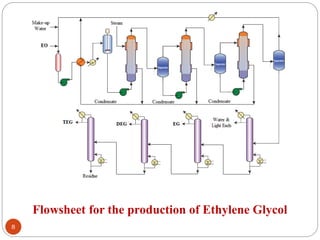
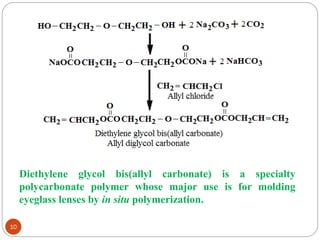
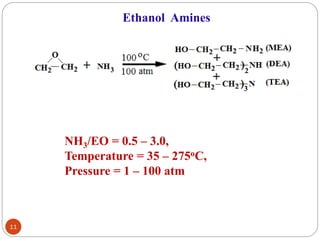
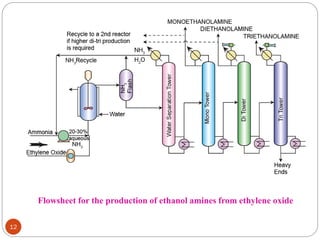
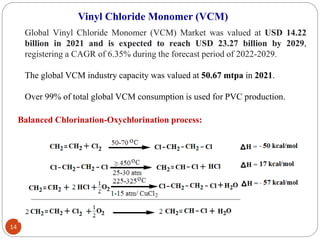
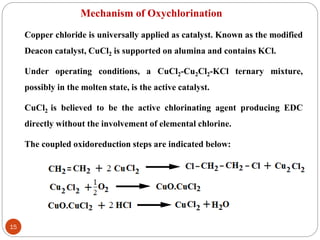
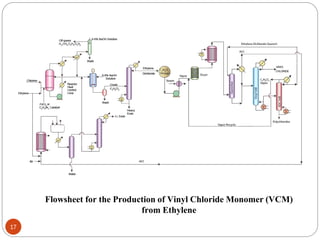
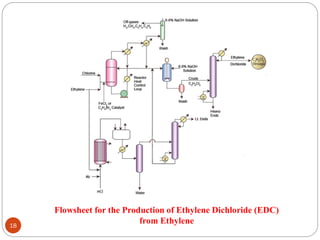
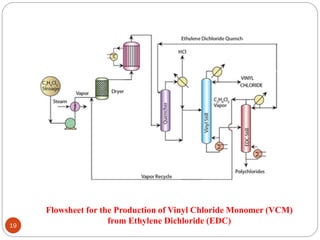
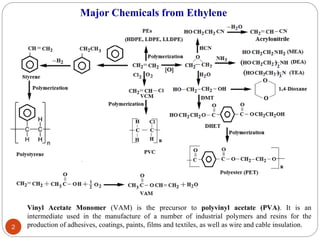
Ethylene is used to produce several major chemicals through catalytic oxidation and other reactions. Vinyl acetate monomer and ethylene oxide are two of the largest volume chemicals produced from ethylene. Ethylene oxide is used to produce ethylene glycol, primarily for PET bottles and antifreeze. It is also used to produce ethanolamines and other derivatives. Vinyl chloride monomer, the precursor to polyvinyl chloride, is produced through the chlorination of ethylene to form ethylene dichloride followed by oxychlorination to vinyl chloride. These processes involve complex catalyst systems and reaction conditions to produce the desired chemicals selectively.


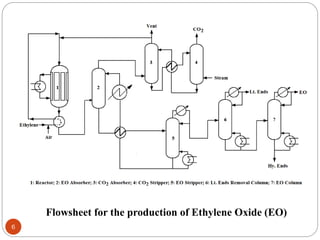
![Catalyst: Ag2O/Al2O3
[Catalyst contains 10-15% of silver and promoters-compounds of
alkalis or alkali earth metals, especially Cs and Ba.]
Oxidation with air : 260-280oC; Oxidation with oxygen: 230oC
Pressure: 10-30 atm
High purity, sulphur-free ethylene is required to avoid poisoning of
the catalyst.
Ethylene concentration is about 20-30 vol% or 5 vol% when oxygen
or air, respectively, is used as oxidant. The main byproducts are CO2
and H2O, and a very small amount of acetaldehyde is formed via
isomerization of ethylene oxide.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalsfromethylene-230915161714-cf096c72/85/Chemicals-from-Ethylene-pdf-4-320.jpg)