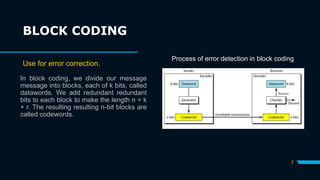
This document discusses error detection and correction. It explains that extra redundant bits are added to transmitted data to detect or correct errors. There are two main types of errors - single bit errors, where one bit is corrupted, and burst errors, where multiple contiguous bits are corrupted. The document introduces block coding, where the message is divided into blocks and redundant bits are added to each block to form codewords. It describes how error detection works by checking if the received codeword is valid. The two main types of error correction are also summarized - backward error correction requires retransmission, while forward error correction allows errors to be fixed without retransmission but uses more bandwidth.