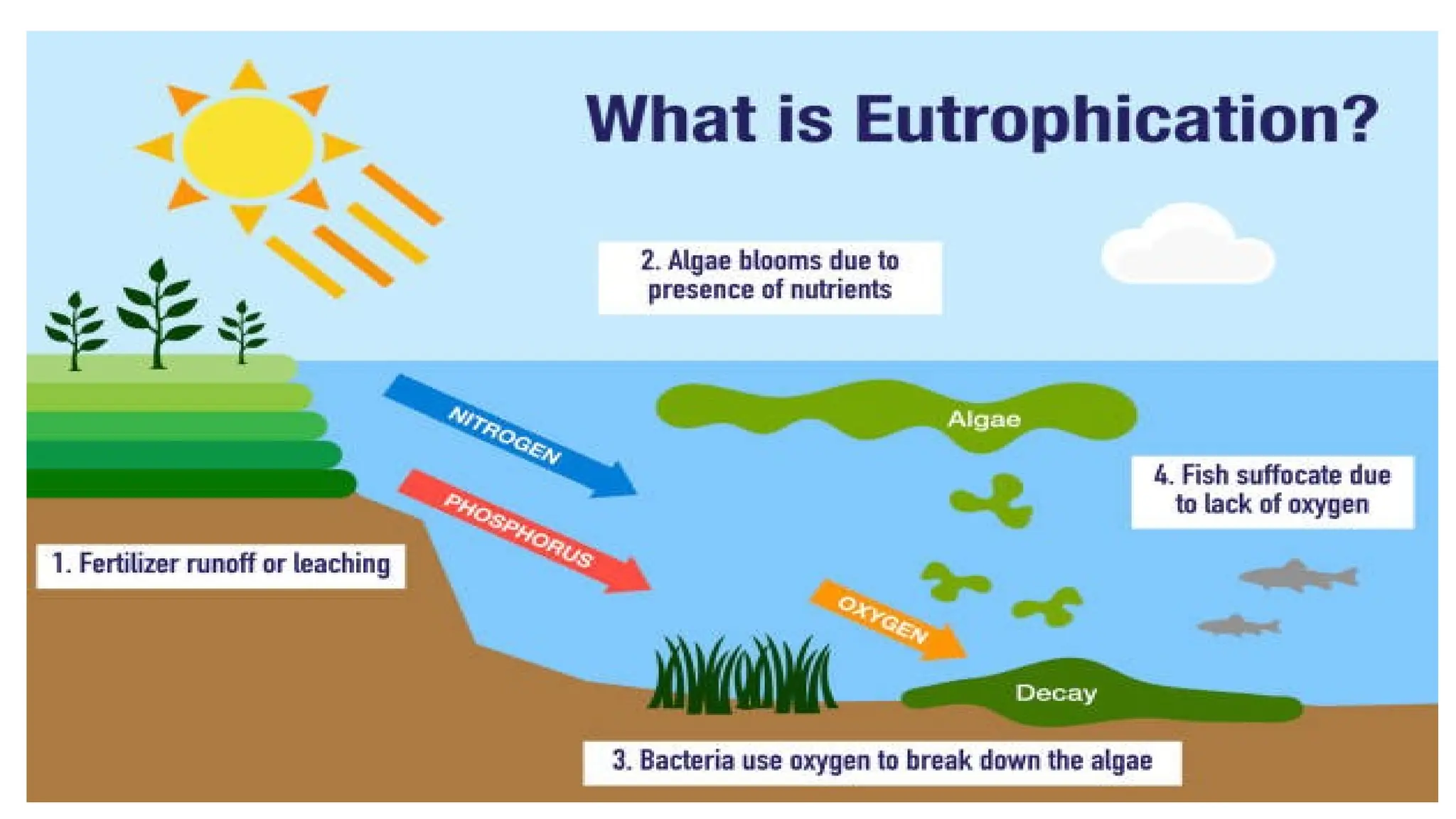
Eutrophication is the enrichment of water bodies with nitrogen and phosphorus, leading to excessive algae growth and detrimental effects on aquatic life. Causes include agricultural runoff, urban discharges, industrial effluents, and natural sources, while consequences involve algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and health risks due to toxins. Control measures involve nutrient management, agricultural practices, stormwater management, and public education.