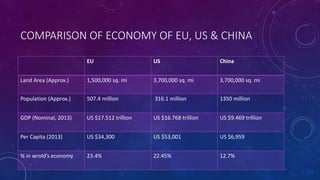
Regional grouping involves countries within a geographic area joining together for mutual benefit. The European Union began in the 1950s with six founding members and has since grown to include 28 member states. Key objectives of the EU include establishing a single market, customs union, and common policies around issues like agriculture, transportation, and social and economic goals. Members benefit from free trade and movement of goods, services, capital and people across borders, as well as increased economic and political influence on the global stage.