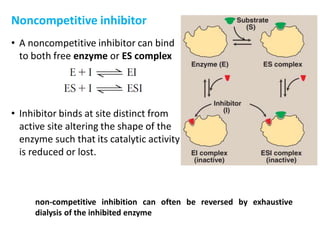
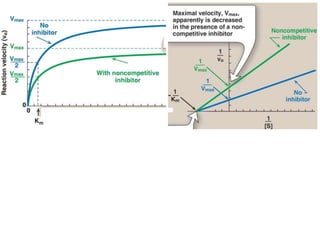
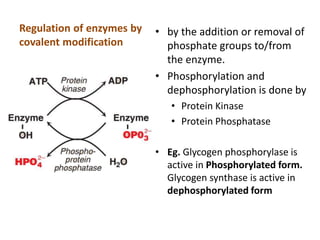
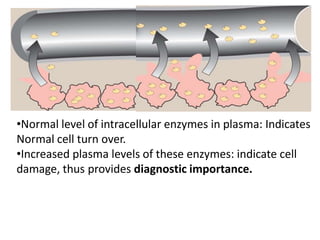
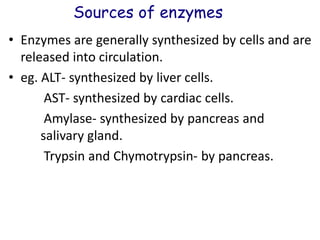
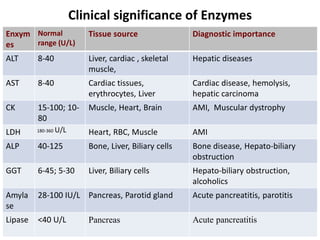
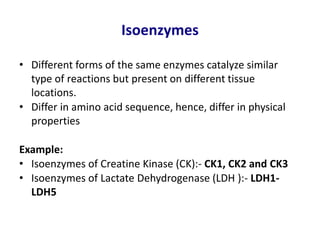
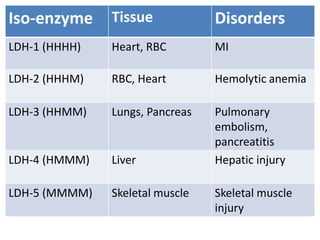
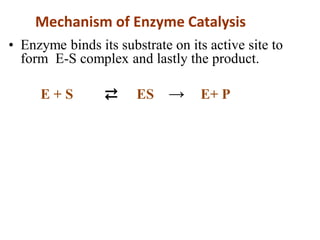
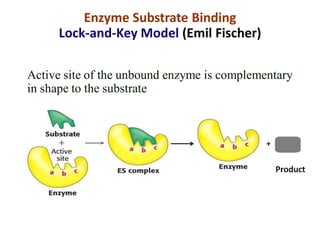
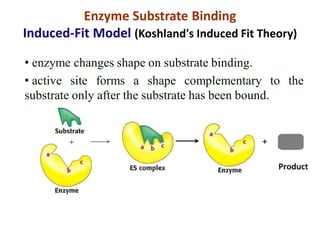
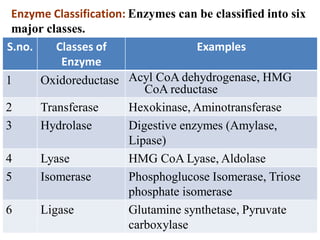
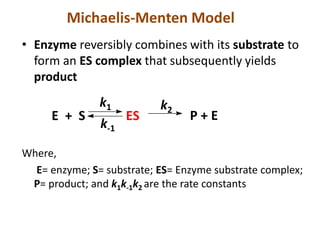
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They are typically proteins that contain an active site which binds to specific substrate molecules. The binding of the substrate lowers the activation energy of the reaction, allowing it to proceed faster. Factors such as temperature, pH, substrate and product concentration can influence an enzyme's activity. Enzymes can be classified based on the type of reaction they catalyze and can be regulated through various mechanisms like allosteric effectors or covalent modification. Measurement of enzymes in clinical samples provides diagnostic information about tissue and organ damage.

