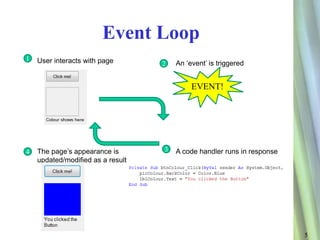
The document discusses event driven programming using Visual Studio and VB.NET. It describes key aspects of event driven programming including event loops, GUI design using forms and controls, trigger functions, and event handlers. It provides examples of how to use these tools and techniques in Visual Studio and VB.NET, demonstrating the development process with code snippets and screenshots.