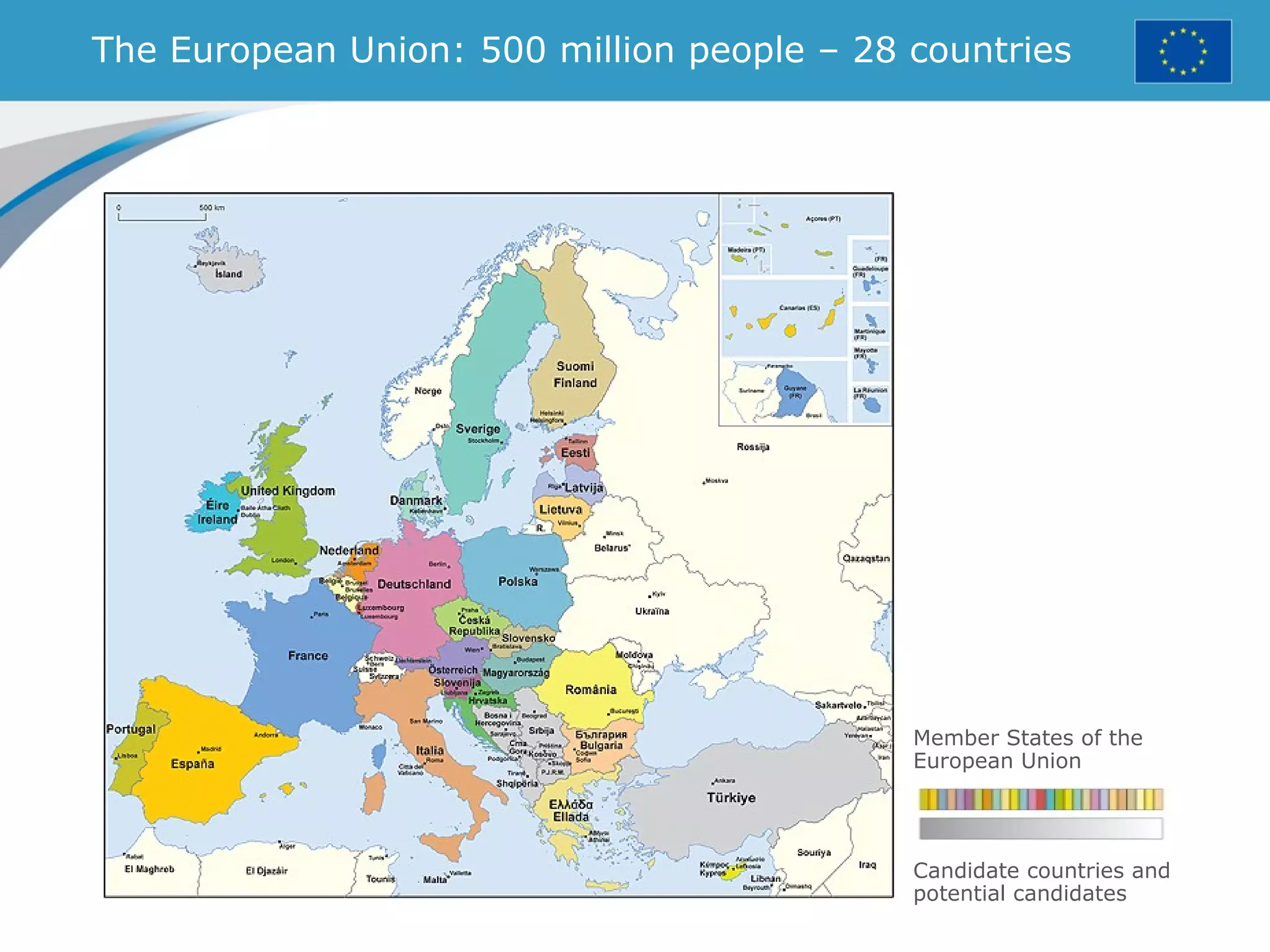
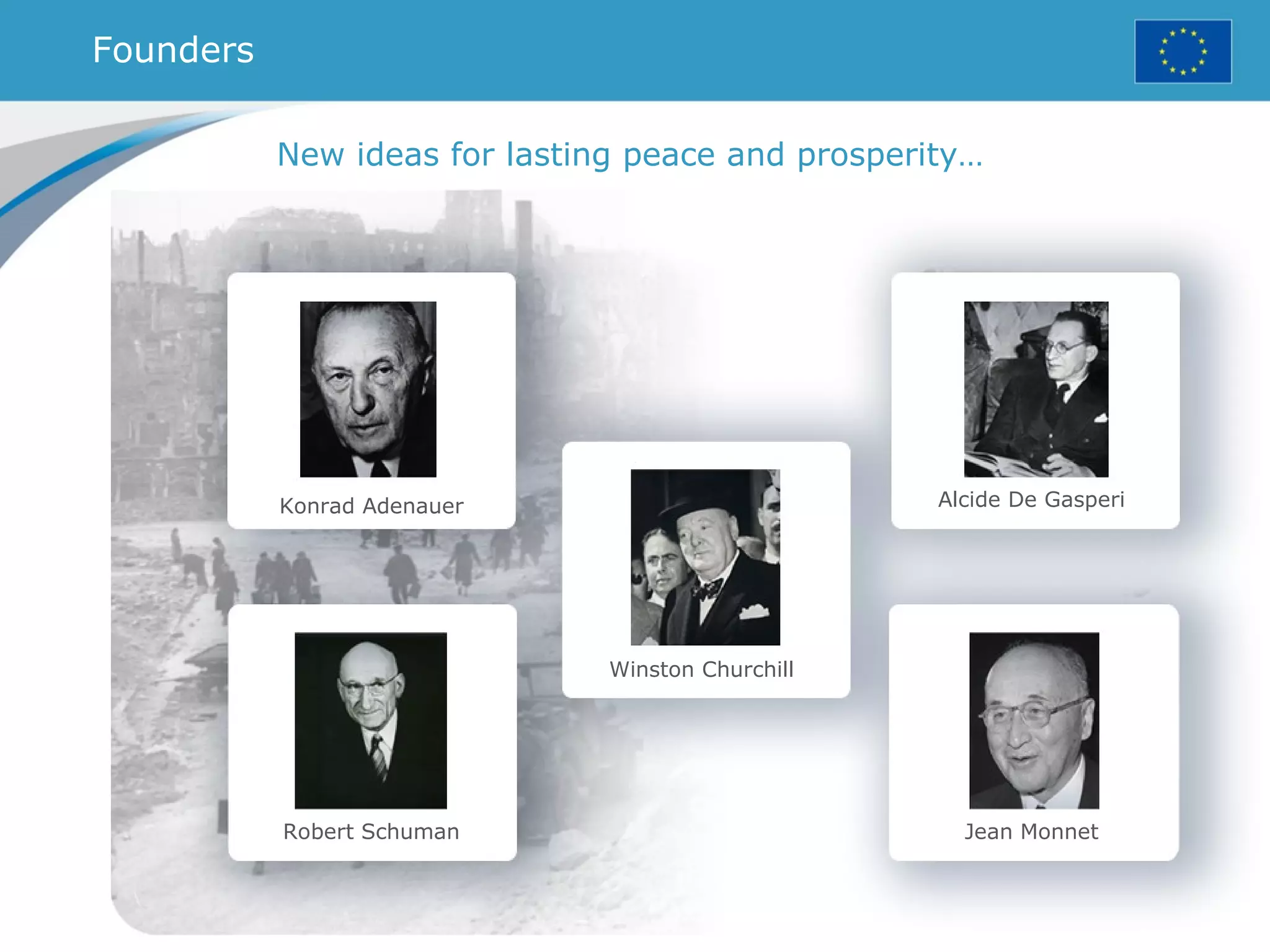
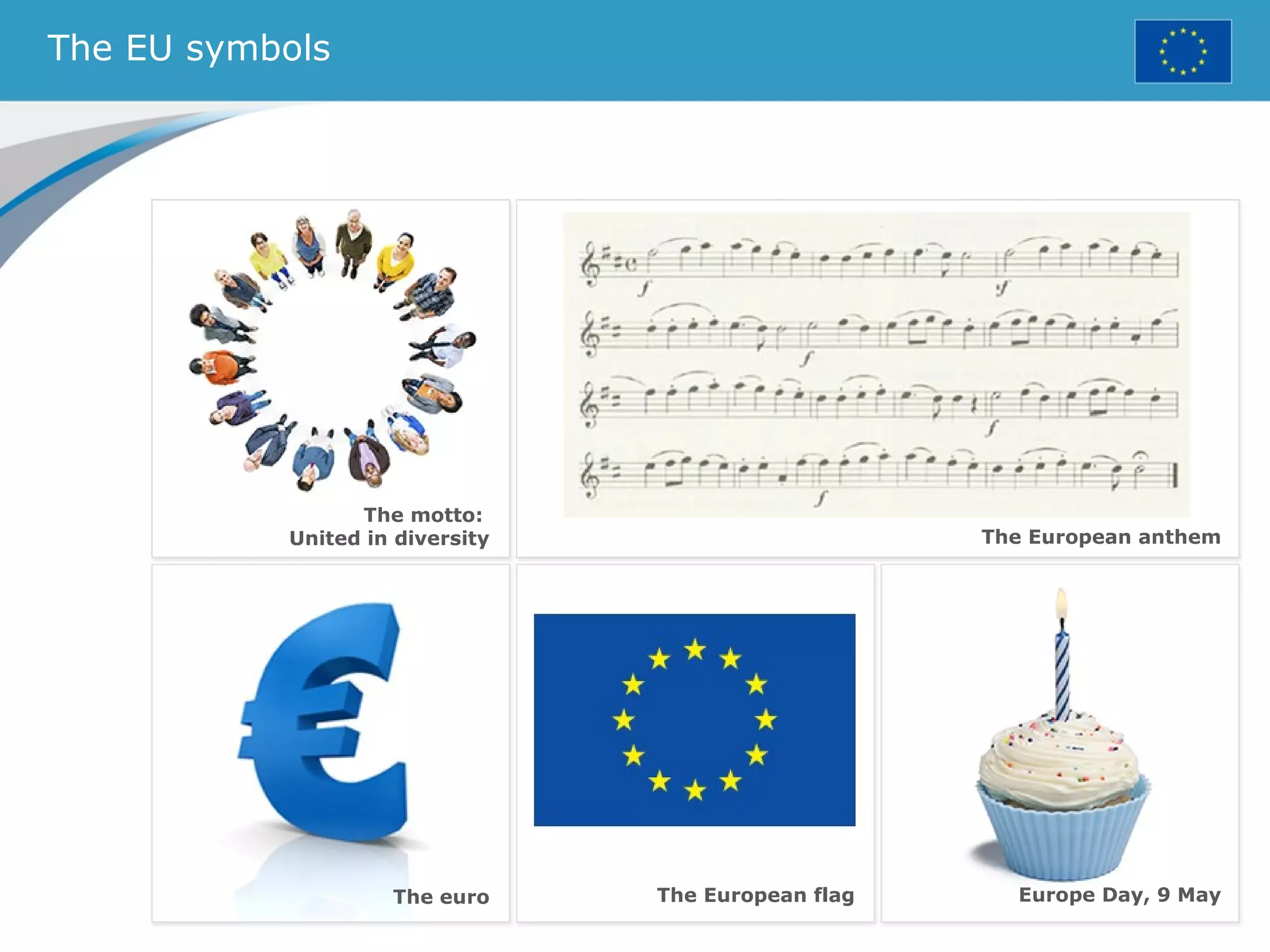
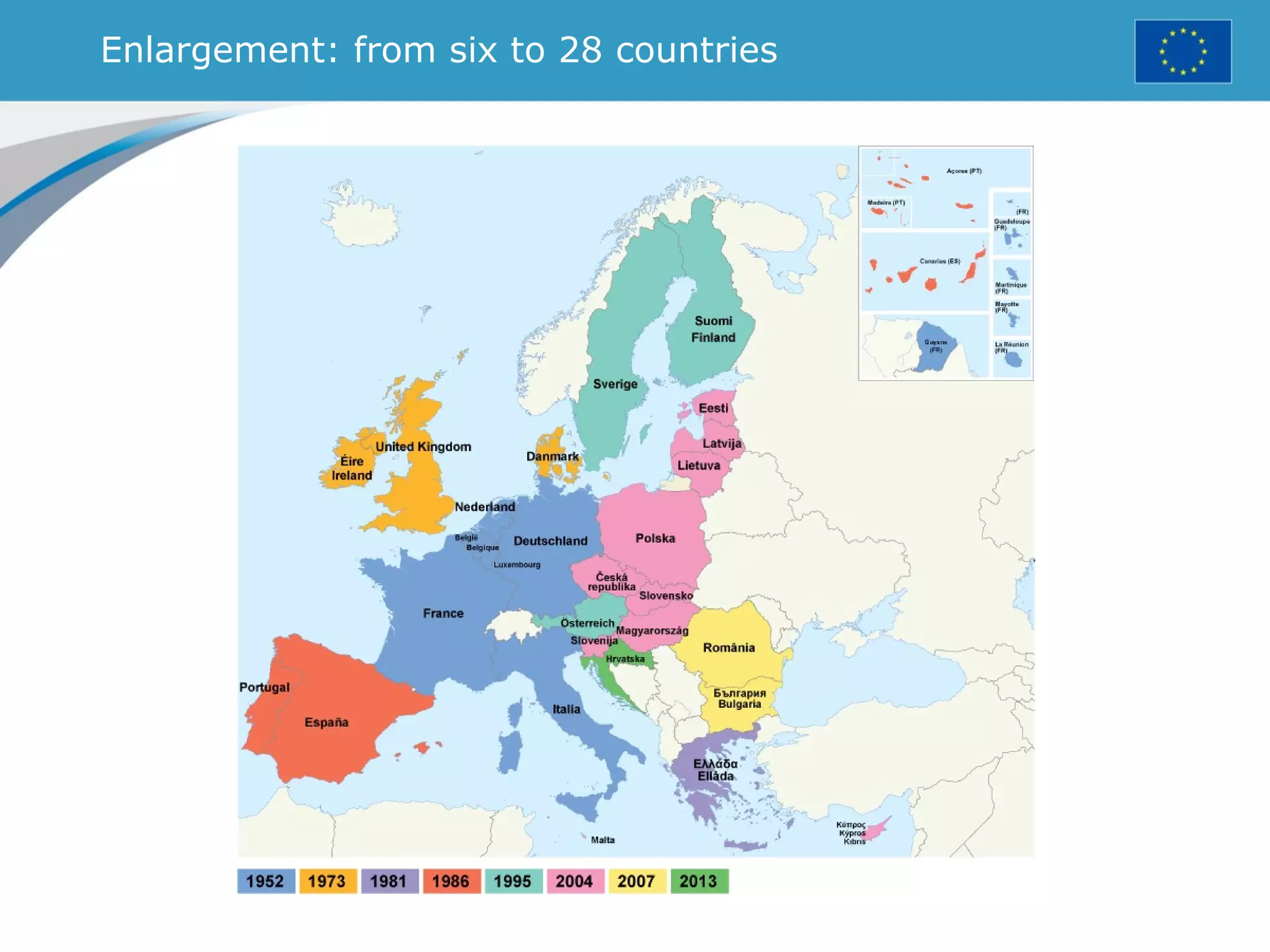
