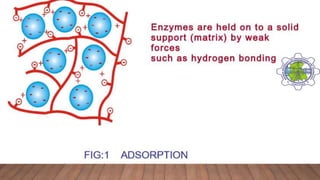
Enzymes can be immobilized to support structures using various techniques. This confines and anchors the enzymes, making them stable and reusable. The main immobilization techniques are adsorption, entrapment, covalent binding, and cross-linking. Adsorption uses weak bonds to attach enzymes to inert supports, but the bonding is weak. Covalent binding and cross-linking form stronger covalent bonds or cross-links between enzymes and supports or between enzyme molecules. Immobilization can impact enzyme properties and kinetics but allows for reuse of enzymes in industrial, analytical, and therapeutic applications.