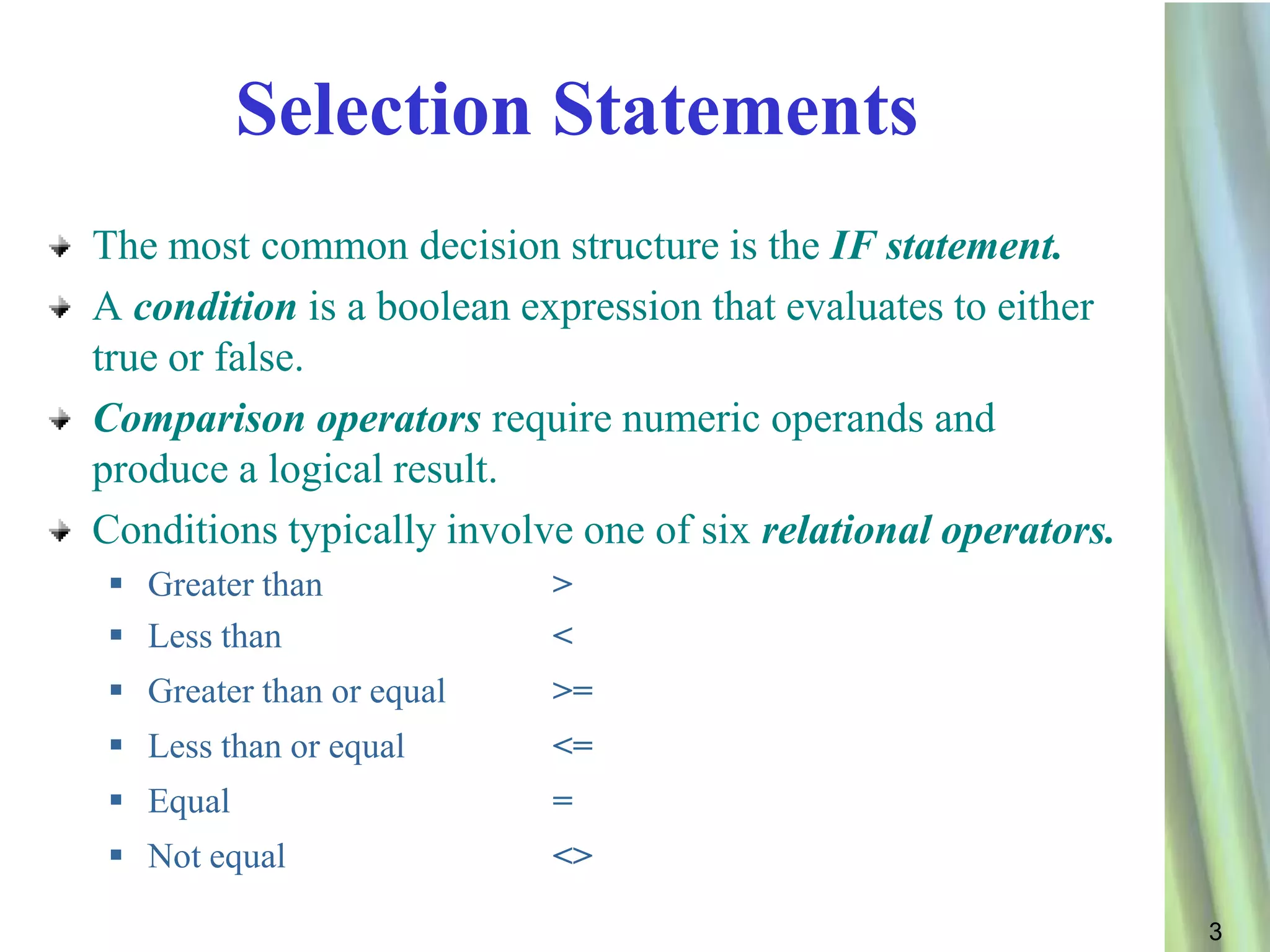
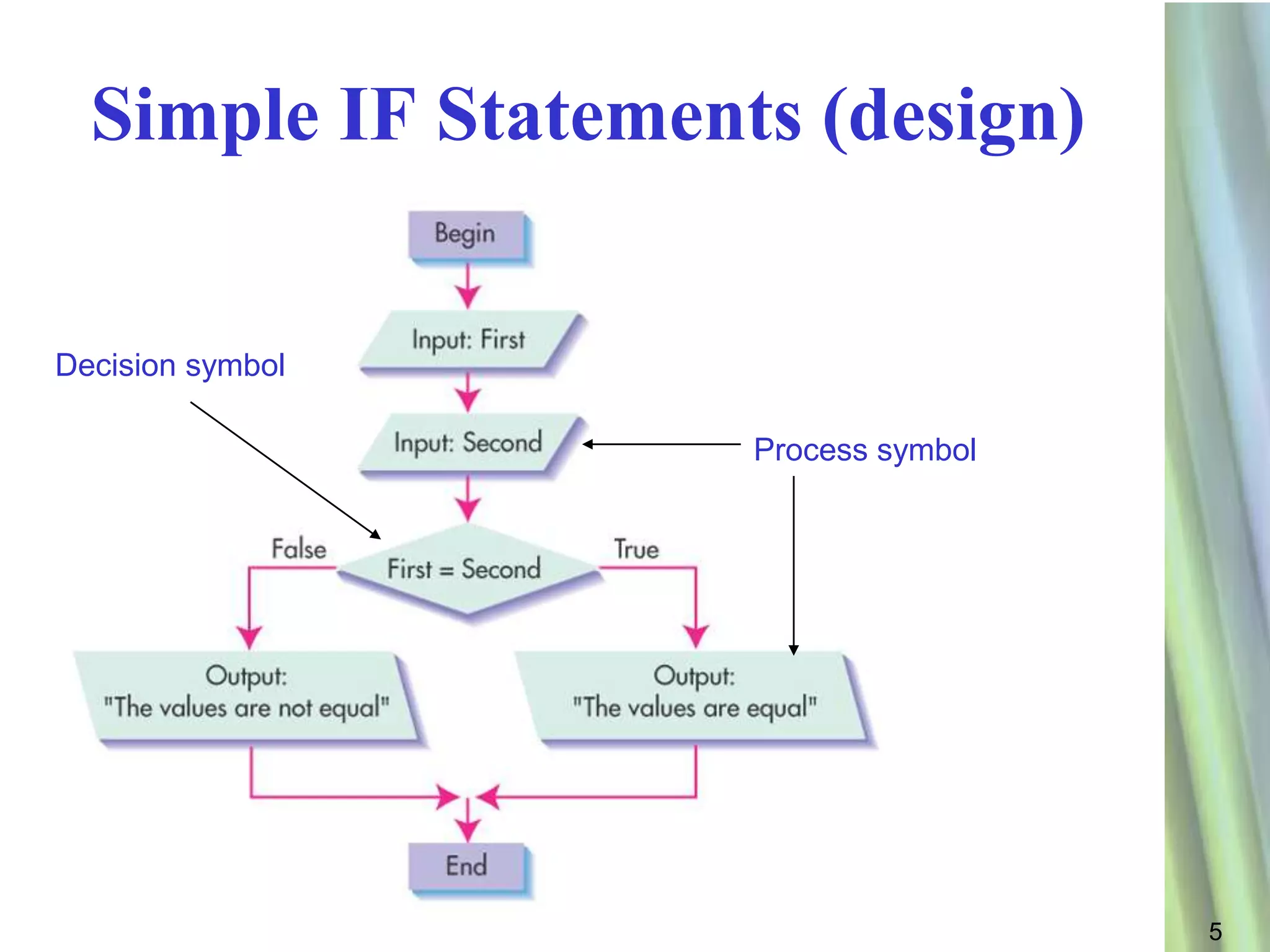
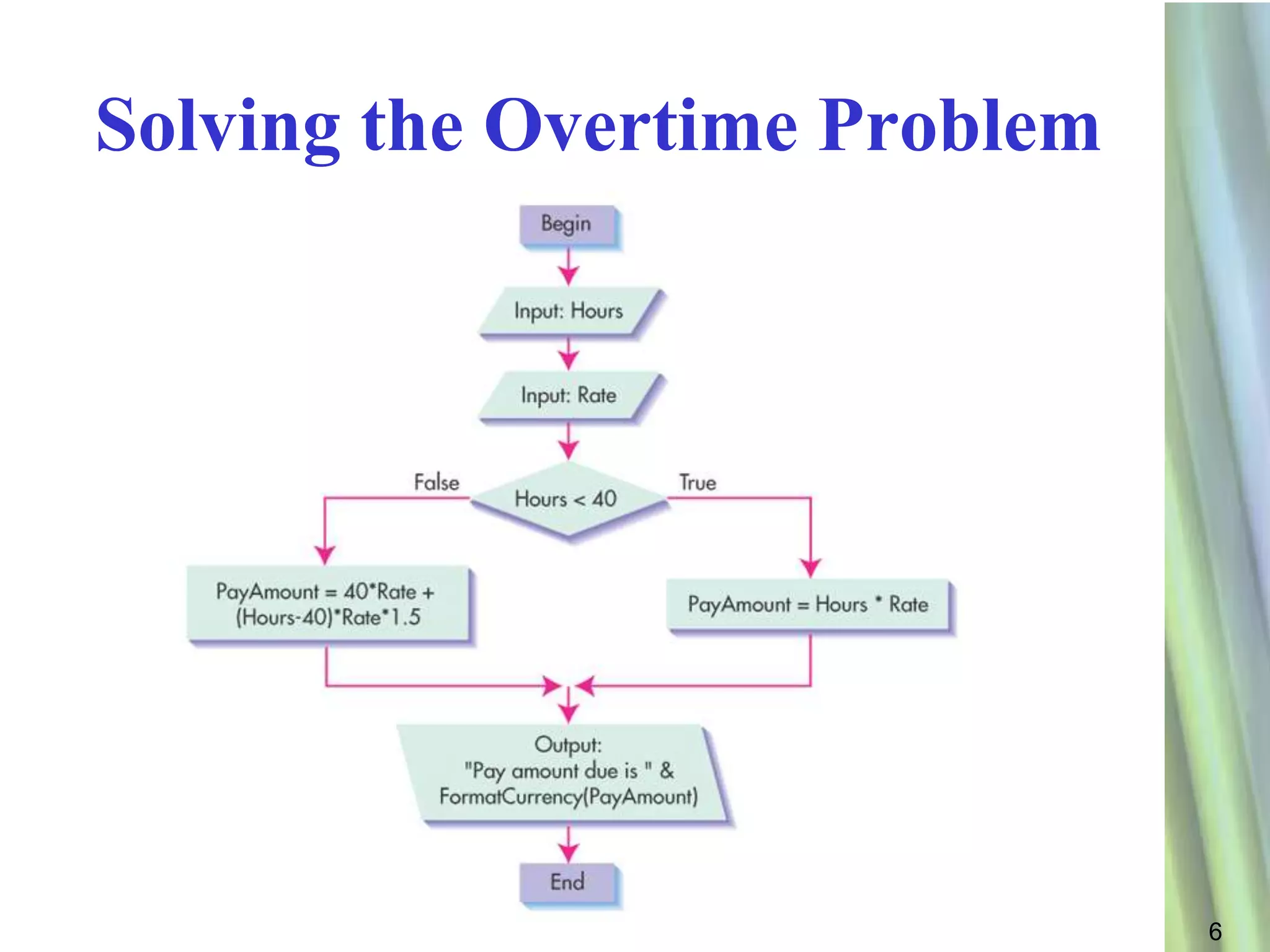
