This document provides a summary of an industrial training lab report on ethical hacking. It discusses key topics including:
- An introduction to ethical hacking terminology, different types of hackers, and the job role of an ethical hacker.
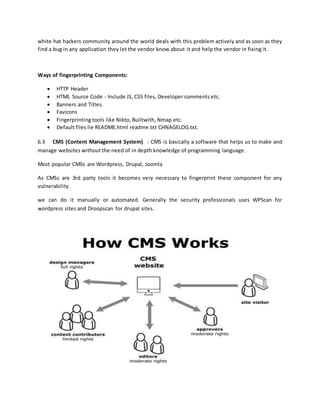
- Information gathering techniques like footprinting and using search engines. It also discusses web server architecture.
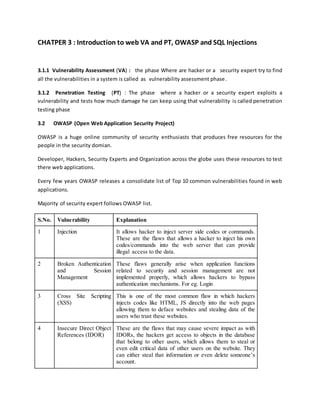
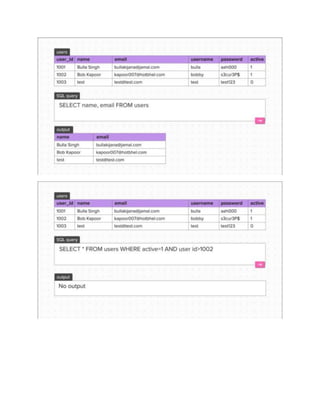
- An introduction to web vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT), the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), and SQL injections.
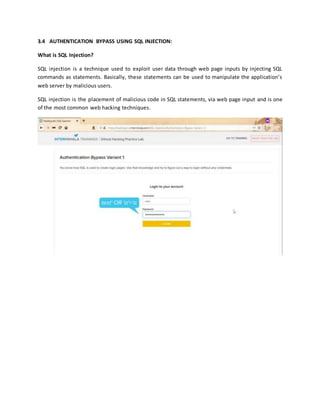
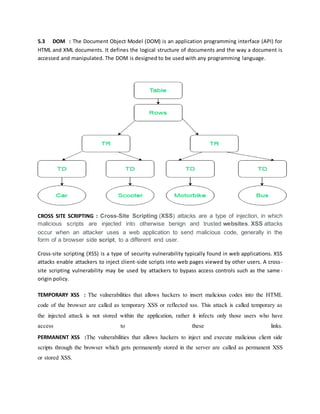
- Other topics covered include bypassing client-side filters, client-side attacks like cross-site scripting, security misconfigurations, and documenting vulnerabilities.