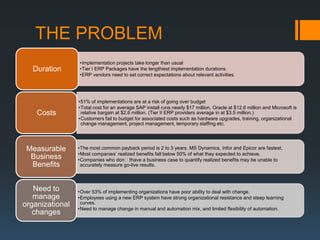
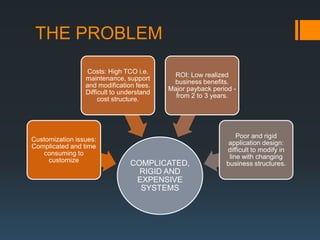
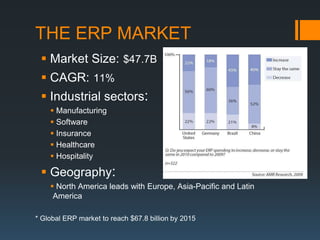
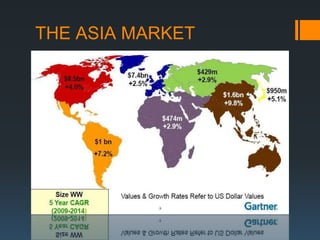
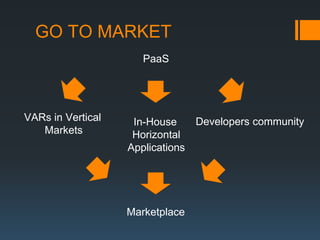
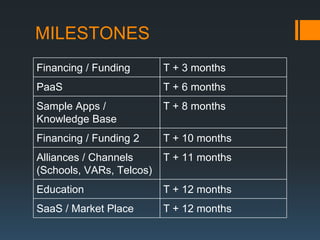
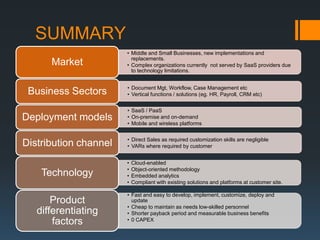
The document discusses the problems with traditional ERP implementations including long durations, high costs, and low realized benefits. It then outlines a proposed RAD & deployment approach to address these issues by enabling faster and cheaper development, implementation, customization, and updates of ERP systems through a cloud-enabled, object-oriented platform.