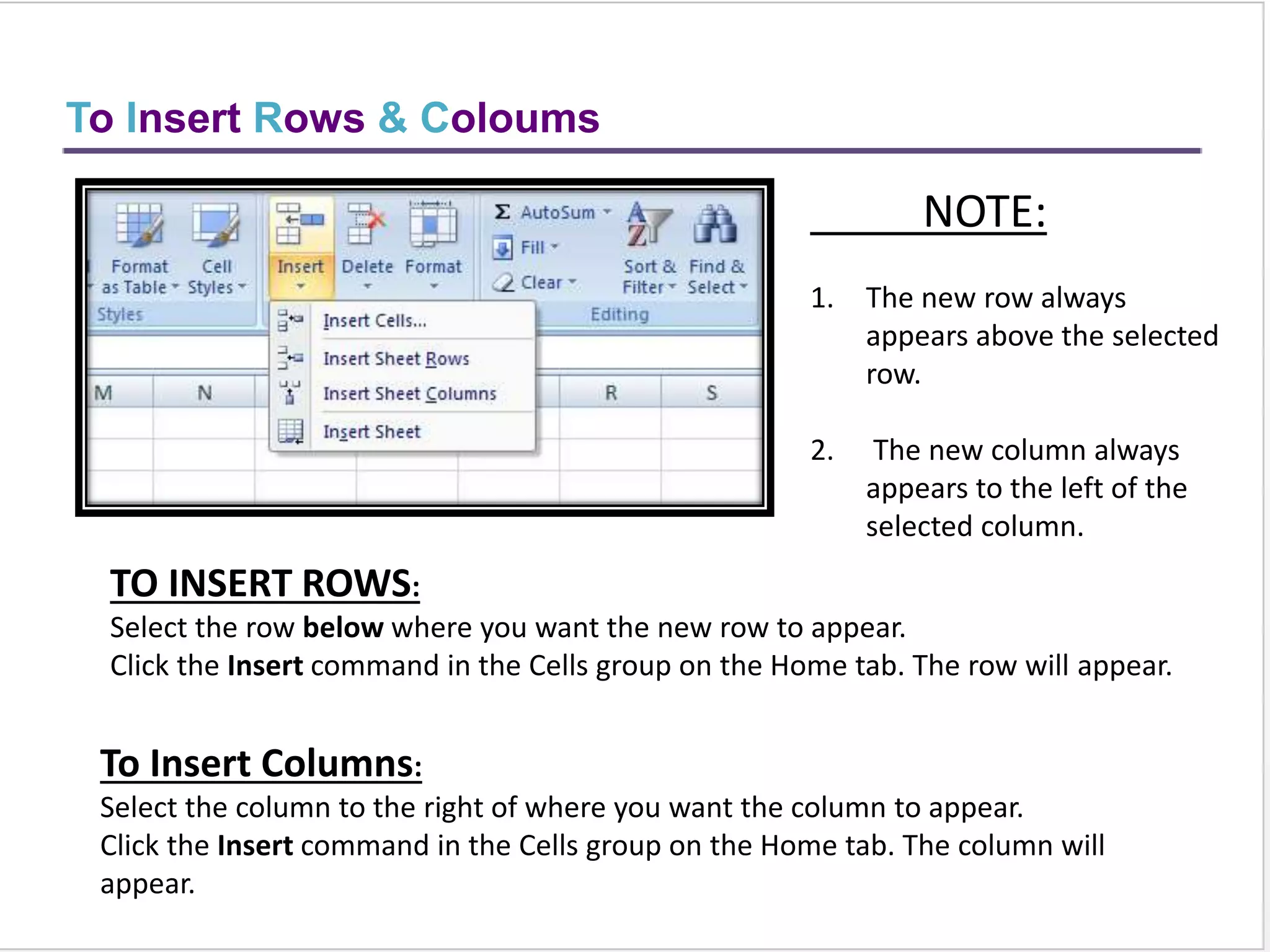
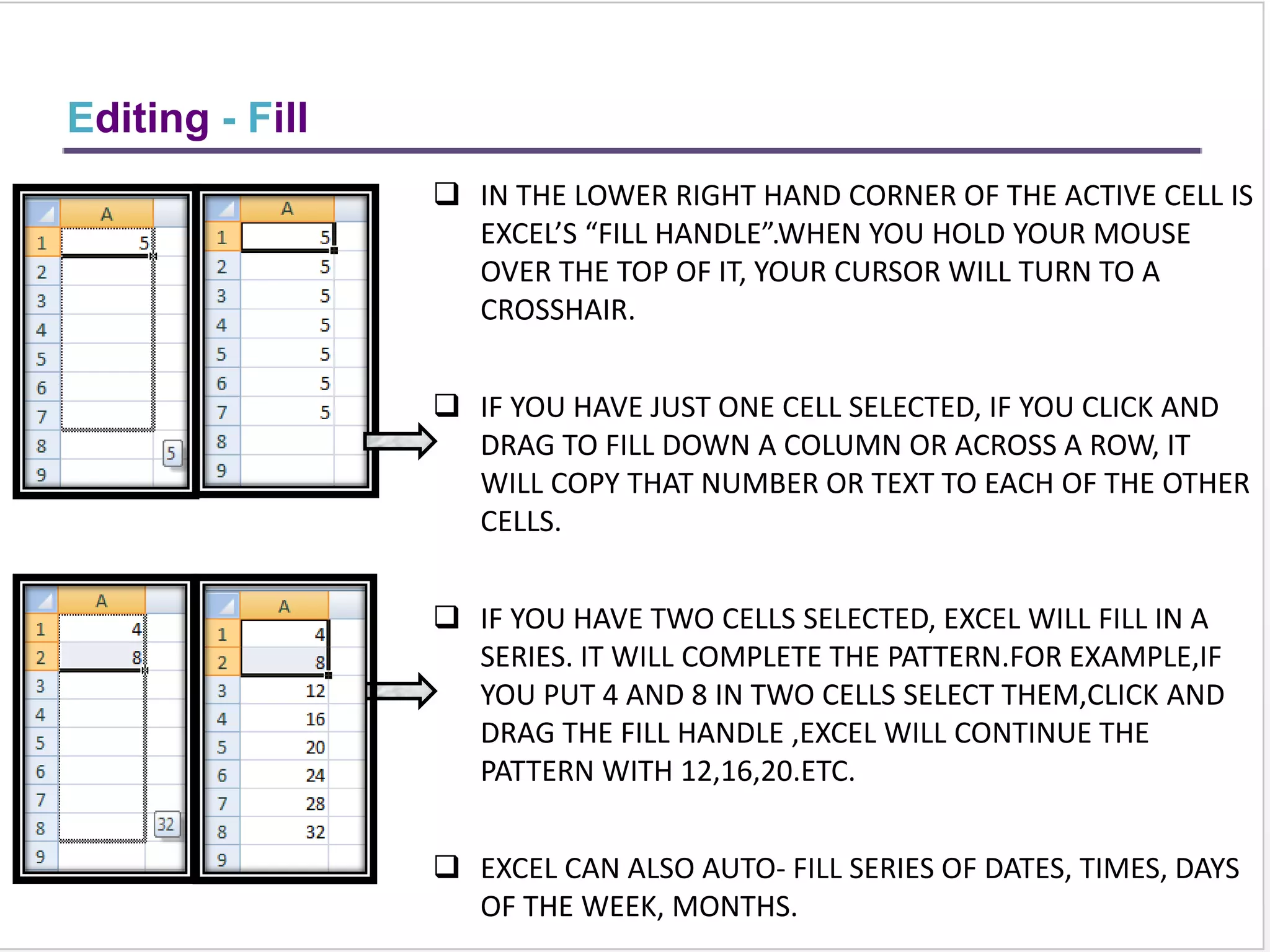
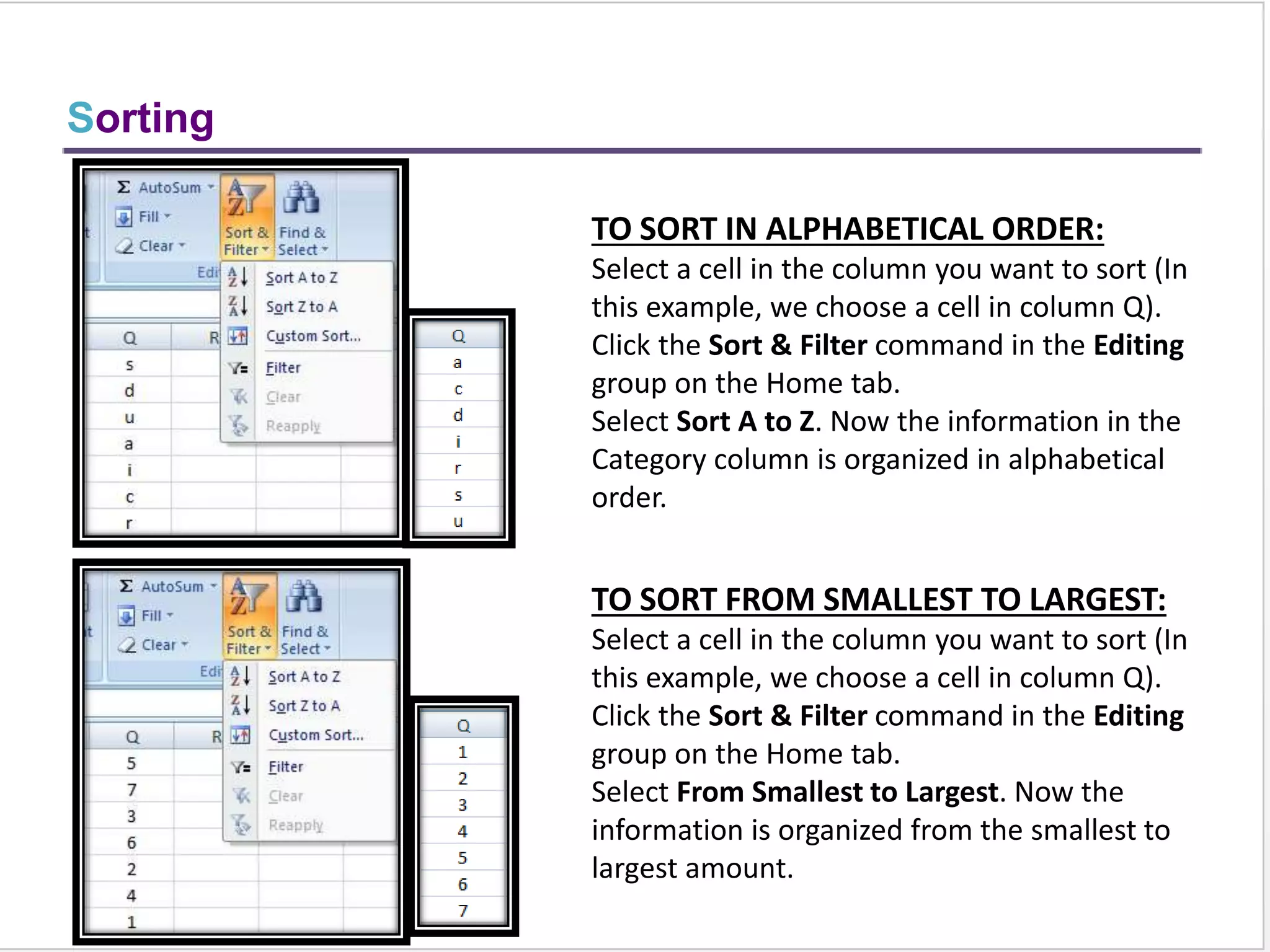
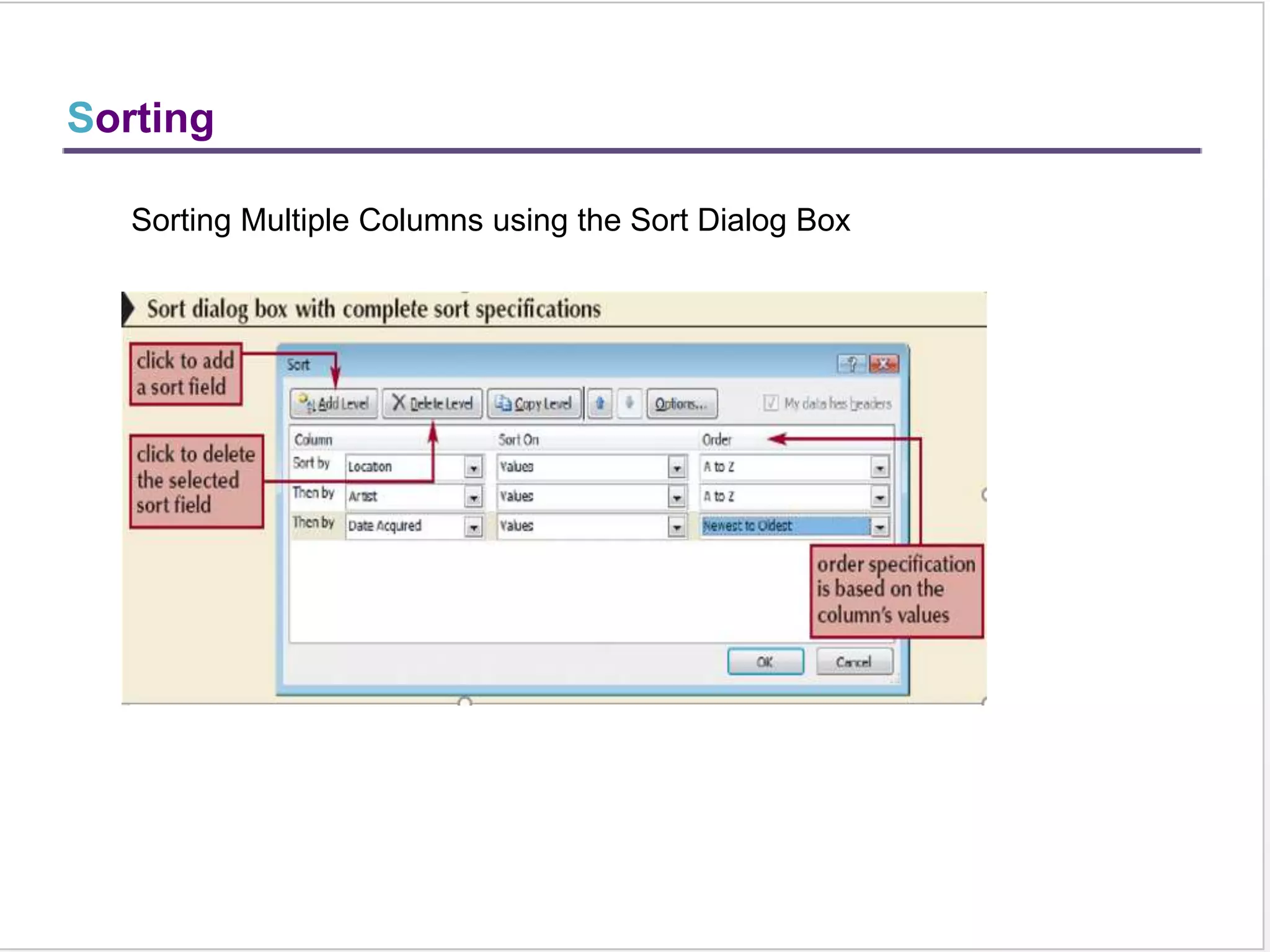
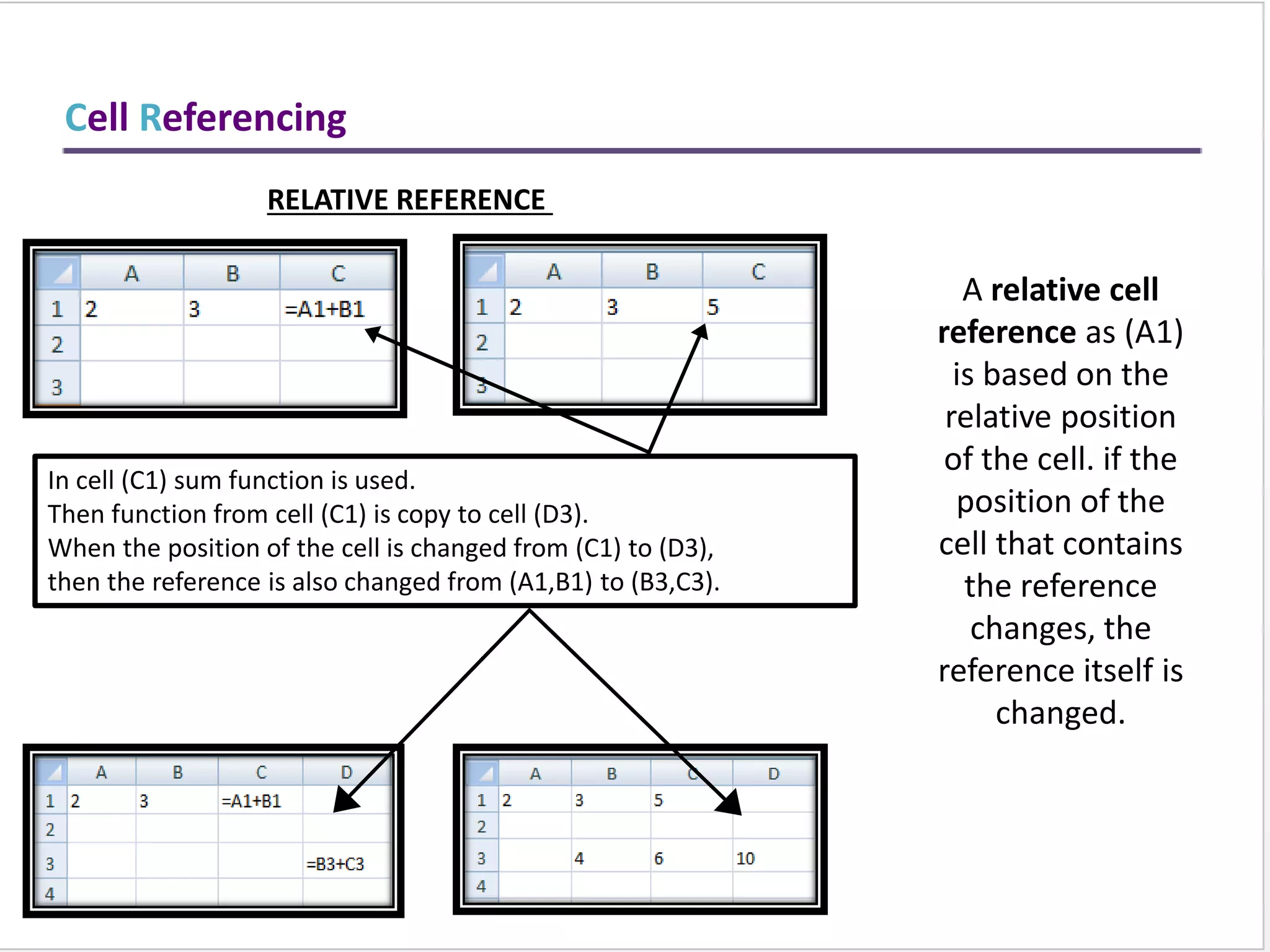
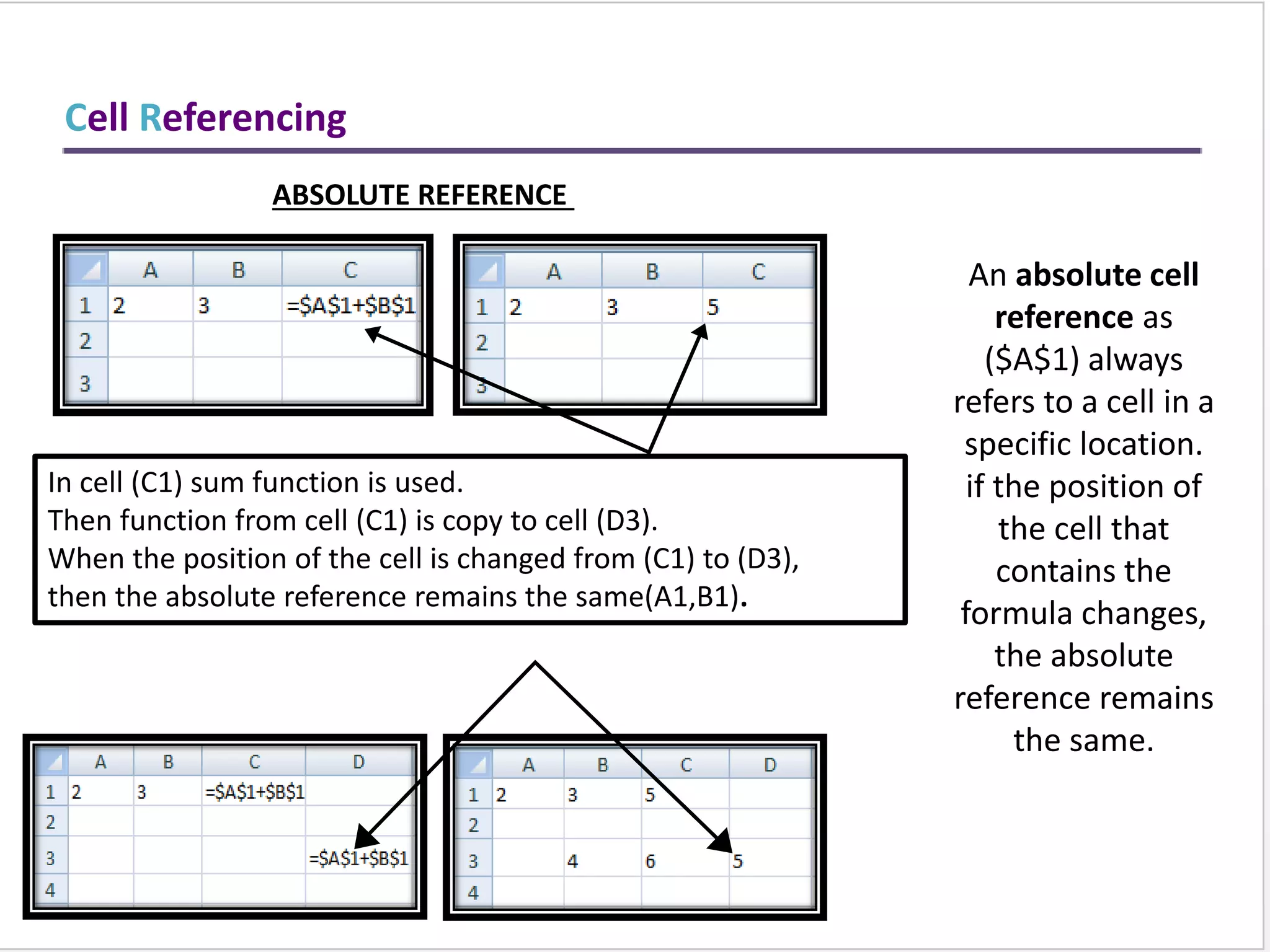
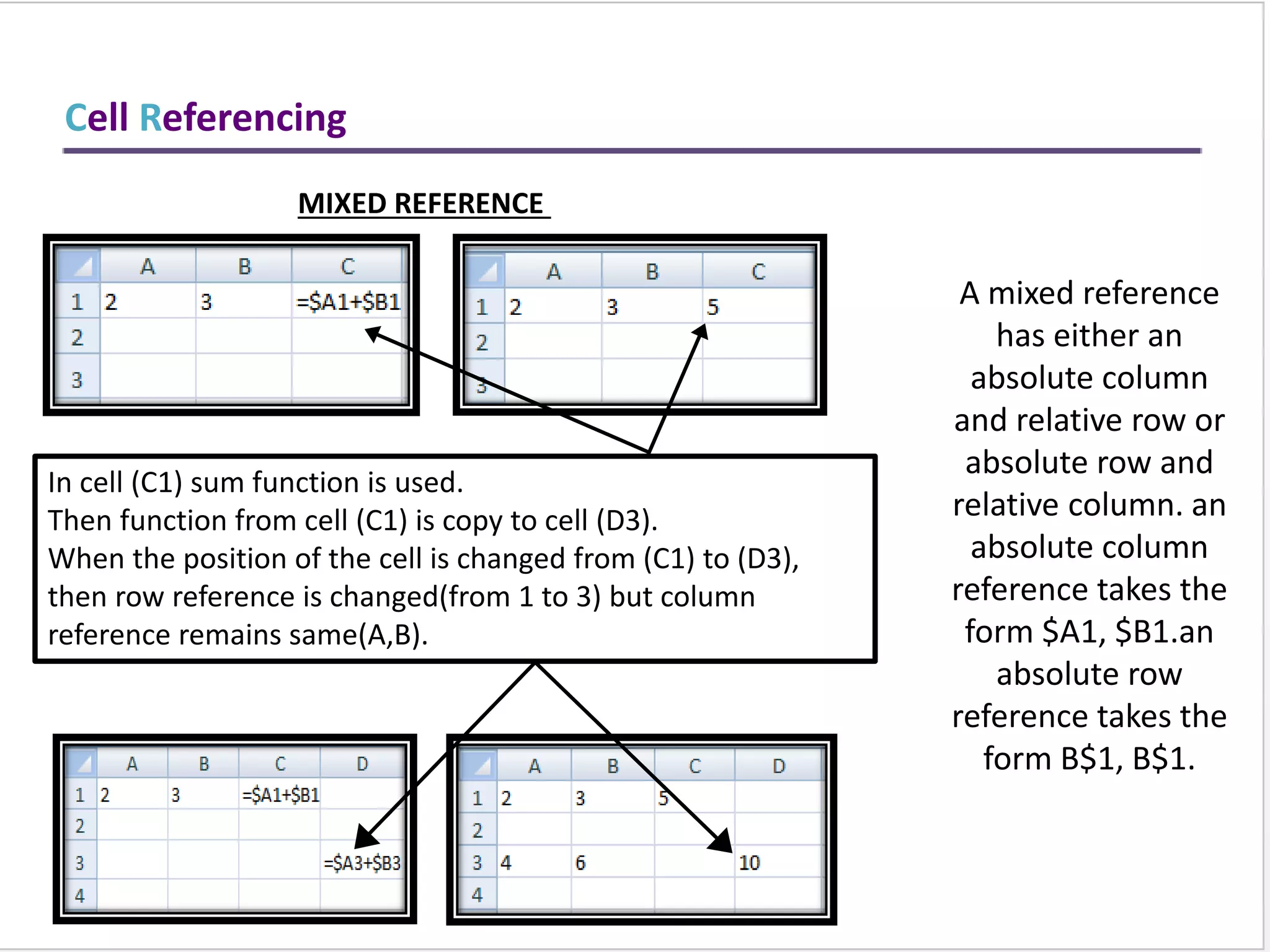
