The document discusses several key aspects of language acquisition in humans:
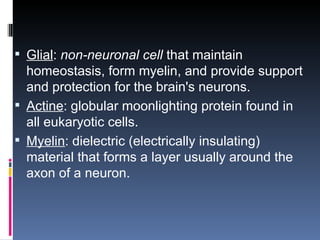
1) Humans are biologically designed for language with modifications that allow for speech like a low larynx.
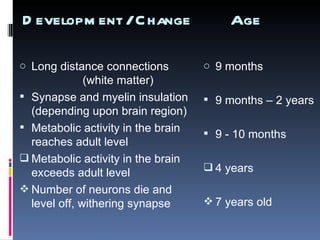
2) Brain development from birth to age 7 supports language learning with connectivity changes and metabolic activity peaks.
3) Language acquisition starts with sounds and moves to words and simple sentences followed by a grammar explosion between ages 2-4.
4) Factors like context, parental interaction styles and the brain's ability to bootstrap rules guide this rapid acquisition process.