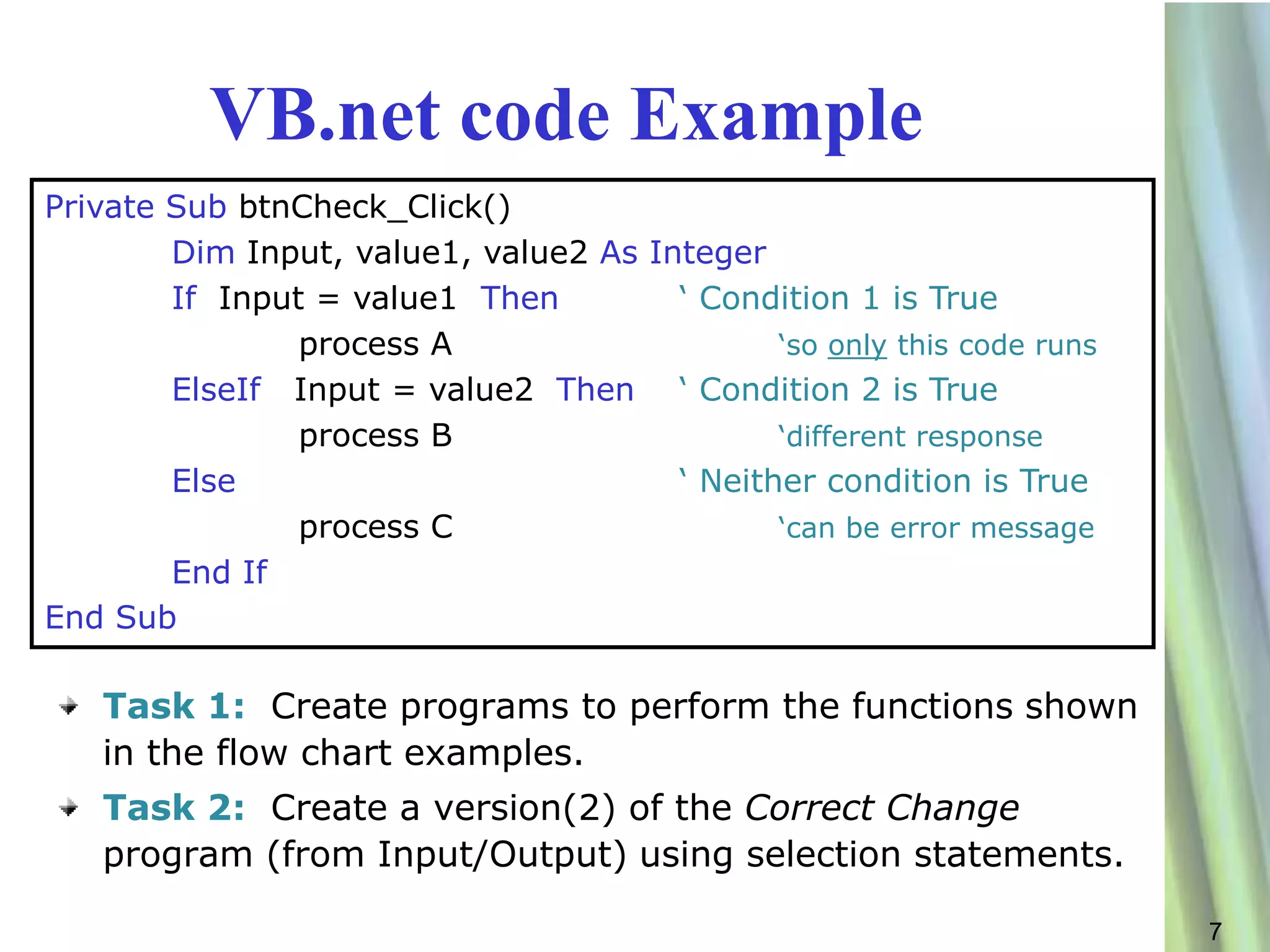
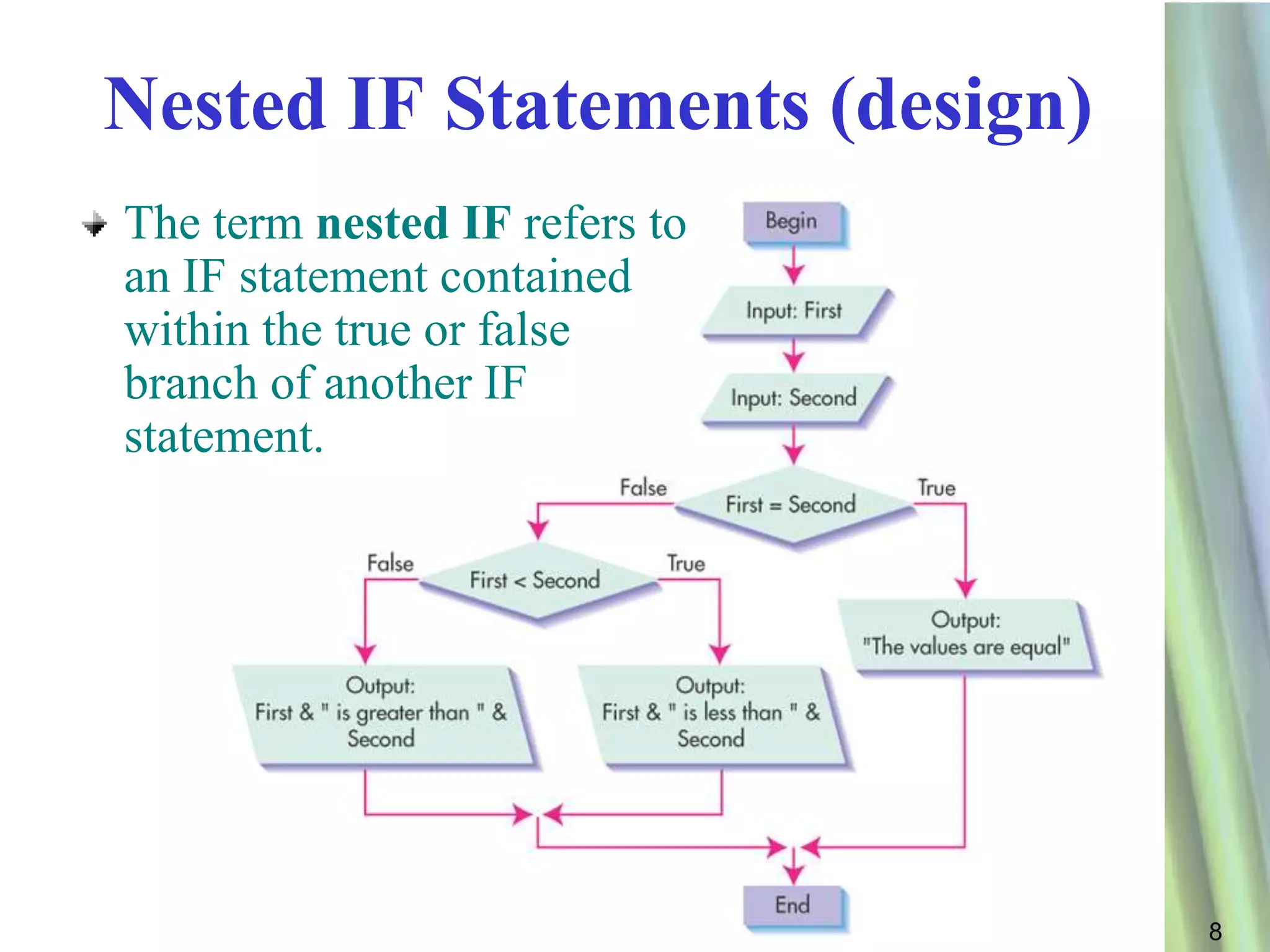
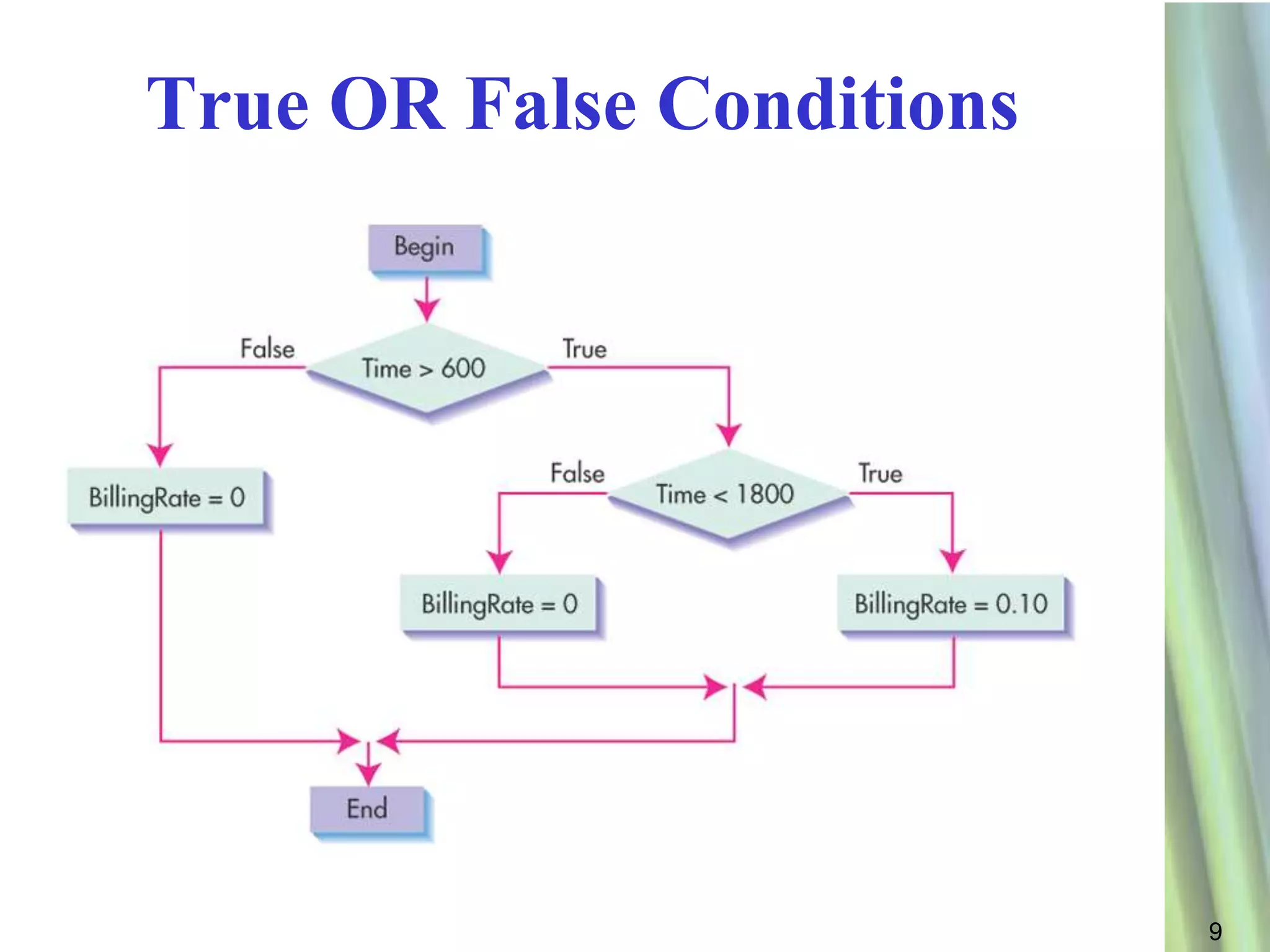