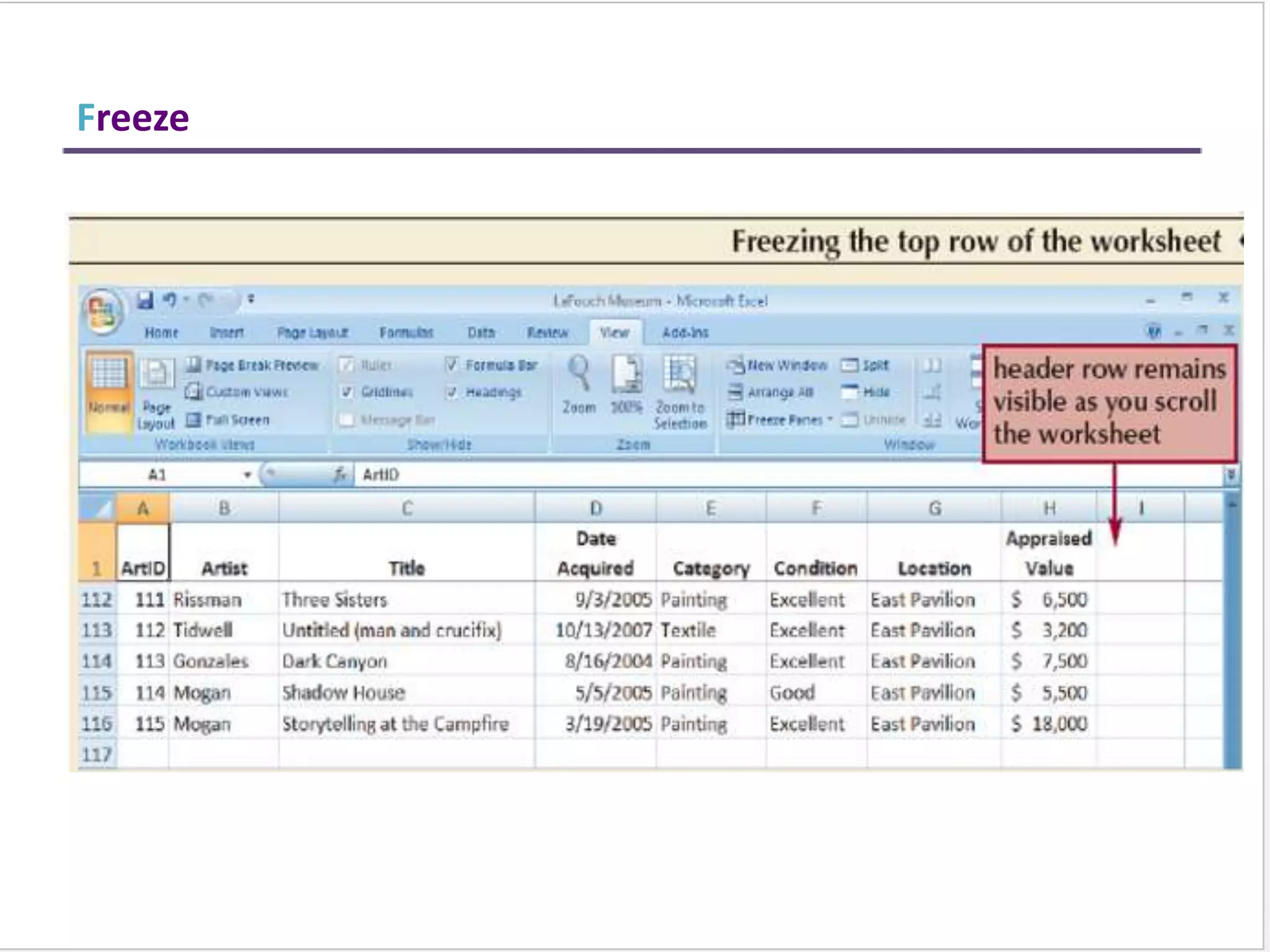
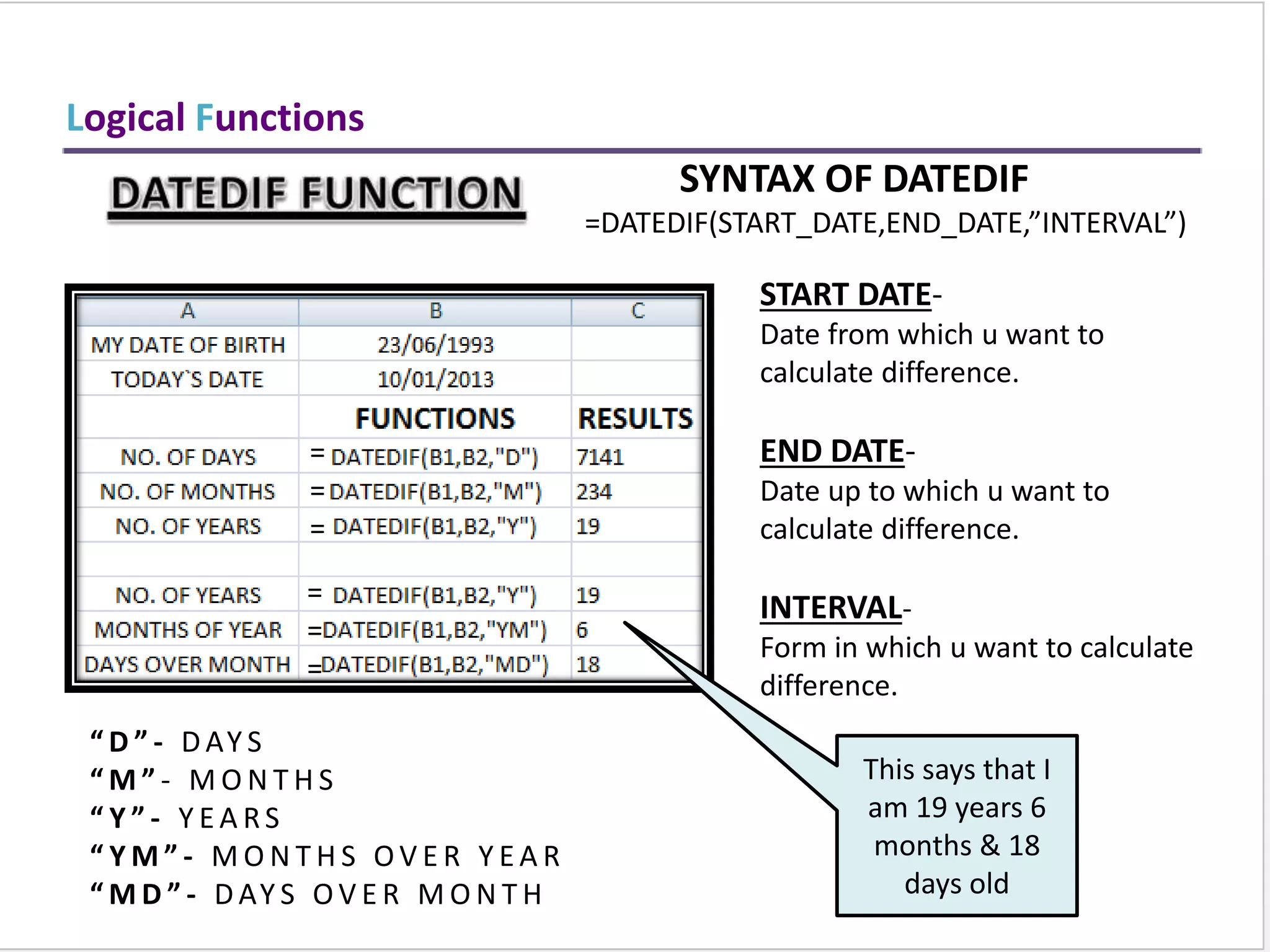
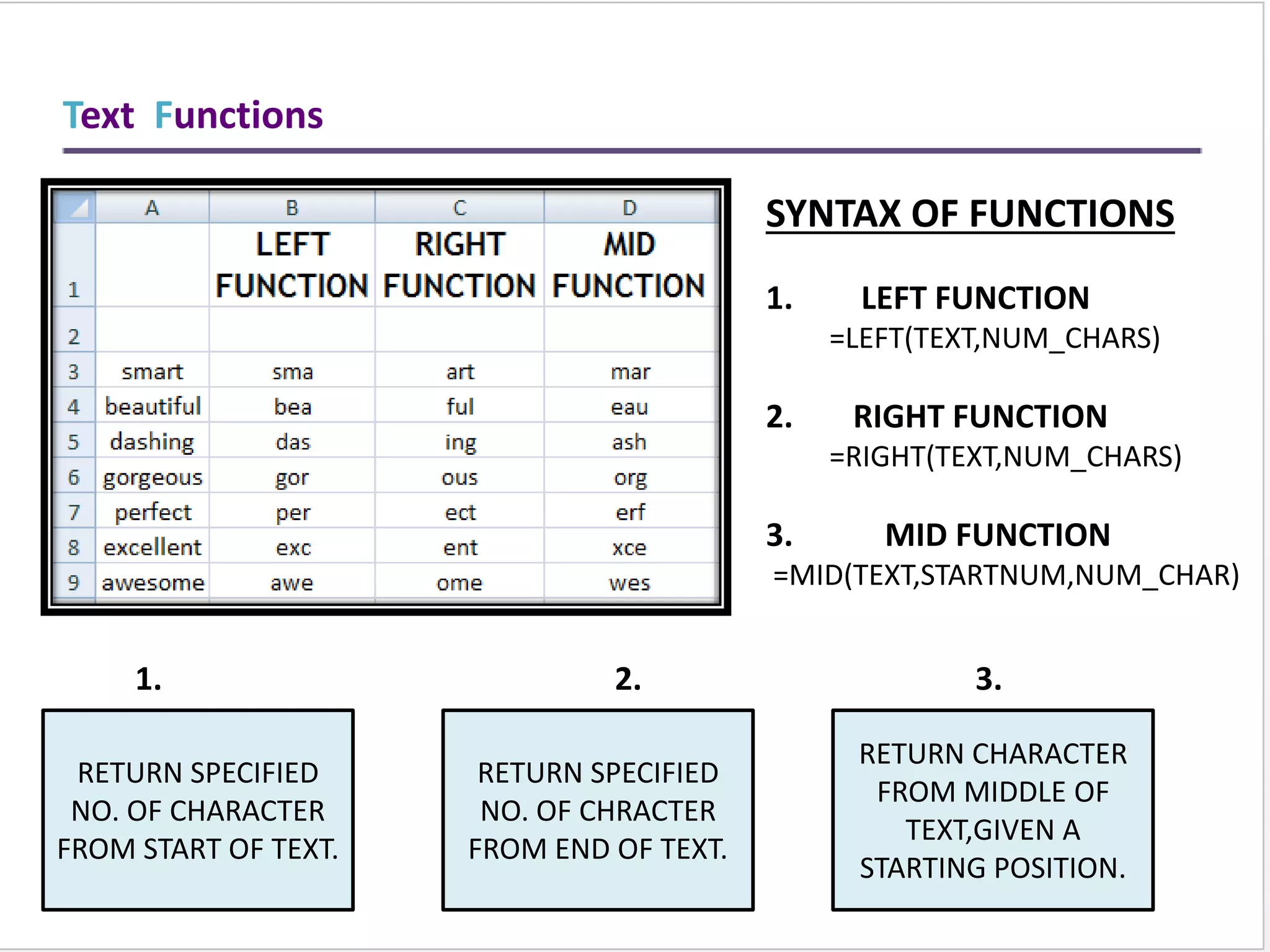
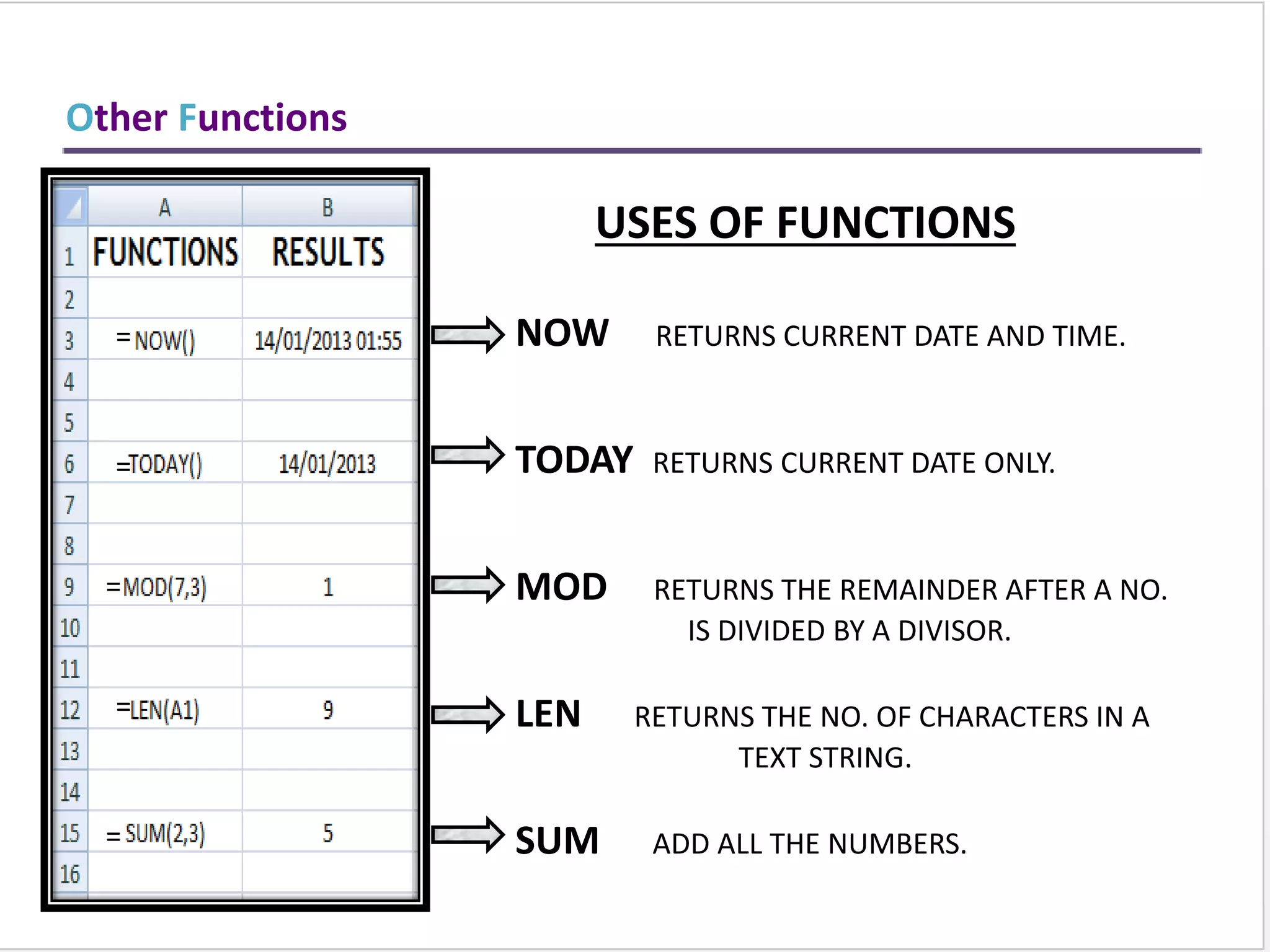
