This document describes the Hamming code system. It introduces Hamming codes, which can detect up to two-bit errors or correct one-bit errors. It discusses different types of errors, the Hamming bound condition, and how to implement Hamming codes by calculating parity bits using a generator matrix and decoding received codewords using a parity check matrix to detect and correct errors through syndrome decoding. The document also includes a MATLAB source code example to simulate the encoding, transmission over an AWGN channel, and decoding of Hamming codes to calculate the bit error rate.







![Implementation of Hamming Code
To implement Hamming code firstly we calculate Parity Bits
Generator Matrix- It is matrix of [I,P] use to encode message bits
For Example
p1 = d2 + d3 + d4
p2 = d1 + d3 + d4
p3 = d1 + d2 + d4
5/30/2020
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment1presentationhammingcodesystem-200530042550/85/Hamming-code-system-8-320.jpg)
![Continued…
So for any Message bits (4 bits) we can get code directly using Generator matrix
C=[d]*[G]
We send this Codeword through Channel and at receiver we decode this codeword
using parity check matrix also we find error is there or not
Let at Receiver we get a received codeword “r”
5/30/2020
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment1presentationhammingcodesystem-200530042550/85/Hamming-code-system-9-320.jpg)
![Syndrome and Decoding
Syndrome-The pattern of errors, called the error syndrome, identifies the bit in error.
If all parity bits are correct, there is no error. Otherwise, the sum of the positions of the
erroneous parity bits identifies the erroneous bit.
S=[r]. [HT]
If S =0 No Errors
S ≠ 0 Errors are there and we got Error Vector e
S also gives location of error and this location vector verified from [HT]
5/30/2020
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment1presentationhammingcodesystem-200530042550/85/Hamming-code-system-10-320.jpg)

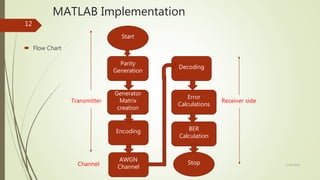
![Source Code
EbN0dB=2; Energy Per Bit
R=4/7; % (7,4) Hamming code Rate
EbN0=10^(EbN0dB/10); % Anti Log
sigma=sqrt(1/2*R*EbN0);
k=4; n=7;
Nerrs=0; Nblocks=1000; % 1000 blocks
for i = 1:Nblocks
msg=randi([0,1],1,k); %Random Msg Generation
%Encoding
cword=[msg mod(msg(1)+msg(2)+msg(3),2)...
mod(msg(2)+msg(3)+msg(4),2)...
mod(msg(1)+msg(2)+msg(4),2)];
s=1-2*cword;% BPSK bit to symbol conversion
r= s+sigma*randn(1,n); % AWGN CHANNEL
% Hard Decoding
b=(r<0); % Thresholg at Zero
dist= mod(repmat(b,16,1)+cwords,2)*ones(7,1);
[mind1,pos]=min(dist);
msg_cap1=cwords(pos,1:4);
%Soft Decoding
corr=(1-2*cwords).*r;
[mind2,pos]=max(corr);
msg_cap2=cwords(pos,1:4); % Decoded msg
Nerrs=Nerrs+sum(msg~=msg_cap1); % Eroors Calculation
end
BER_sim=Nerrs/k/Nblocks; % BER Calculation
% Name:
disp([EbN0dB BER_sim Nerrs k*Nblocks]);
5/30/2020
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment1presentationhammingcodesystem-200530042550/85/Hamming-code-system-13-320.jpg)
![Output
For EbN0dB=2 ;
disp([EbN0dB R BER_sim Nerrs k*Nblocks]);
2 0.57143 0.05505 2202 40000
msg = % Random Input msg
0 0 0 1
cword =
0 0 0 1 0 1 1
%After AWGN Channel Received Code
r =
1.9644 0.455 1.1051 -1.89 1.2222
-0.62404 2.2142
msg_cap1 =% Decoded Msg
0 0 0 1
For EbN0dB=4 ;
disp([EbN0dB R BER_sim Nerrs k*Nblocks]);
4 0.57143 0.01545 618 40000
msg = % Random Input msg
0 1 0 0
cword =
0 1 0 0 1 1 1
%After AWGN Channel Received Code
r = 1.4018 -0.29702 0.51536 0.94538 -1.5975 -1.9073
0.36304
msg_cap1 =
0 1 0 0
5/30/2020
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment1presentationhammingcodesystem-200530042550/85/Hamming-code-system-14-320.jpg)

