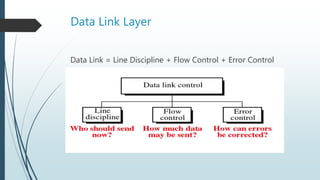
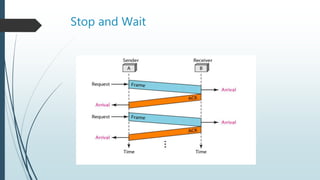
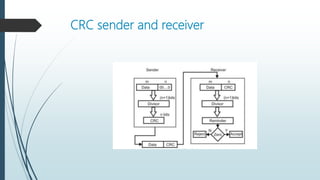
This document provides information about flow control and error control techniques in data link layer protocols. It discusses three mechanisms: stop-and-wait, go-back-N ARQ, and selective-repeat ARQ. Stop-and-wait flow control involves a sender keeping a copy of the last frame until receiving an acknowledgement and resending any unacknowledged frames. Cyclic redundancy check (CRC) is described as an error detection code used to detect accidental changes to data by dividing the data and CRC by a generator polynomial. The document also includes an explanation of how CRC works at the sender and receiver.