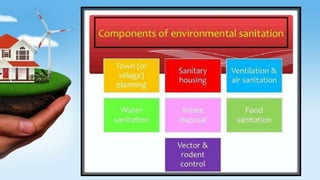
Environmental sanitation aims to improve health through applying sanitation principles to control the environment. It promotes health and prevents disease. Components include water sanitation through safe drinking water and toilets, waste disposal through proper management and methods like dumping and composting, food sanitation through hygienic practices, and air sanitation to prevent pollution and its health effects. Sanitation must be maintained at both household and community levels, such as through community-level campaigns in India like Swachh Bharat Mission and laws protecting the environment.