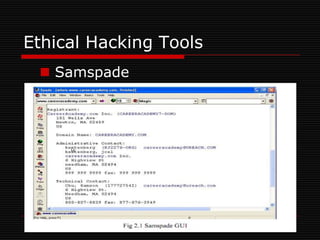
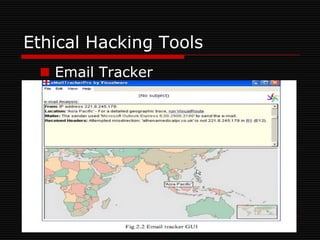
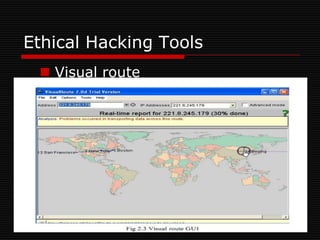
The document discusses ethical hacking, which involves authorized penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities in an organization's cybersecurity. Ethical hackers use the same techniques as criminals but do not cause damage or steal information. They must be trustworthy, have strong technical skills, and continuously update their knowledge. There are different types of hackers - black hat hackers cause harm, while white hat hackers help security. Ethical hacking tools help test application servers, firewalls, networks, and wireless security. The goals are to improve security awareness, assess and mitigate risks, and assist decision making. Ethical hacking is important to understand vulnerabilities and manage risks, though security professionals are always working to stay ahead of attackers.