This document discusses common data structures and programming concepts in VB.NET, including:
1. It describes how data is processed after being entered into a program and common "structures" used for organizing data, such as variables, arrays, and collections.
2. It explains how a program runs by declaring and initializing variables in memory and executing lines of code sequentially.
3. It outlines different types of conditional statements (If/Then, If/Then/Else) that allow a program to make choices based on conditions.
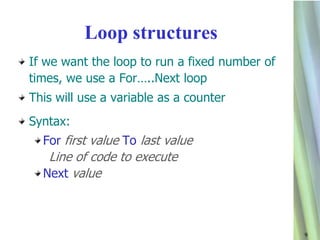
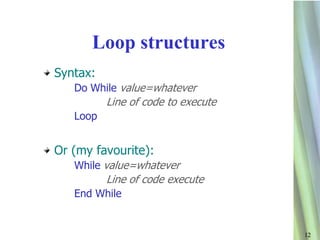
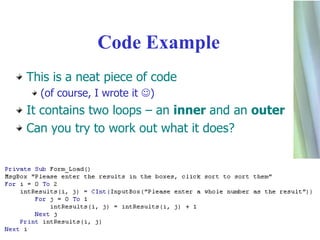
4. It details various loop structures (For/Next, Do/While, While/End While) that repeat lines of code a specified number of times or until a condition