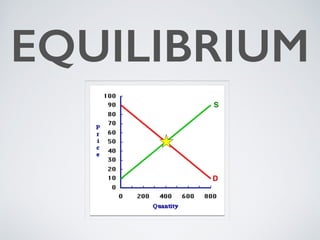
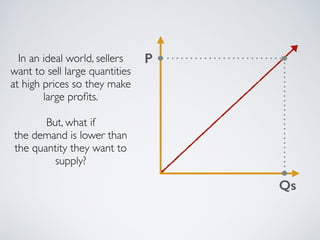
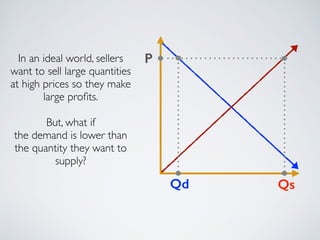
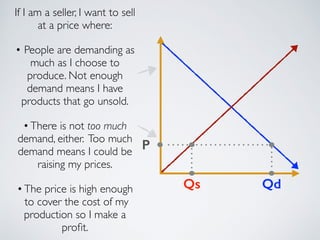
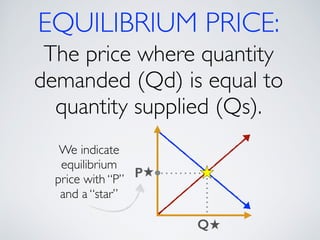
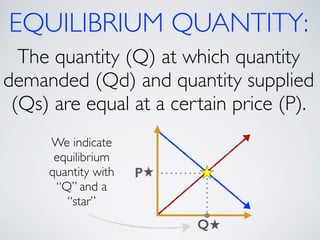
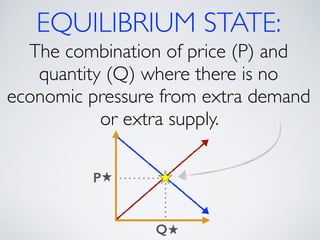
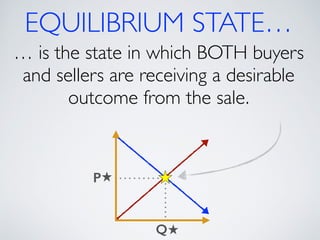
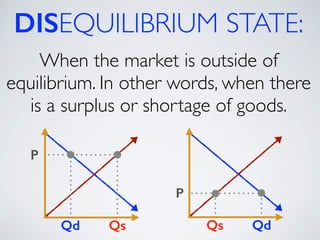
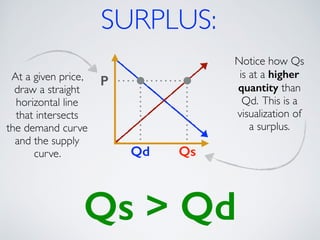
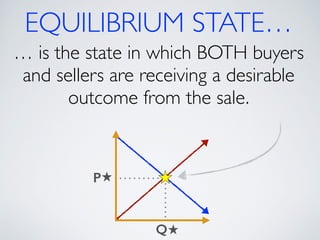
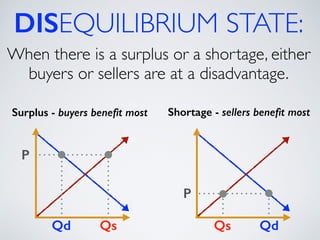
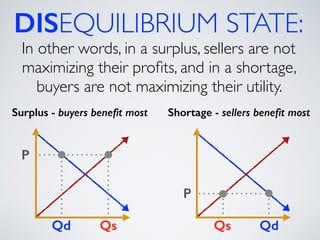
The document introduces the concept of supply and demand equilibrium in a classroom market simulation. Students will propose prices for snack packs and those prices will be used to create a demand schedule. Students will then think like suppliers and choose a price for the snack packs that maximizes sales and profits by matching supply to demand. The market reaches equilibrium when the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied at a certain equilibrium price. Disequilibrium states like surpluses and shortages occur when demand and supply are not equal.