![Definition
• biological catalysts that increase the velocity of
chemical reactions
• no change in overall process
• protein in nature. [except- Ribozymes]
• having the suffix –‘ase’ (exception- pepsin, trypsin, etc.)
• more than 3000 enzymes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-2-320.jpg)
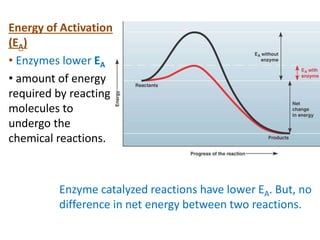

![Properties of Enzyme
• Enzymes are biological catalysts and are protein in nature
• Enzyme molecules contain active site, which bind the
substrate to form product.
• Efficiency- Enzyme catalyzed reactions are million times
faster than uncatalyzed reactions.
[turn over number= 102–104s-1 (substrate transformed/sec]
• Specificity- Enzymes are highly specific catalyzing only one
type of chemical reactions.
• Regulations- Enzyme activity can be regulated, i.e.
Enzymes can be activated or inhibited.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-8-320.jpg)
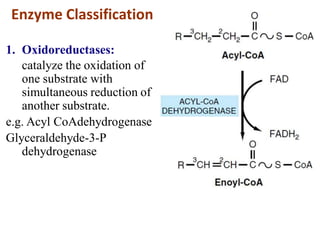
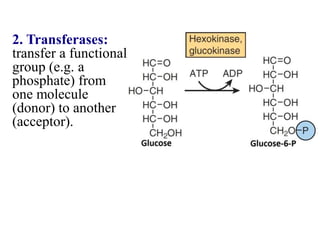
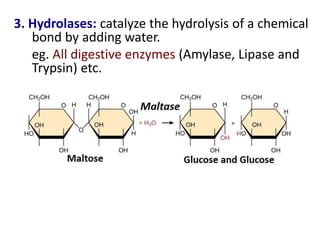
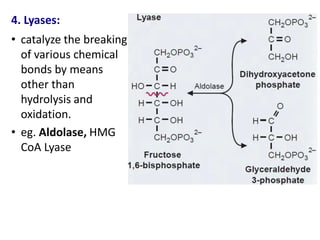
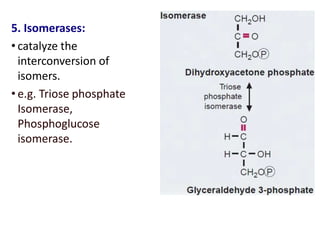
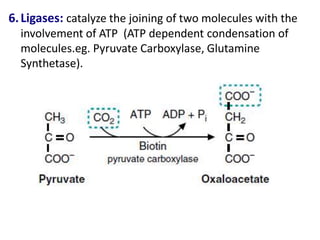
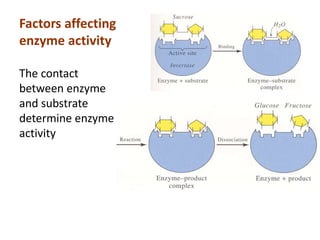

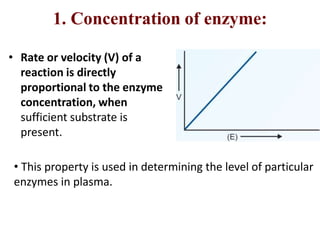
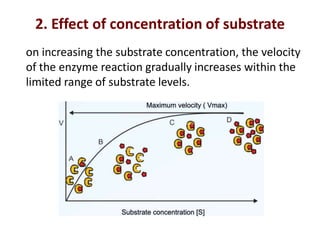
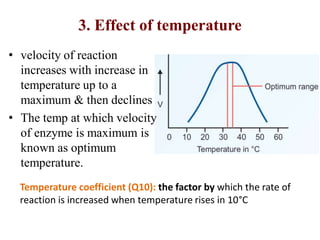
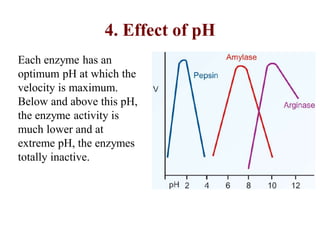