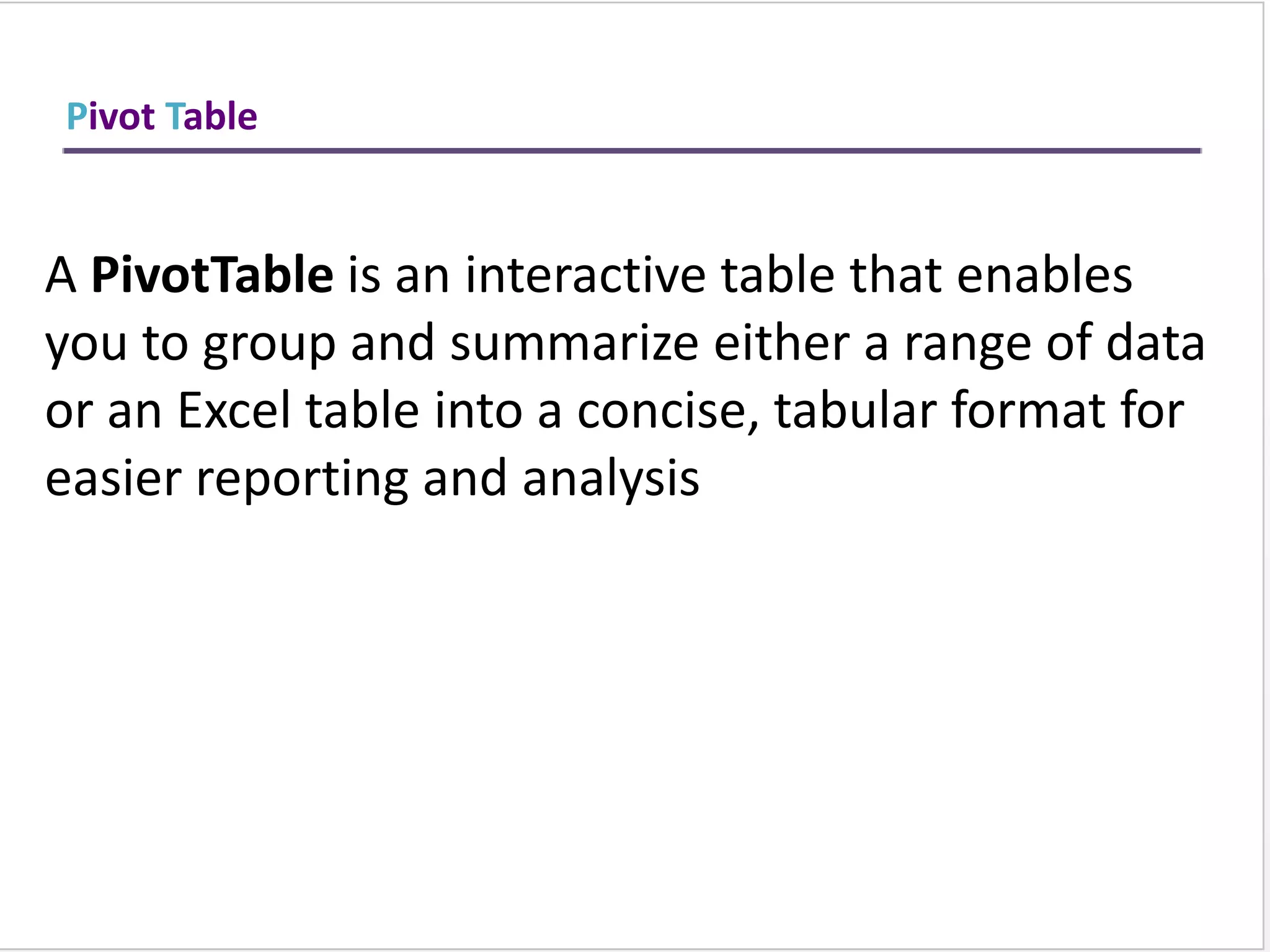
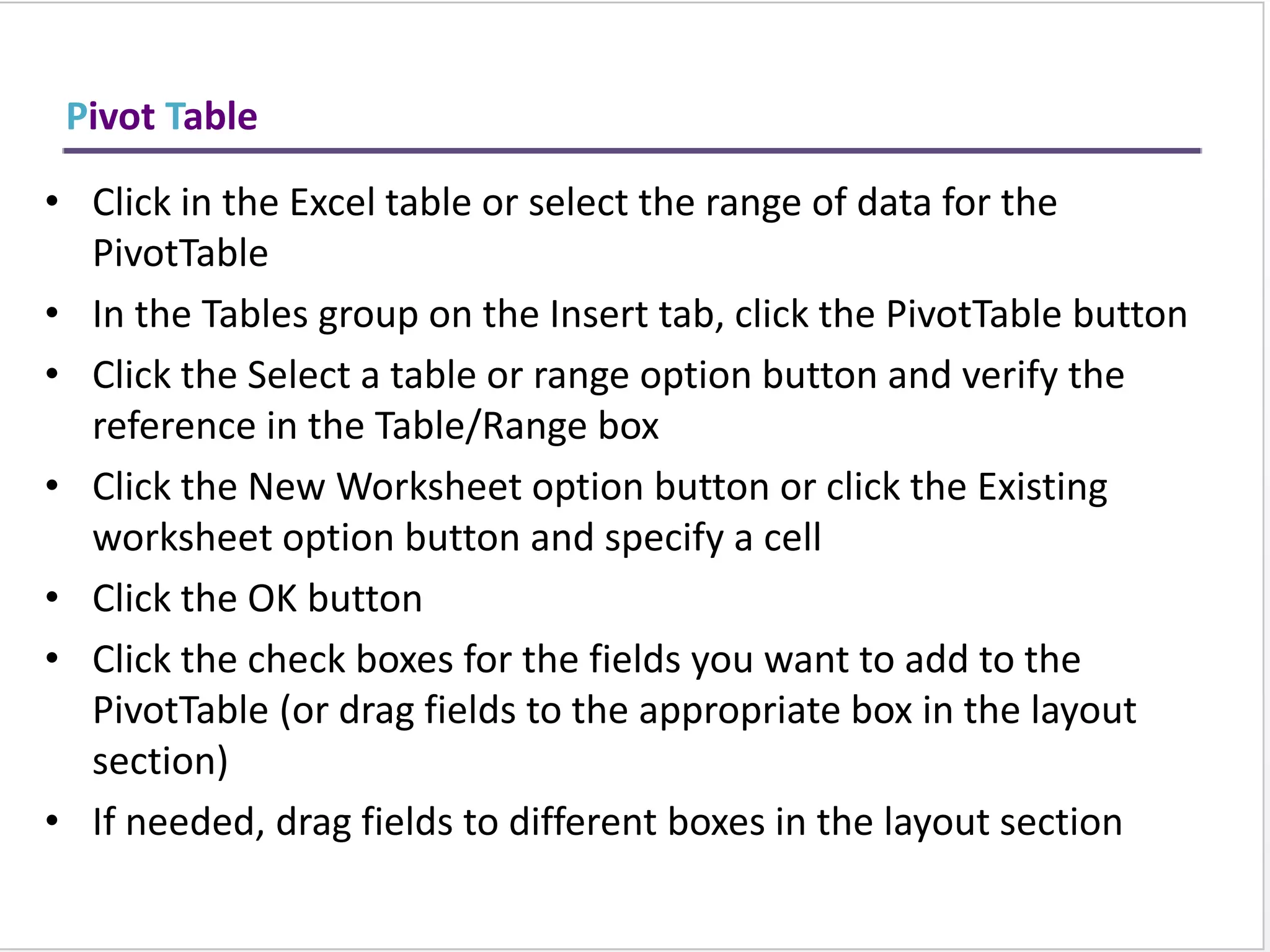
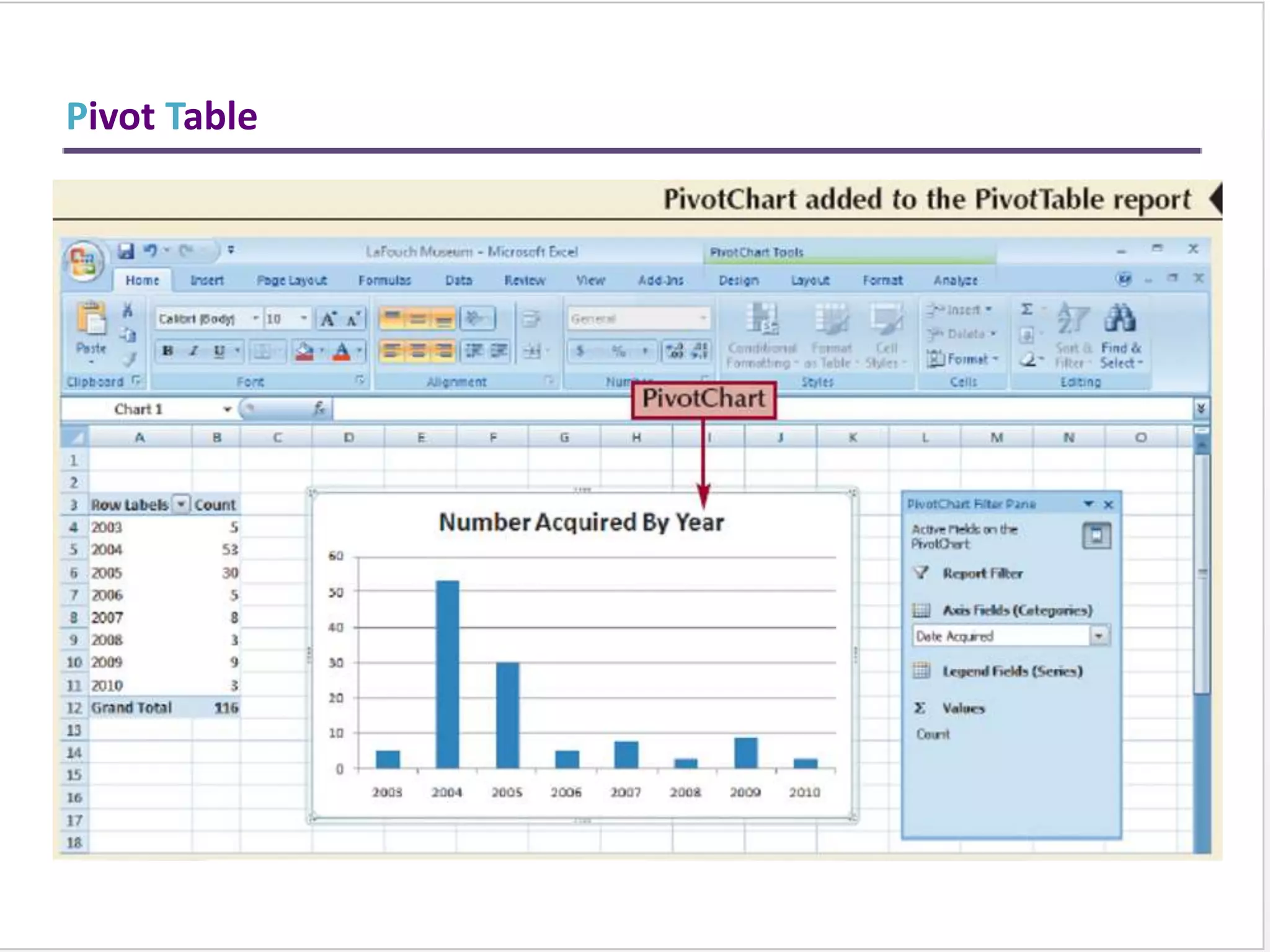
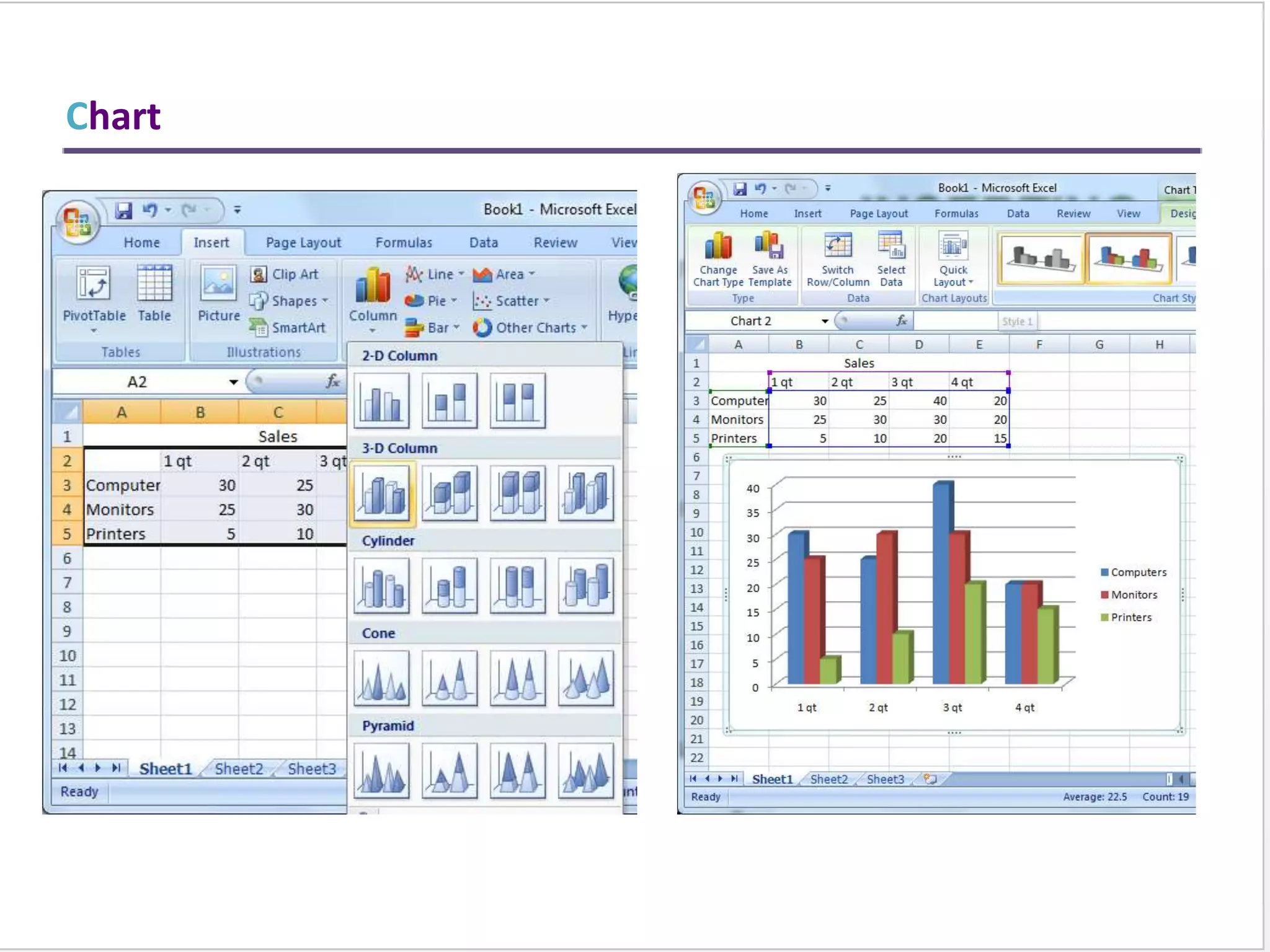