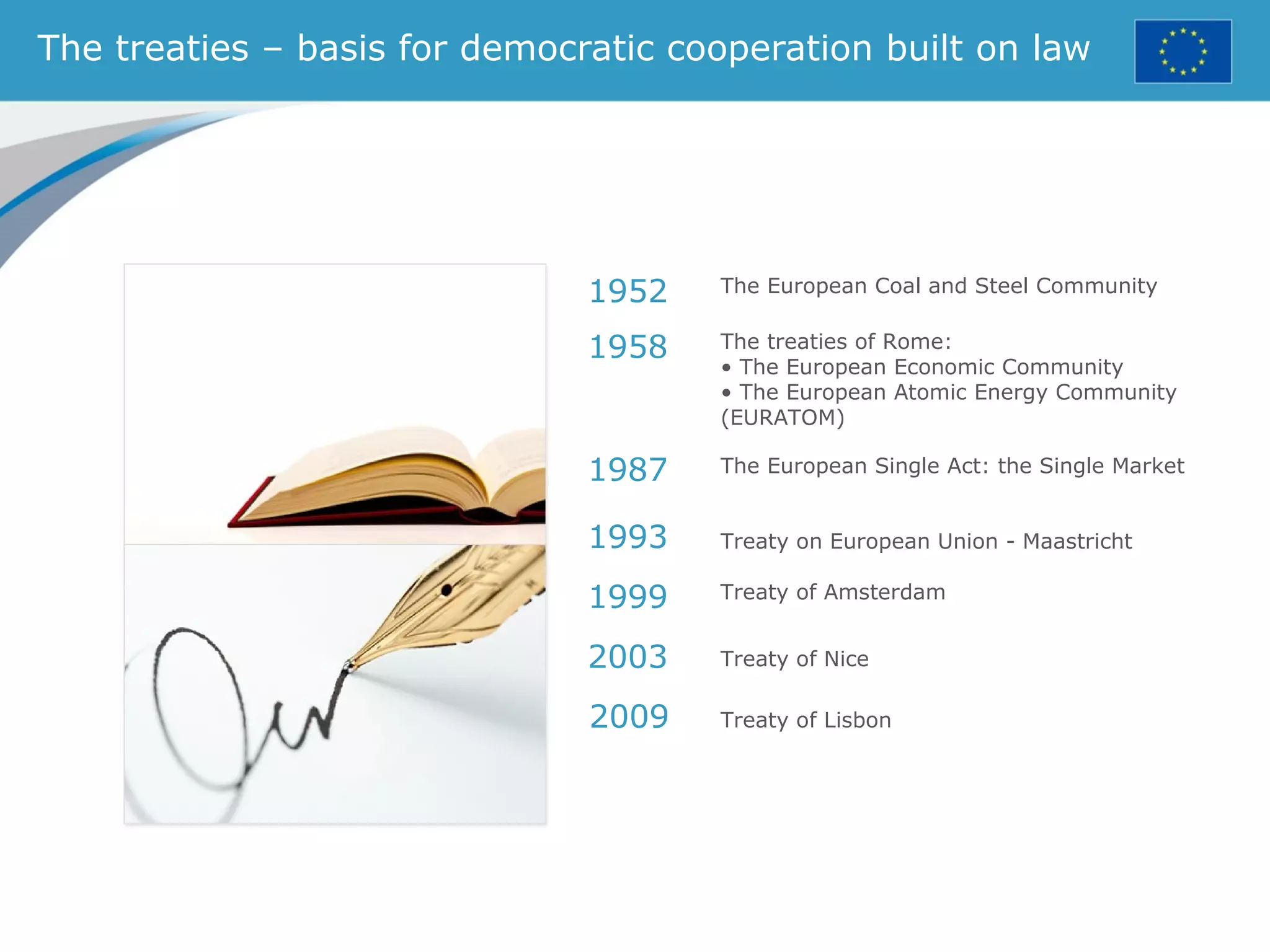
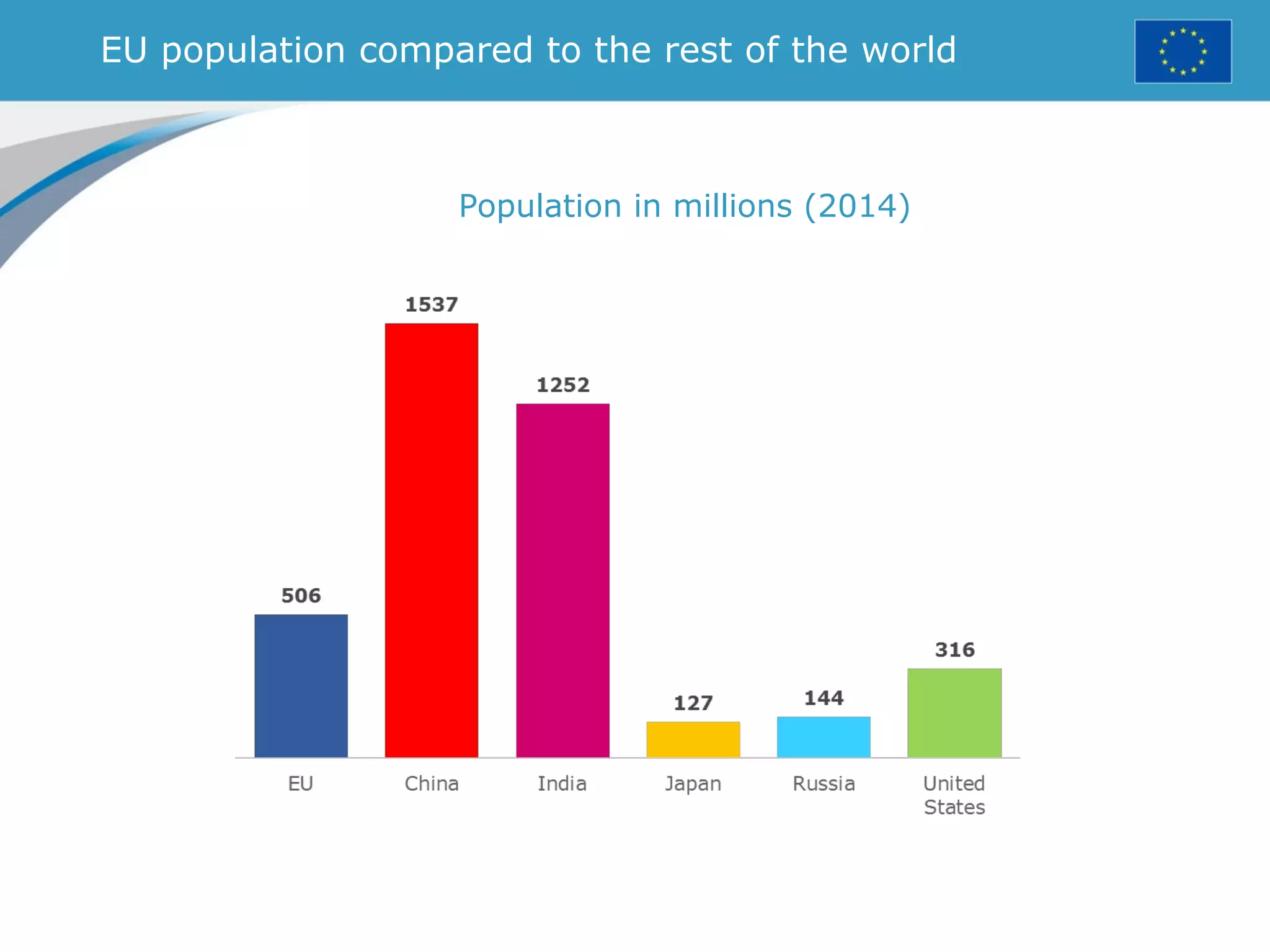
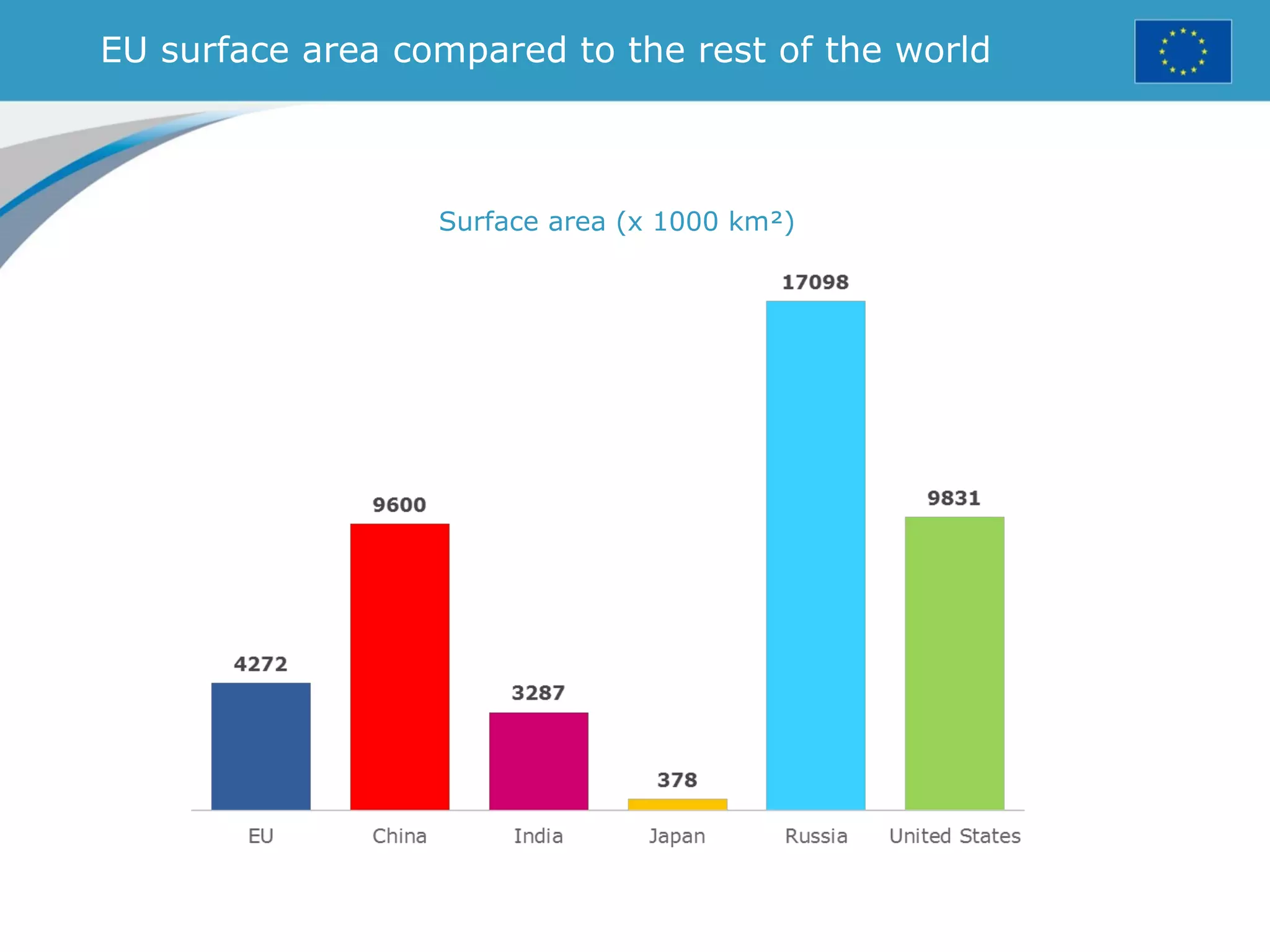
