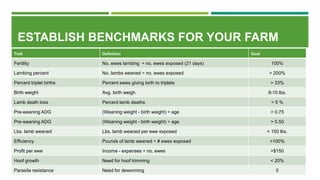
This document discusses how to improve ewe efficiency in sheep production. It defines ewe efficiency as measures like lambs born and weaned per ewe, pounds of lamb produced per ewe, and profit per ewe. The key factors that determine efficiency are size, longevity, lambing percentage, lamb weights, feed efficiency, and health. The document provides tips for improving these factors through selection, nutrition management, health programs, and data recording to establish farm-specific efficiency benchmarks.