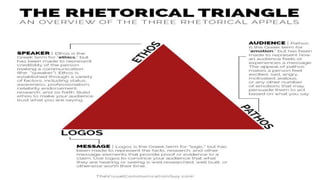
The document discusses Aristotle's rhetorical appeals: ethos, pathos, and logos, which are fundamental tools for persuasion in communication. Ethos refers to the credibility of the speaker, pathos relates to evoking emotions in the audience, and logos emphasizes logical reasoning and evidence. These concepts are crucial in fields like advertising and speech writing to influence perspectives.