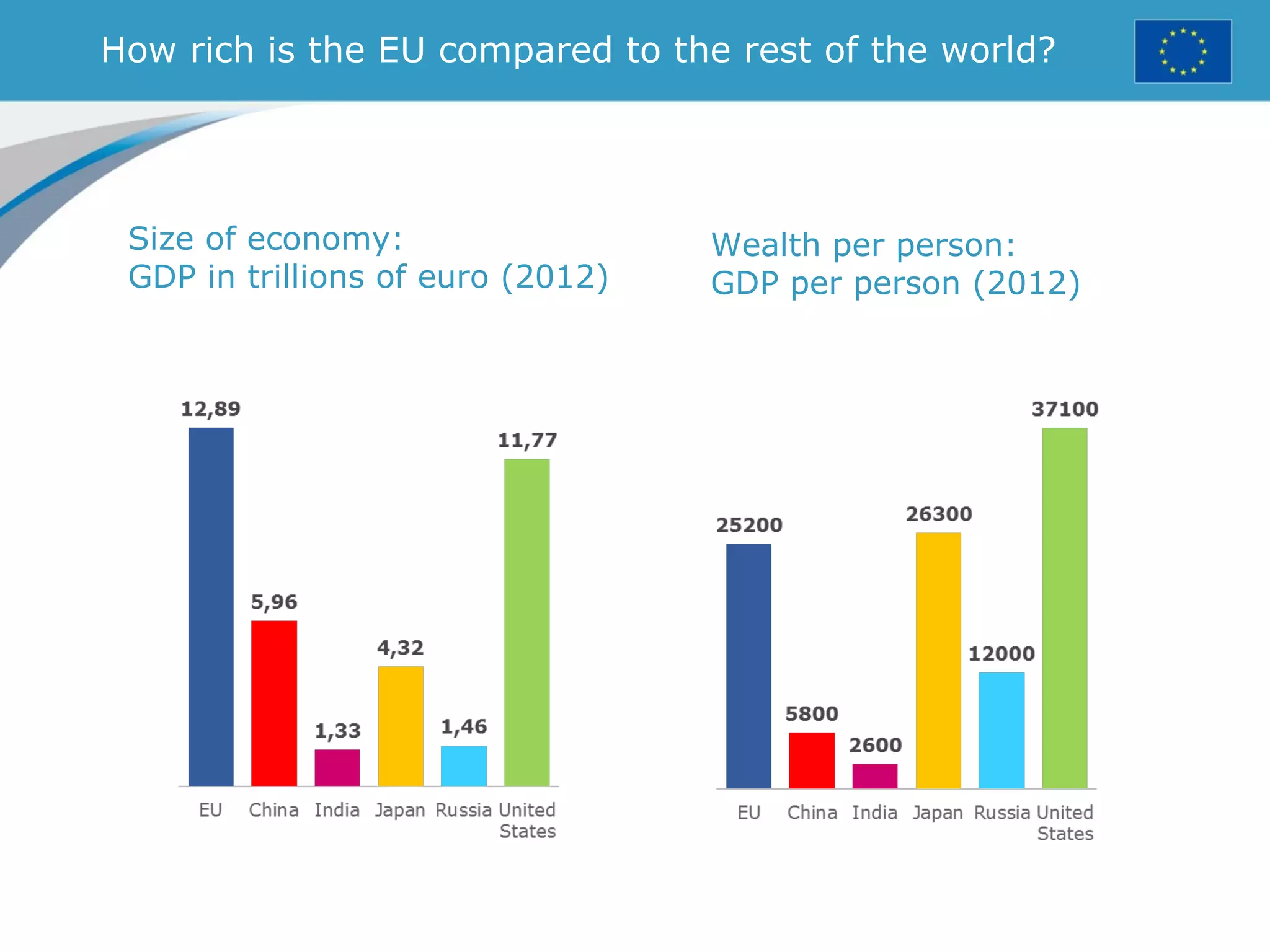
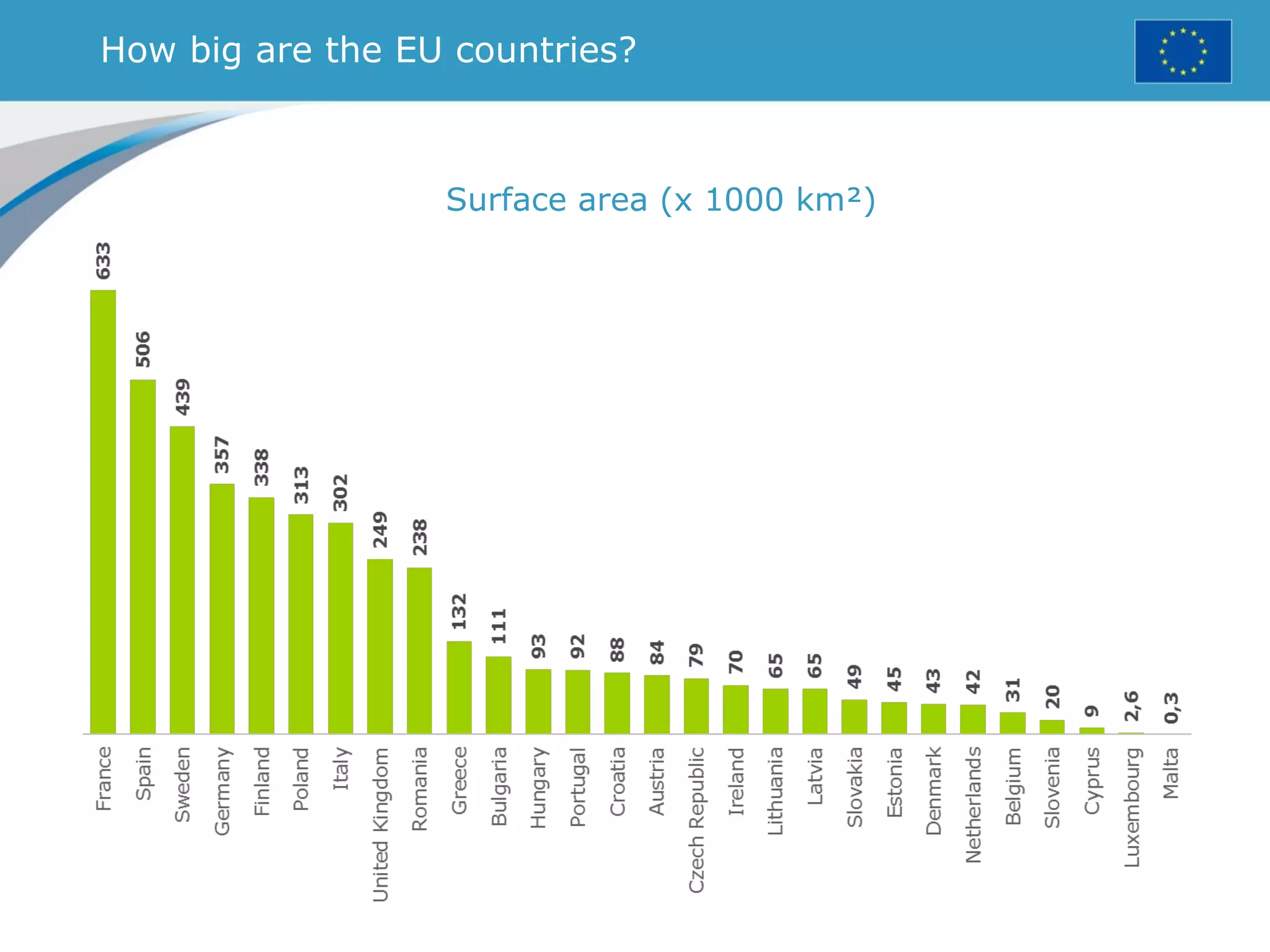
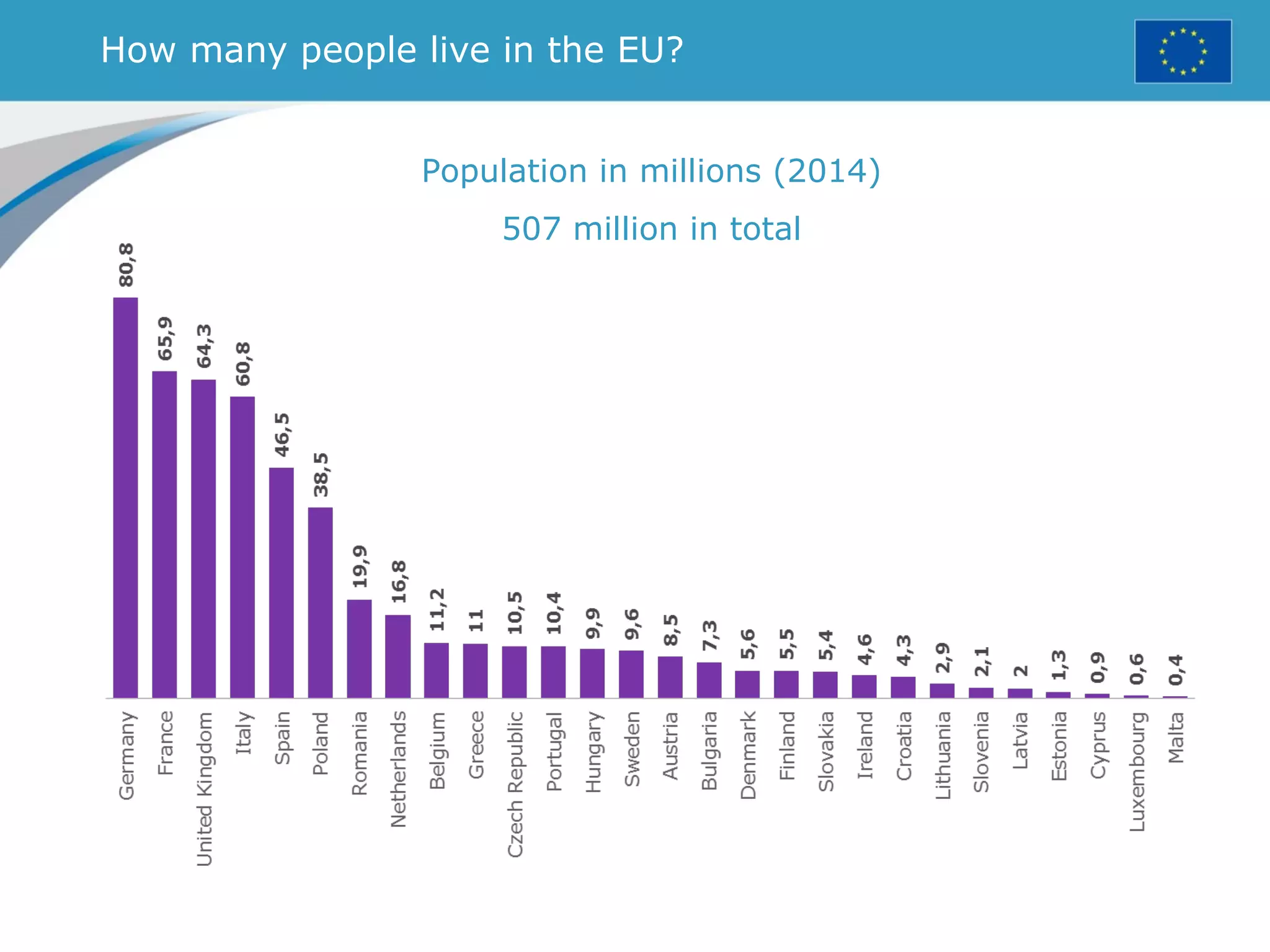
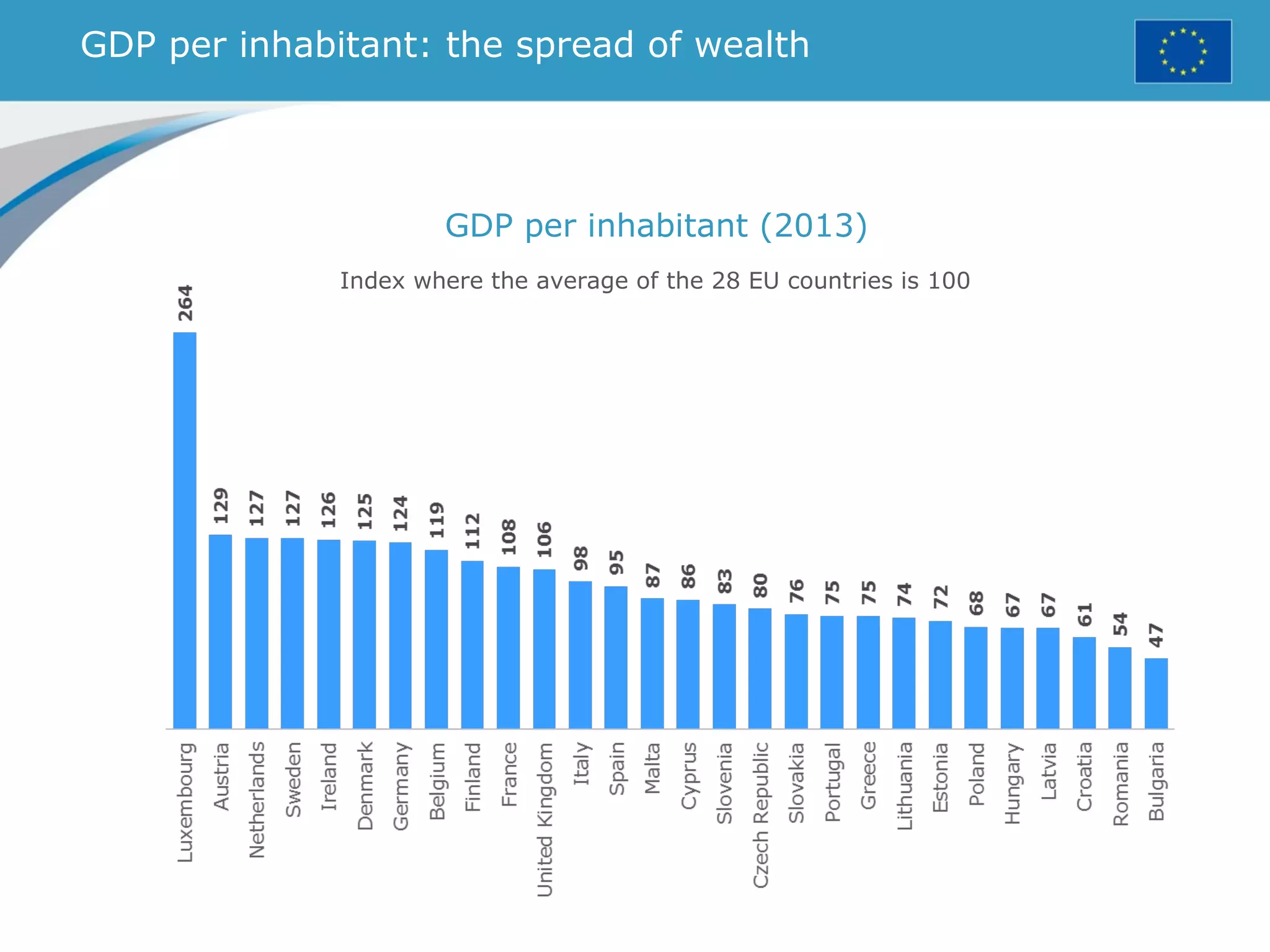