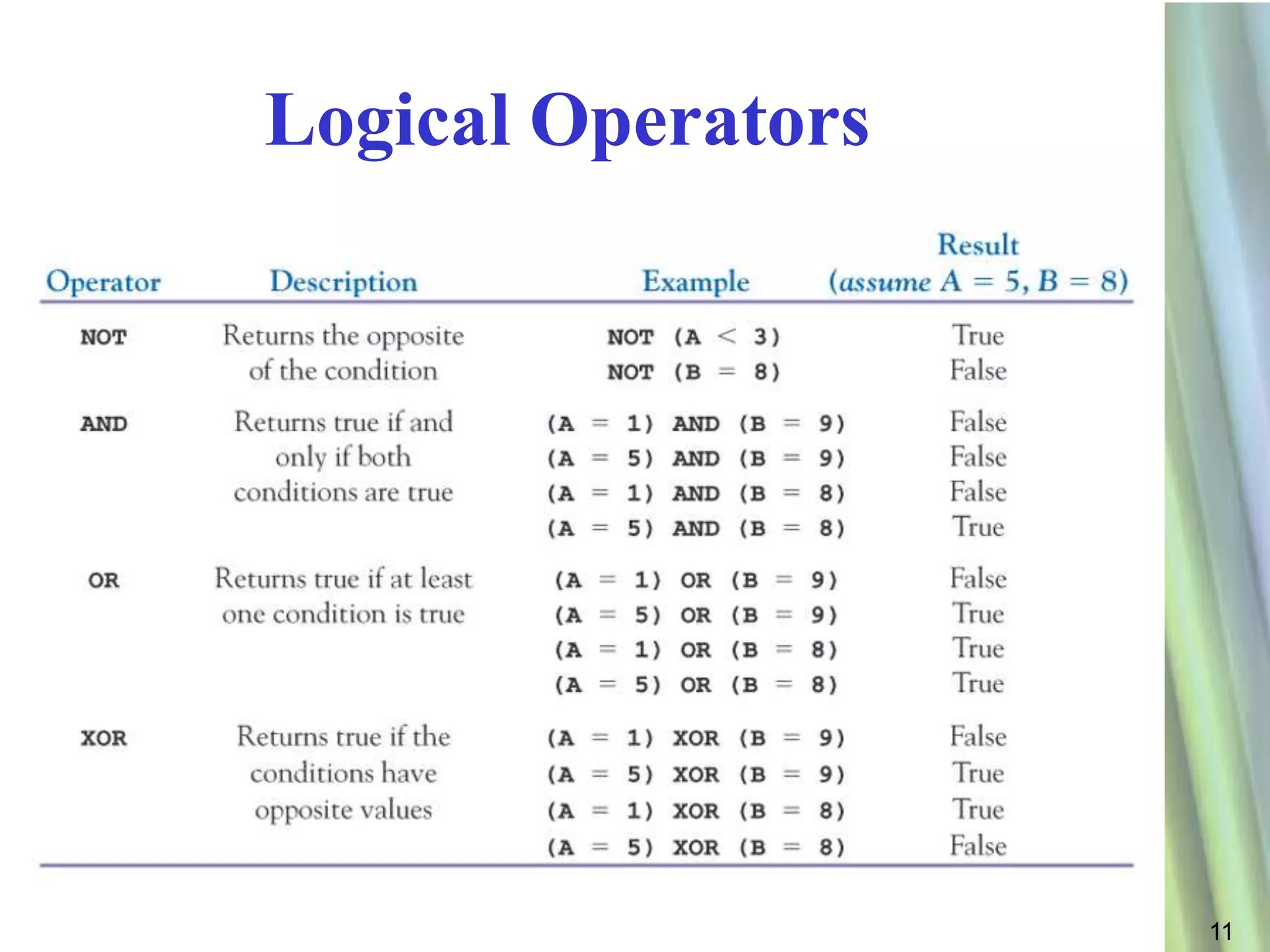
This document discusses decision making and selection statements in VB.NET. It explains how IF statements use relational operators in conditions to choose between different code blocks. Nested IF statements allow IF statements within the true/false branches of other IF statements. Compound conditions combine two or more conditions with logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT. The document provides examples of simple IF statements, nested IF statements, compound conditions, and the Select Case statement.