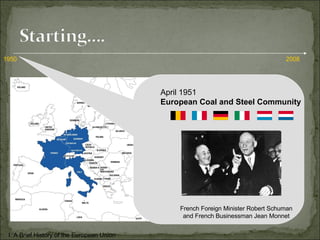
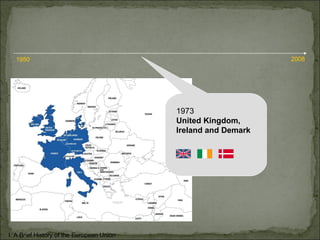
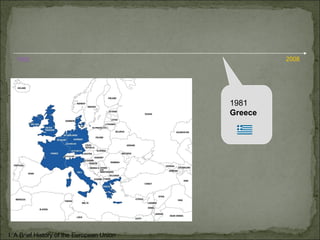
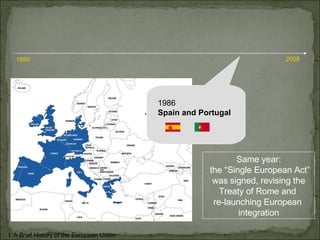
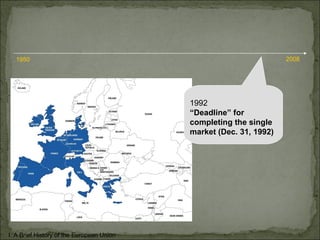
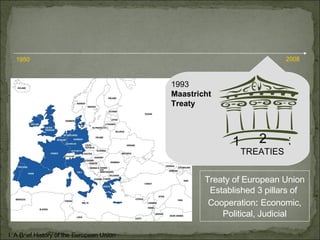
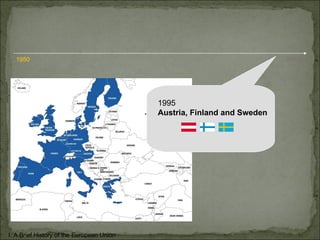
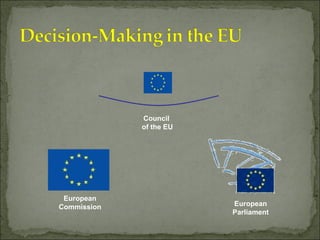
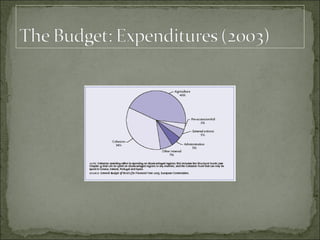
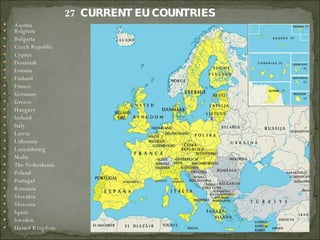
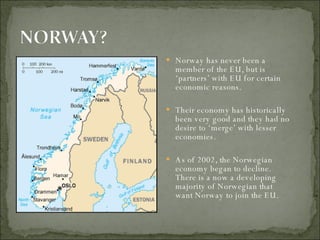
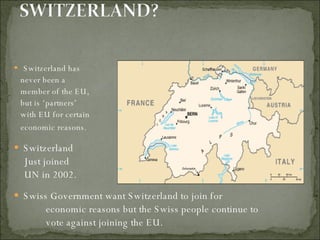
The European Union has gone through many changes over its 57 year history, starting as the European Coal and Steel Community in 1950 with 6 founding members and growing to 27 members today. It was established to regulate trade and form a single market, and later took on goals like environmental protection, human rights, and asserting its role globally. Key events included the introduction of the Euro currency in 1999 and the expansion of membership over the decades through various treaties.