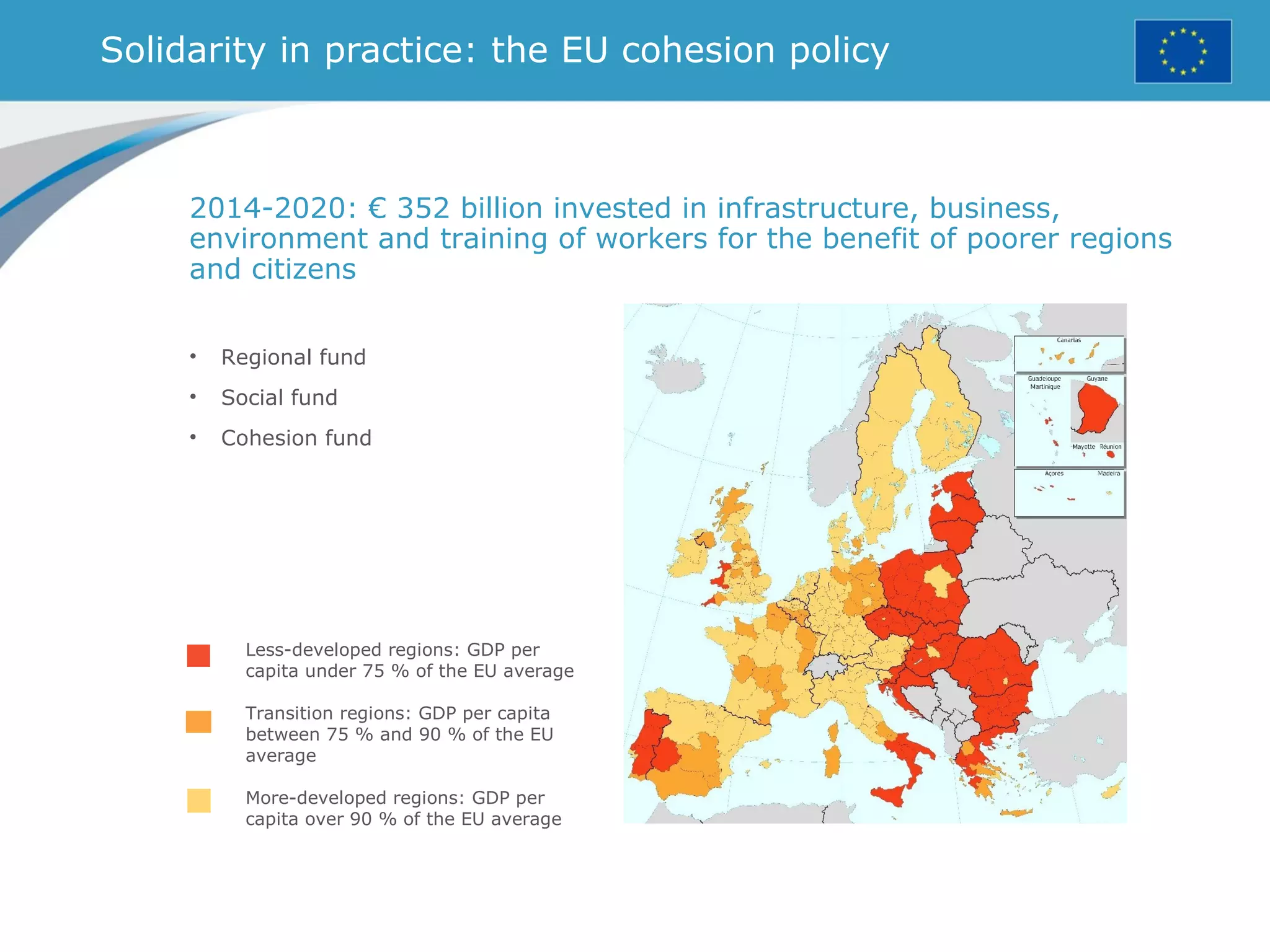
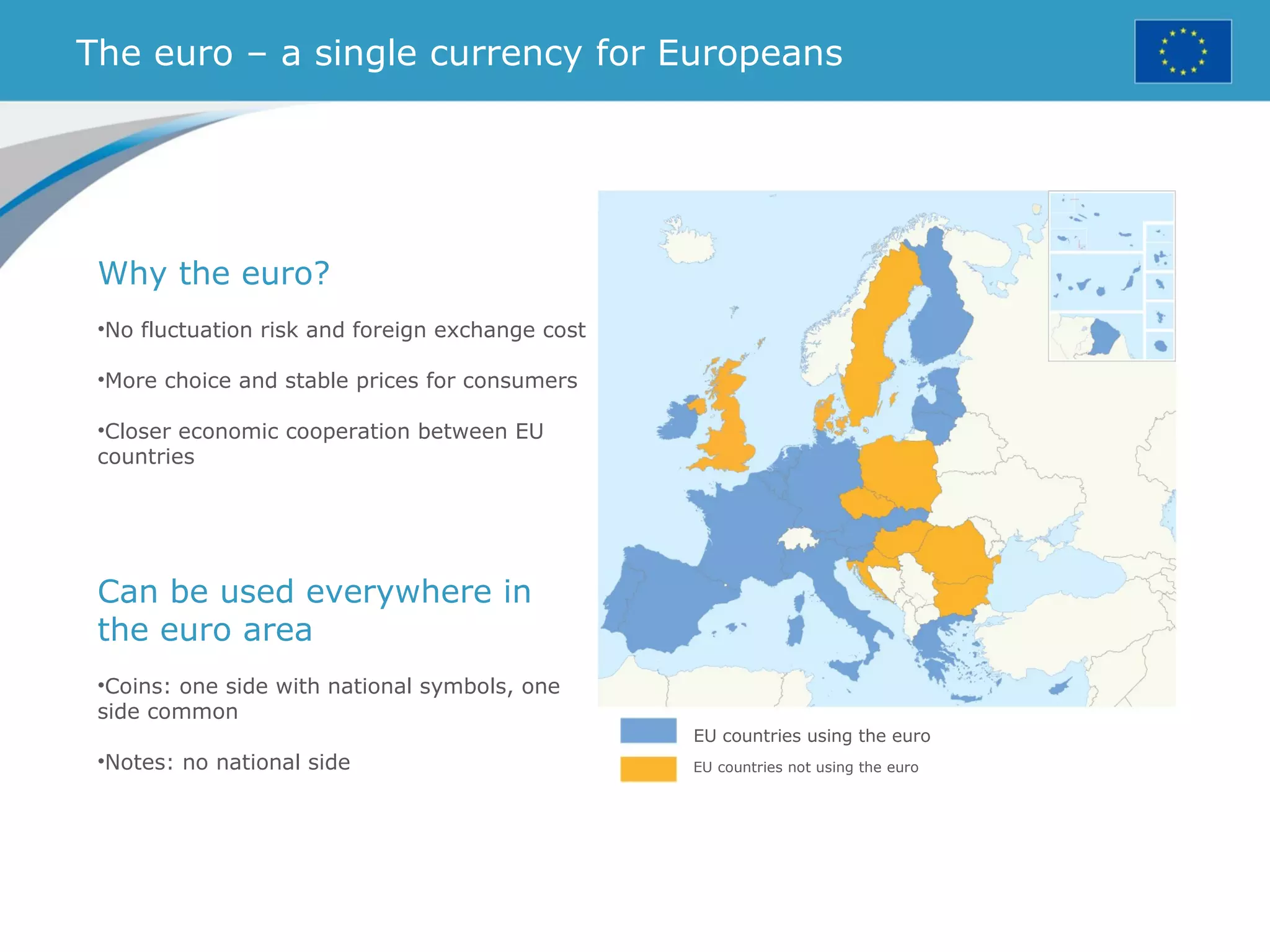
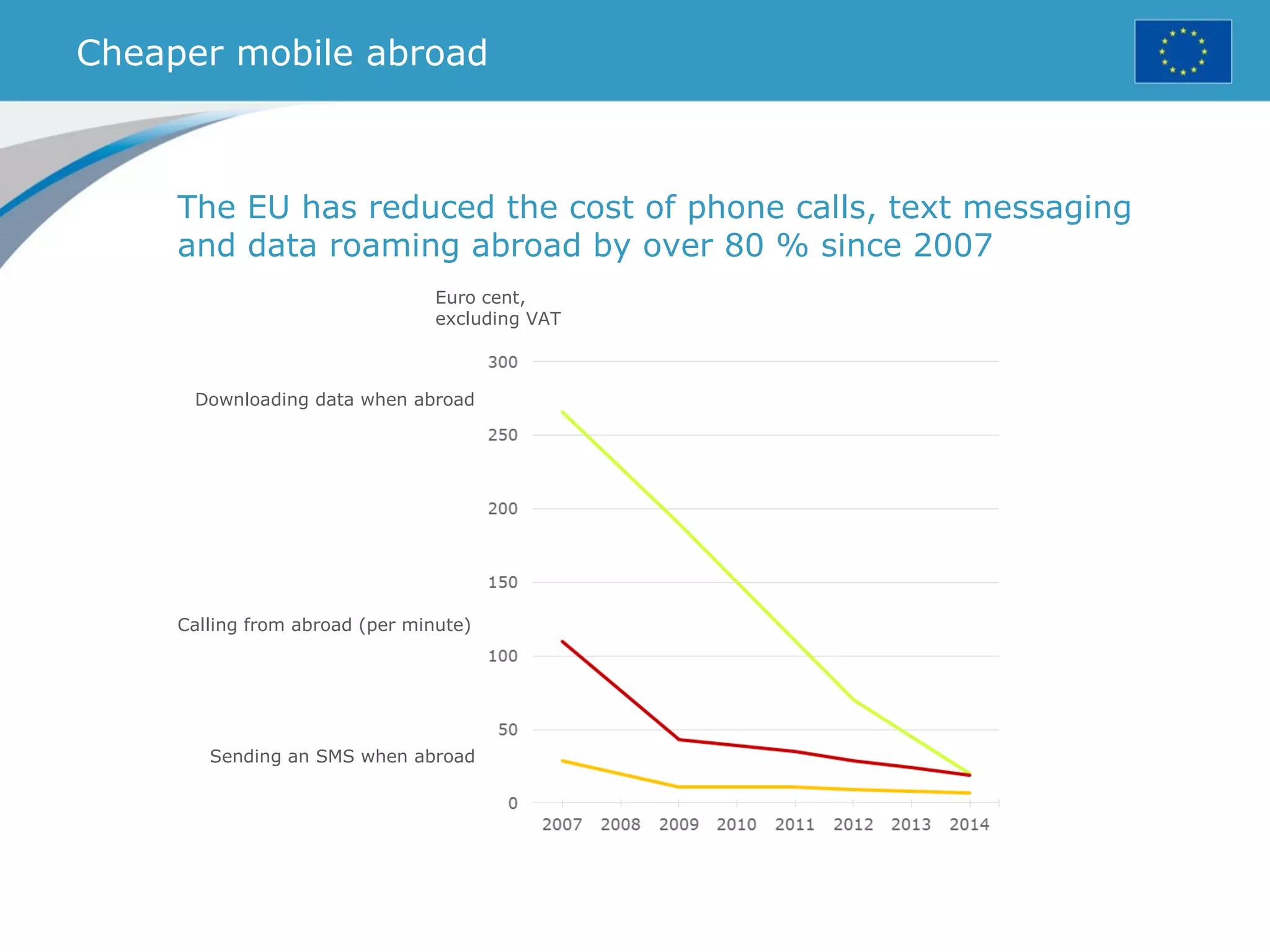
