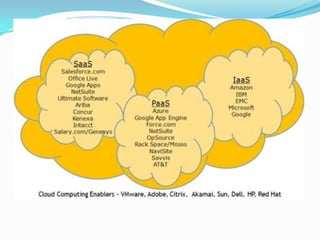
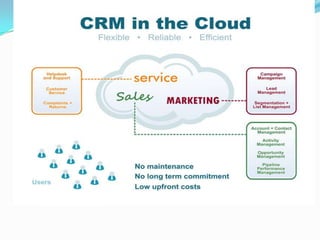
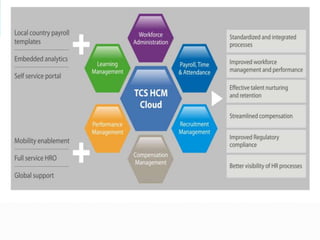
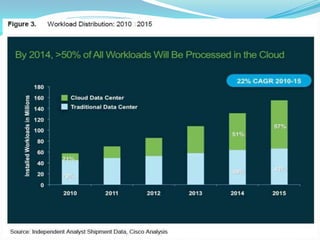
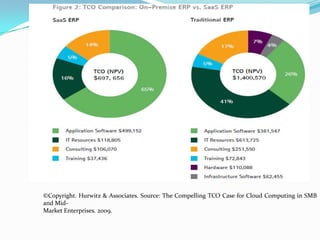
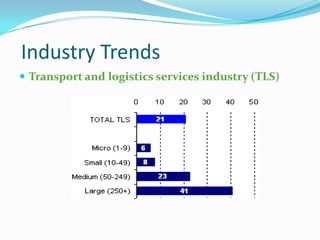
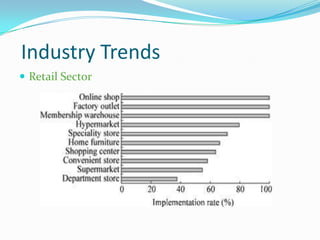
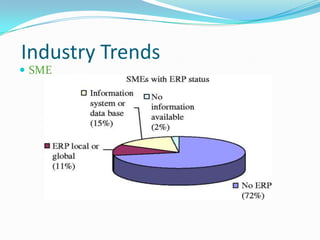
This document discusses ERP trends based on survey results from Panorama Consulting Solutions. It finds that around 70% of companies customize ERP systems up to 25% and only about 50% of projected benefits are realized. Future trends discussed include increased adoption of cloud/SaaS models, mobile and wireless technologies, social integration, and a blurring of lines between ERP, CRM and SCM systems. The document also notes growth in ERP adoption among SMEs and in public sectors.
![Reema[ M110007MS]
Vivek[ M110009MS]
Meethu [M110016MS]
Prabhu [M110017MS]
Kalyan[ M110021MS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpfuture-130118025507-phpapp02/75/Erp-future-1-2048.jpg)
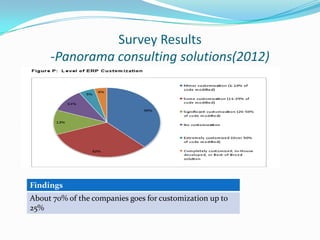
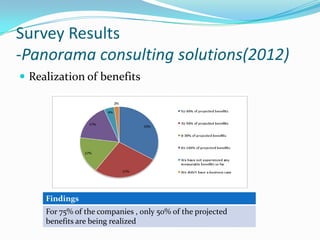
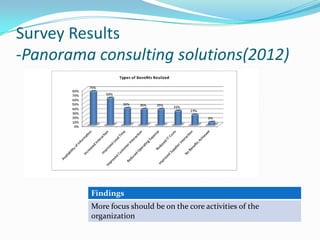


![Survey Results
-Panorama consulting
Comparison in the SME segment-SaaS Vs On Premise
SaaS[Software as a On Premise
Service]
Months 11.6 18.4
Cost[% of annual 6.2 6.9
revenue]
Executive level of 52.6% 50%
satisfaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/erpfuture-130118025507-phpapp02/85/Erp-future-8-320.jpg)