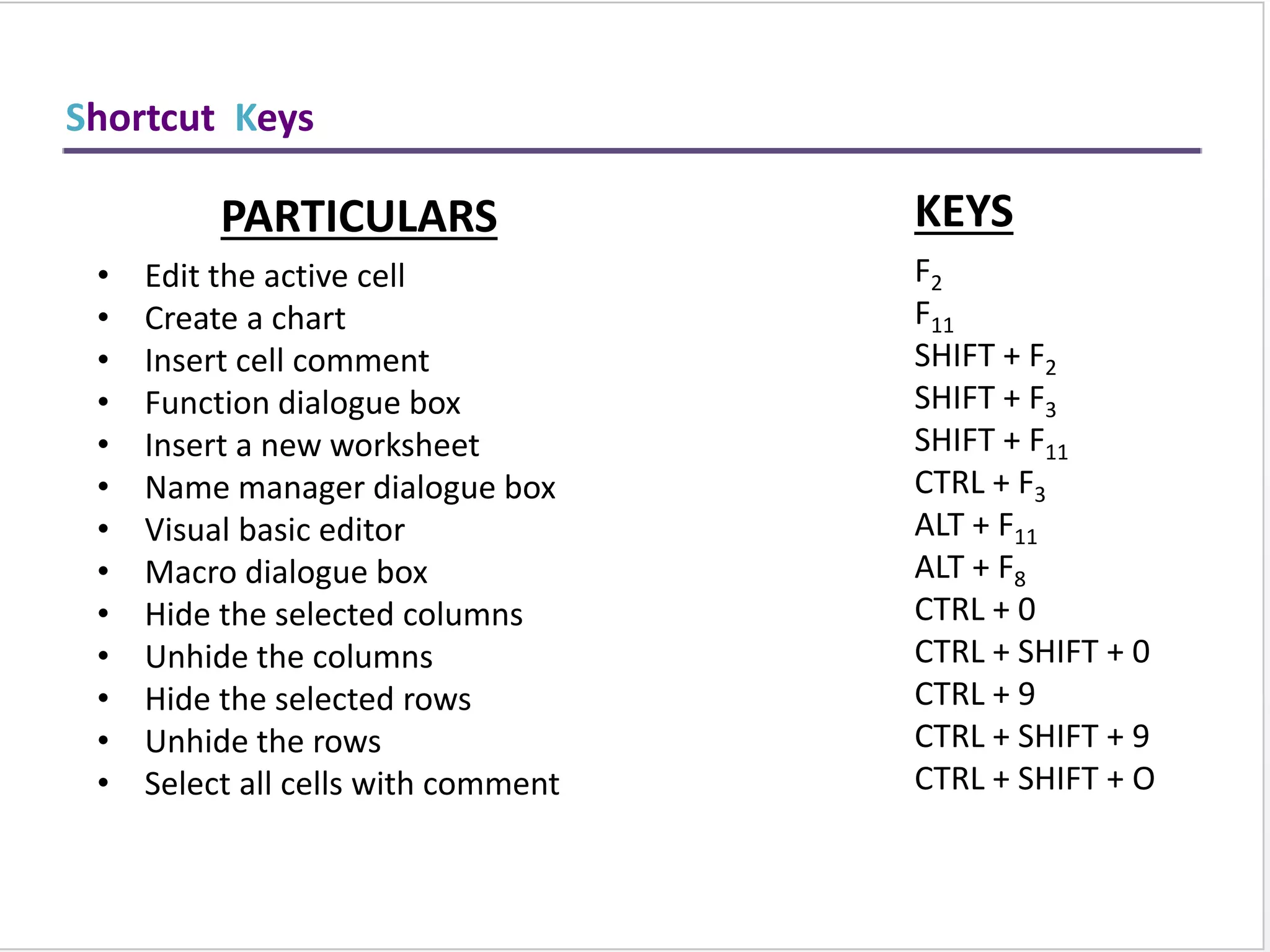
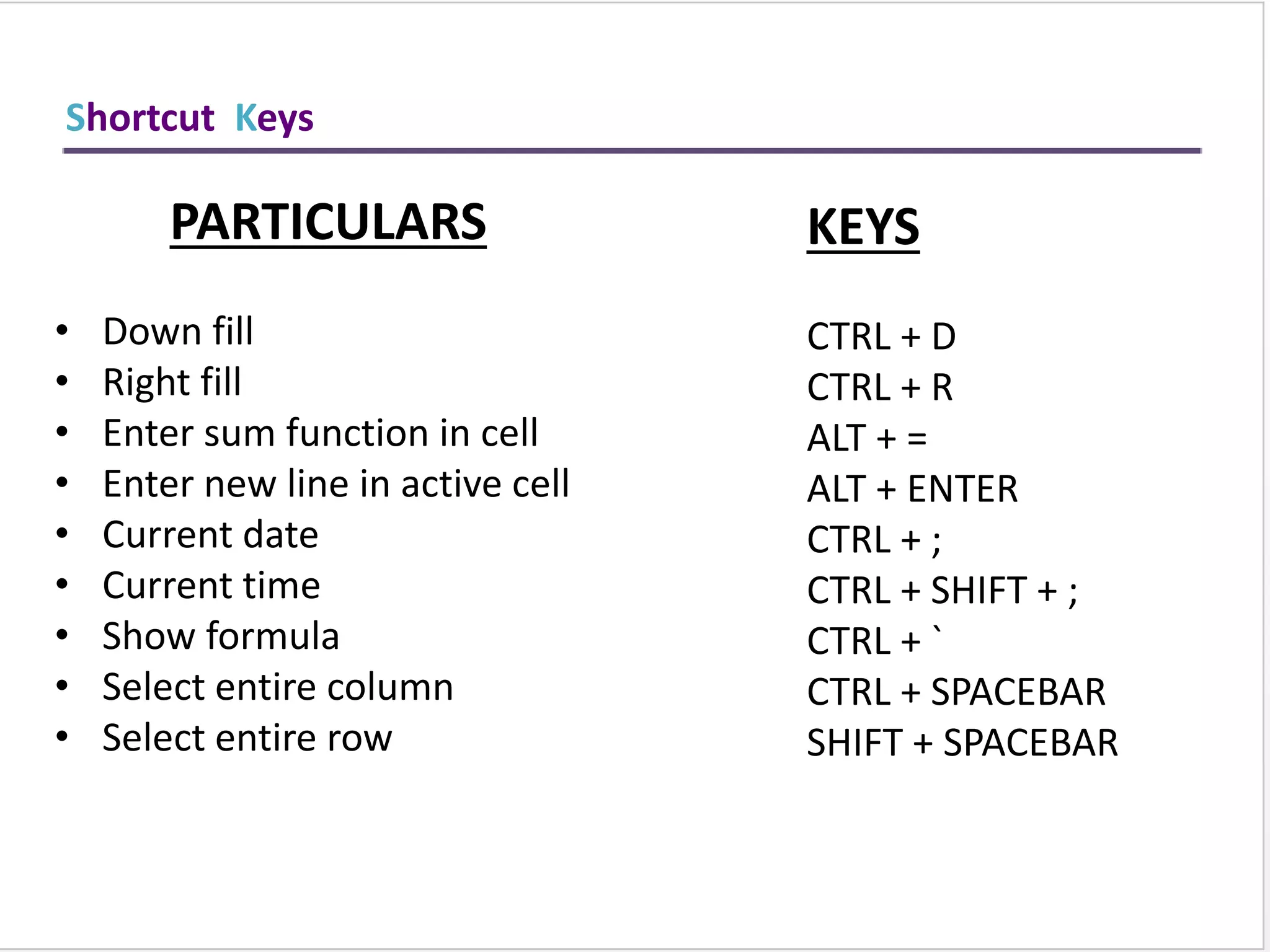
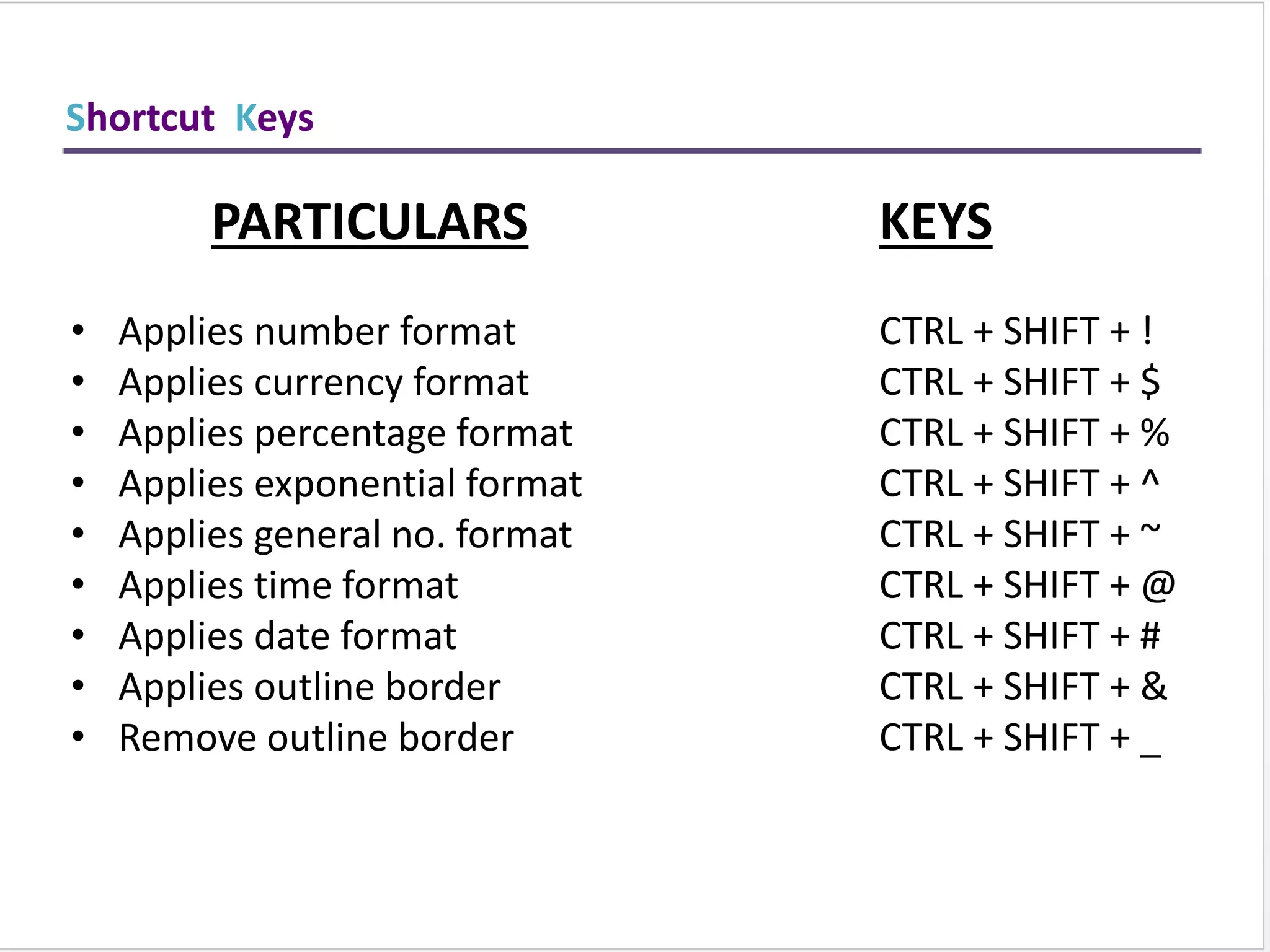
This training document provides an overview and summary of Microsoft Excel topics that will be covered, including: the Excel interface and ribbons, working with cells, formatting text, conditional formatting, inserting rows and columns, editing and fill, sorting, cell referencing, freezing panes, functions, pivot tables, charts, and shortcut keys. The training objectives are to introduce participants to Excel and provide contents on these fundamental Excel functions and features.