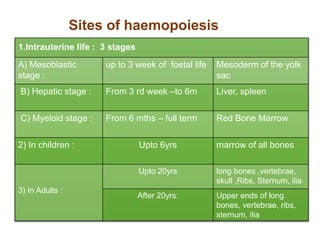
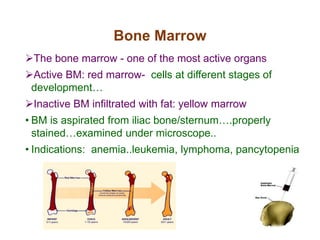
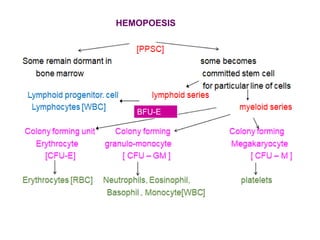
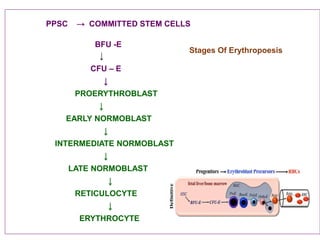
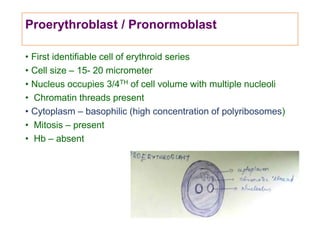
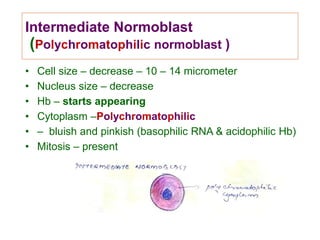
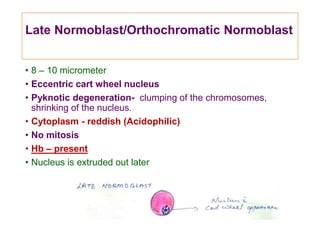
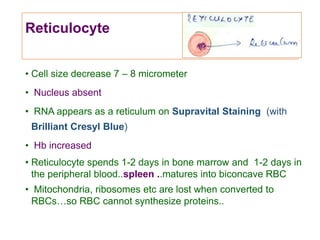
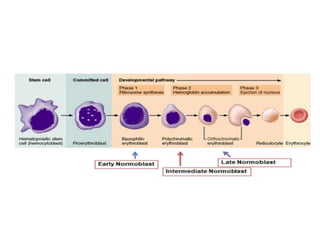
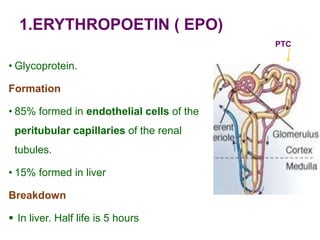
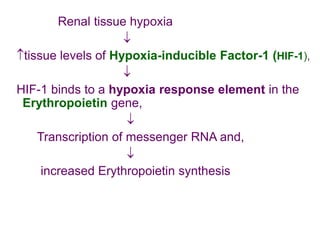
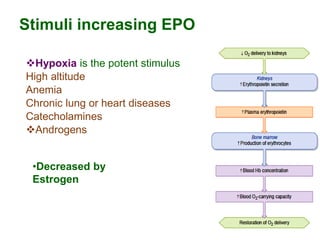
This document discusses haemopoiesis, the development of blood cells. It describes the three main sites of haemopoiesis - the yolk sac, liver, and bone marrow. It focuses on erythropoiesis, the formation of red blood cells, outlining the stages from pronormoblast to reticulocyte to erythrocyte. Key regulators of erythropoiesis discussed are erythropoietin, growth factors, hormones, and nutritional factors like iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid.