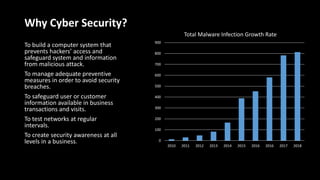
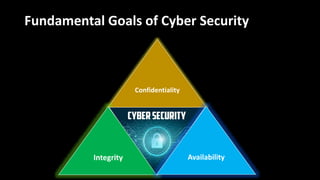
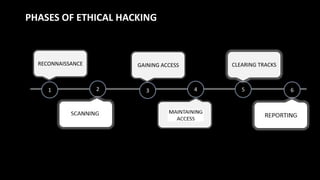
The document discusses cyber security and ethical hacking. It introduces a student group project on this topic and provides an agenda that covers common cyber attacks, cyber security goals and threats, the roles of different types of hackers, the process of ethical hacking, careers in cyber security, and tips to avoid being hacked. Ethical hacking involves authorized testing of systems to identify vulnerabilities by simulating hacking attacks with the permission of system owners. The goals are to improve security and protect against data breaches and cyber threats.