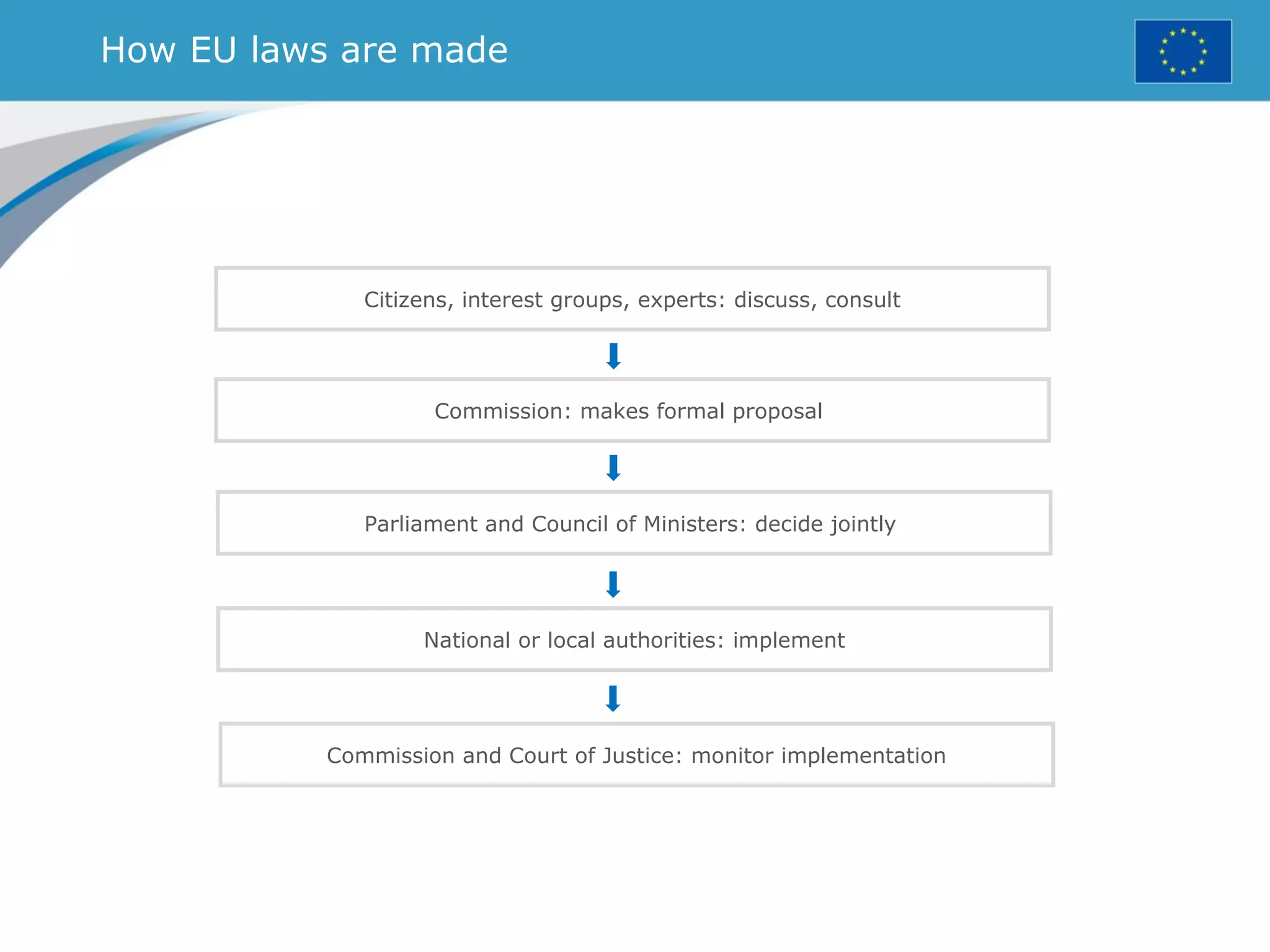
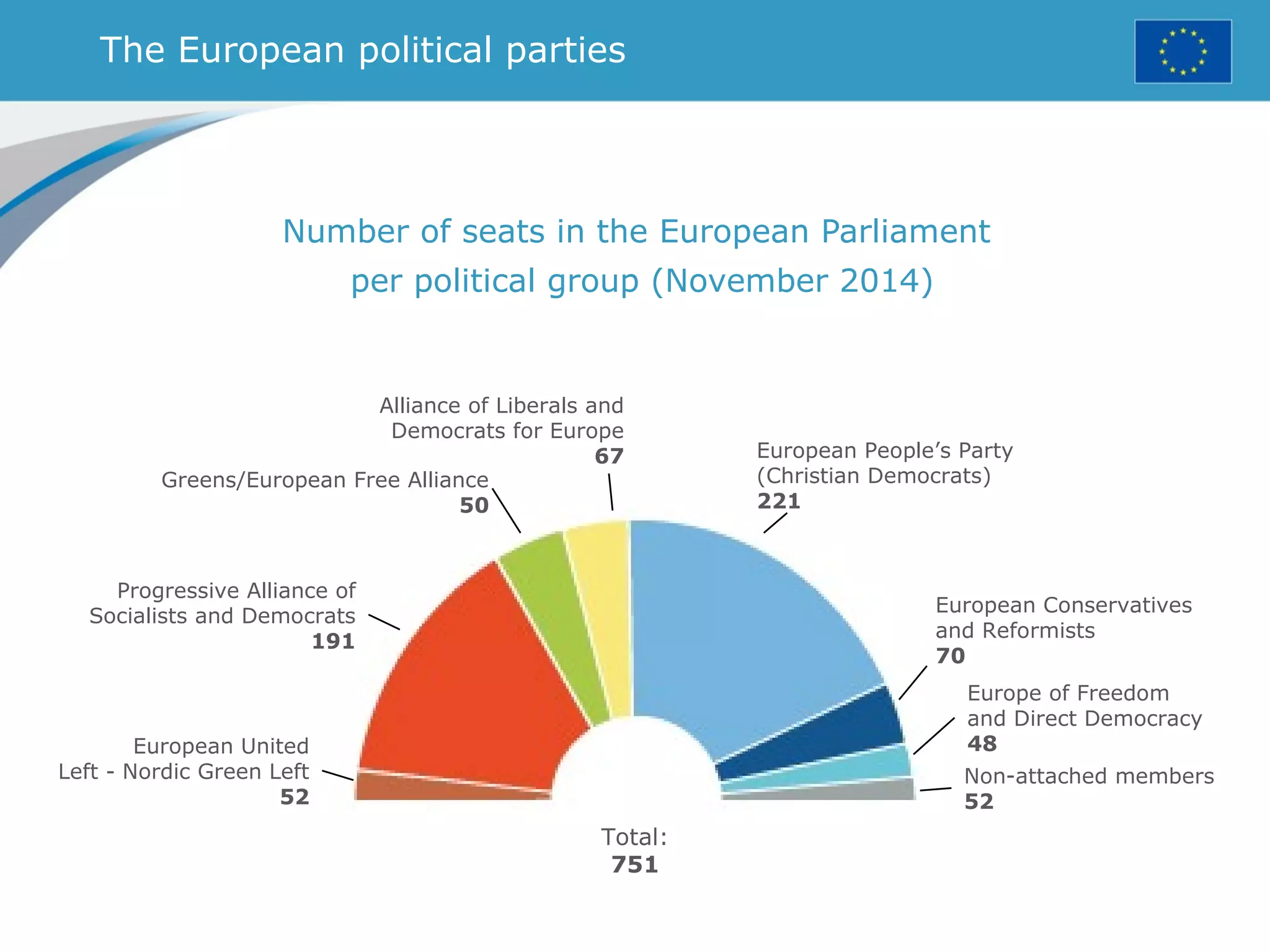
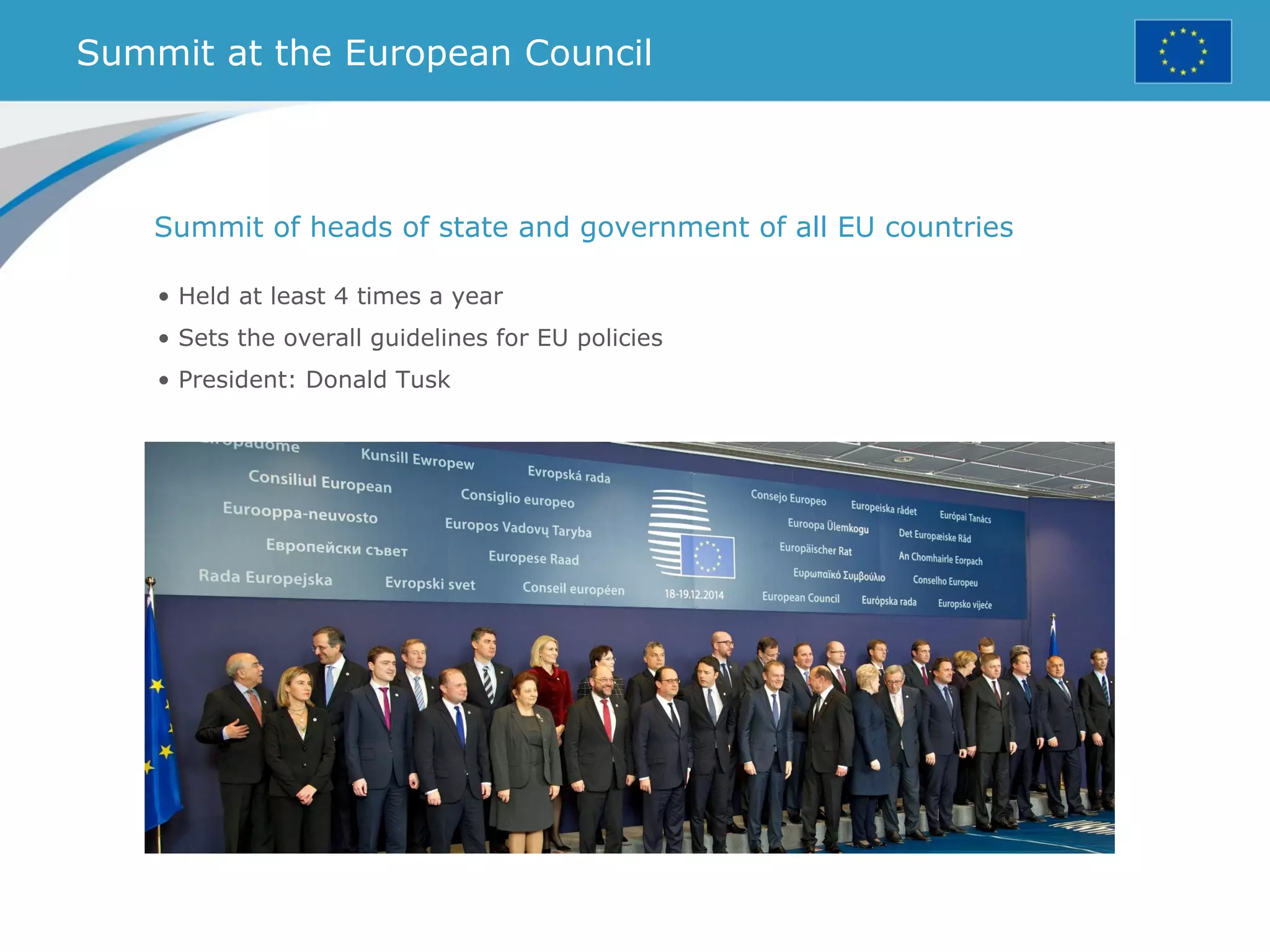
The document provides an overview of the European Union, including its history, institutions, policies, and key facts and figures. It summarizes that the EU is a political and economic union of 28 member countries with over 500 million citizens. Key institutions that govern the EU include the European Parliament, Council of Ministers, European Commission, and European Council. The document outlines the EU's founding principles of cooperation, unity, and shared prosperity.