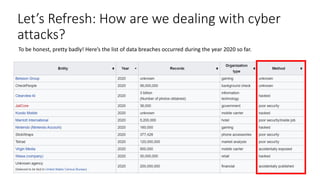
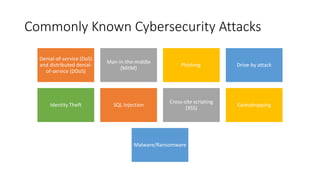
Krutarth Vasavada presented on ethical hacking and cybersecurity. He began with definitions of ethical and hacking. Ethical hacking involves authorized access to computer systems to test security without malicious intent. Vasavada discussed why individuals and organizations are interested in hacking, including to understand current security status. He covered common types of attacks like denial of service, malware, and social engineering. The causes of attacks include footprinting, sniffing, fingerprinting and password hacking. Prevention requires unique approaches depending on the target. Ethical hackers can help by understanding vulnerabilities and having no malicious intent. Career opportunities in ethical hacking require skills and certifications in computer systems, programming, and networking.