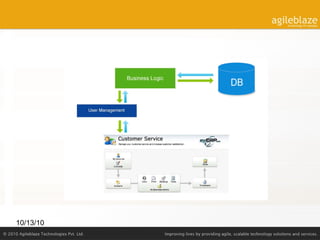
The document discusses enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, their users, and the evolution towards cloud computing and SaaS models. It emphasizes that ERPs are utilized by organizations of all sizes and details the components, benefits, and implementation challenges involved. Additionally, it highlights the importance of integrating customer relationship management (CRM) with ERP systems and outlines the future trends in the ERP landscape.