![Michaelis-Menten Equation (simplified form)
v =
vmax [S]
[S] + KM
if [S] >> KM then v = vmax
if [S] = KM,then v =
vmax
2
Therefore KM can be viewed as the substrate concentration
with half-maximal velocity.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-30-320.jpg)

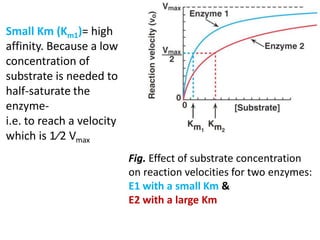
![Km does not vary with the [E]
• Large Km: reflects a low affinity of enzyme for
substrate [↑S is needed to half-saturate the
enzyme].
• Small Km: reflects a high affinity of enzyme for
substrate, [↓S is needed to half-saturate the
enzyme].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-32-320.jpg)
![Relationship of velocity to [S]
• [S] is much less than Km, the velocity of the reaction
is approximately proportional to the substrate
concentration [first order].
• [S] is much greater than Km, the velocity is constant
and equal to Vmax.
[rate of reaction is then independent of substrate
concentration, and is said to be zero order].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-34-320.jpg)
![Michaelis-Menten plot
v
[S]
vmax
KM
vmax
2
Effect of substrate concentration
on reaction velocity
At Low [S], velocity
of reaction is
proportional to [S]
At high [S], velocity is
independent of [S]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-35-320.jpg)
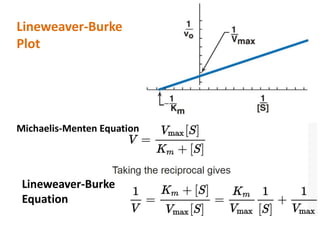
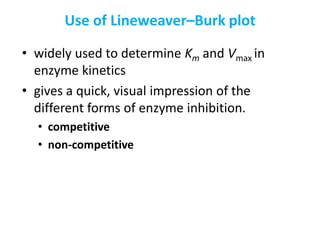
![Lineweaver-Burk plot
• When v is plotted against [S], it is not always
possible to determine when Vmax has been achieved
• However, if 1/v is plotted versus 1/[S], a straight line
is obtained.
• This, a double-reciprocal plot can be used to
calculate Km and Vmax, as well as to determine the
mechanism of action of enzyme inhibitors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-36-320.jpg)

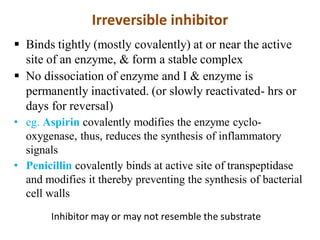
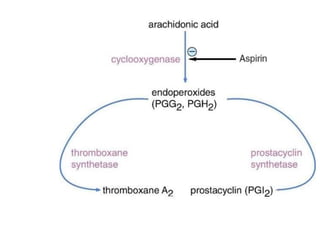

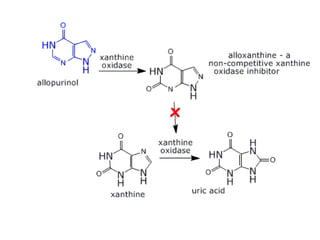


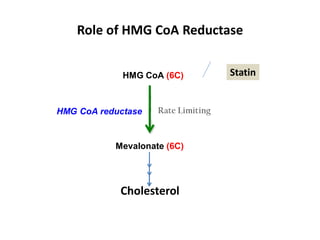
![Competitive inhibition: Effect on Vmax and on Km
Effect on Vmax:
• The effect of a competitive inhibitor is reversed by
increasing [S].
• At a sufficiently high substrate concentration, the
reaction velocity reaches the ‘Vmax’
Effect on Km
• in the presence of a competitive inhibitor, more
substrate is needed to achieve 1⁄2 Vmax.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-47-320.jpg)
![Vmax is the same in the
presence of a
competitive inhibitor
Km is increased in
presence of
competitive inhibitor
↑[S]- velocity becomes Vmax
↑[S]- required to achieve Vmax/2
Km- increased by competitive inhibitor
Competitive inhibition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enzymem-i024-240317004749-46a13641/85/Enzyme-notes-biochemistry-Satyanarayan-pdf-48-320.jpg)