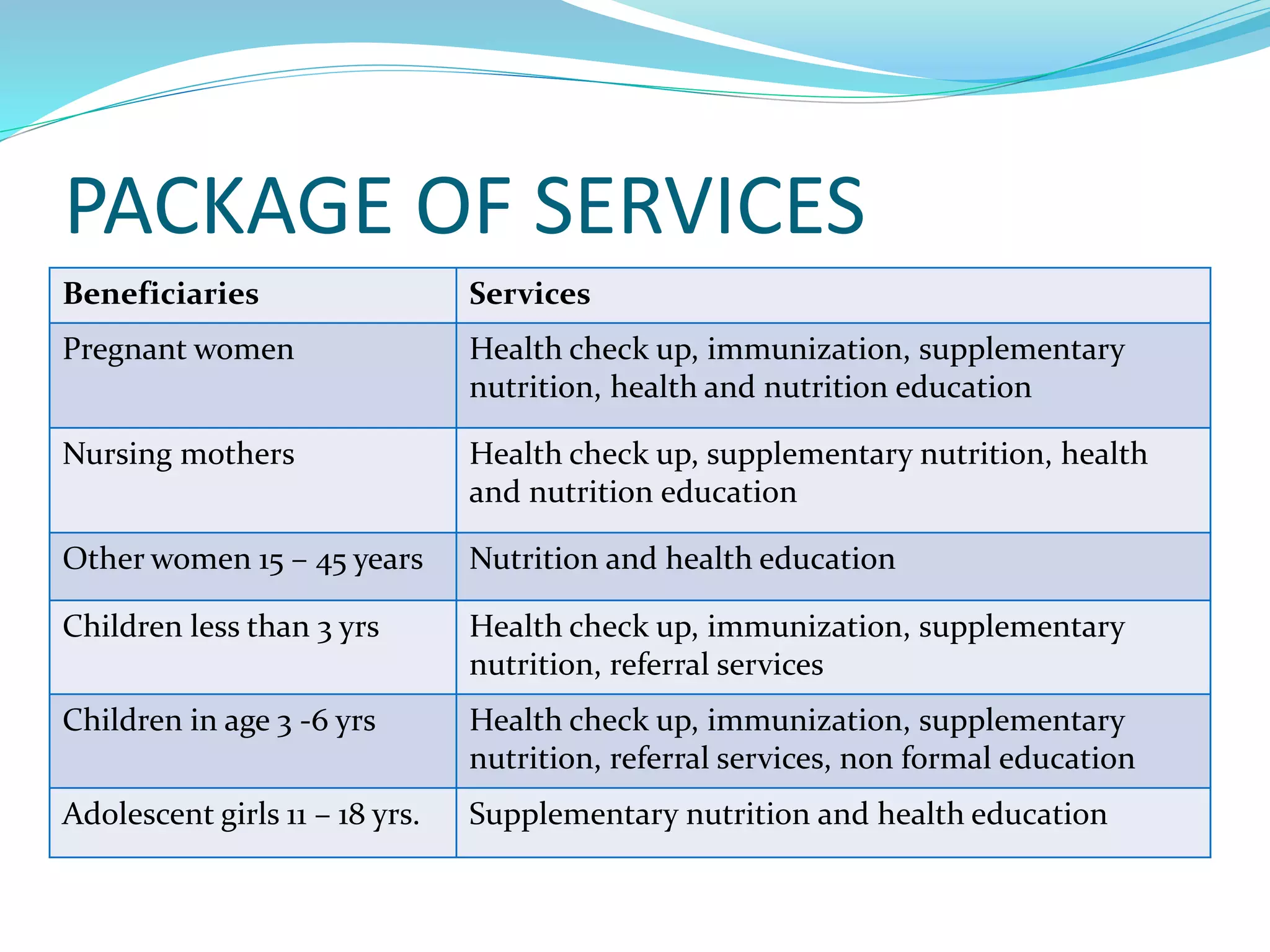
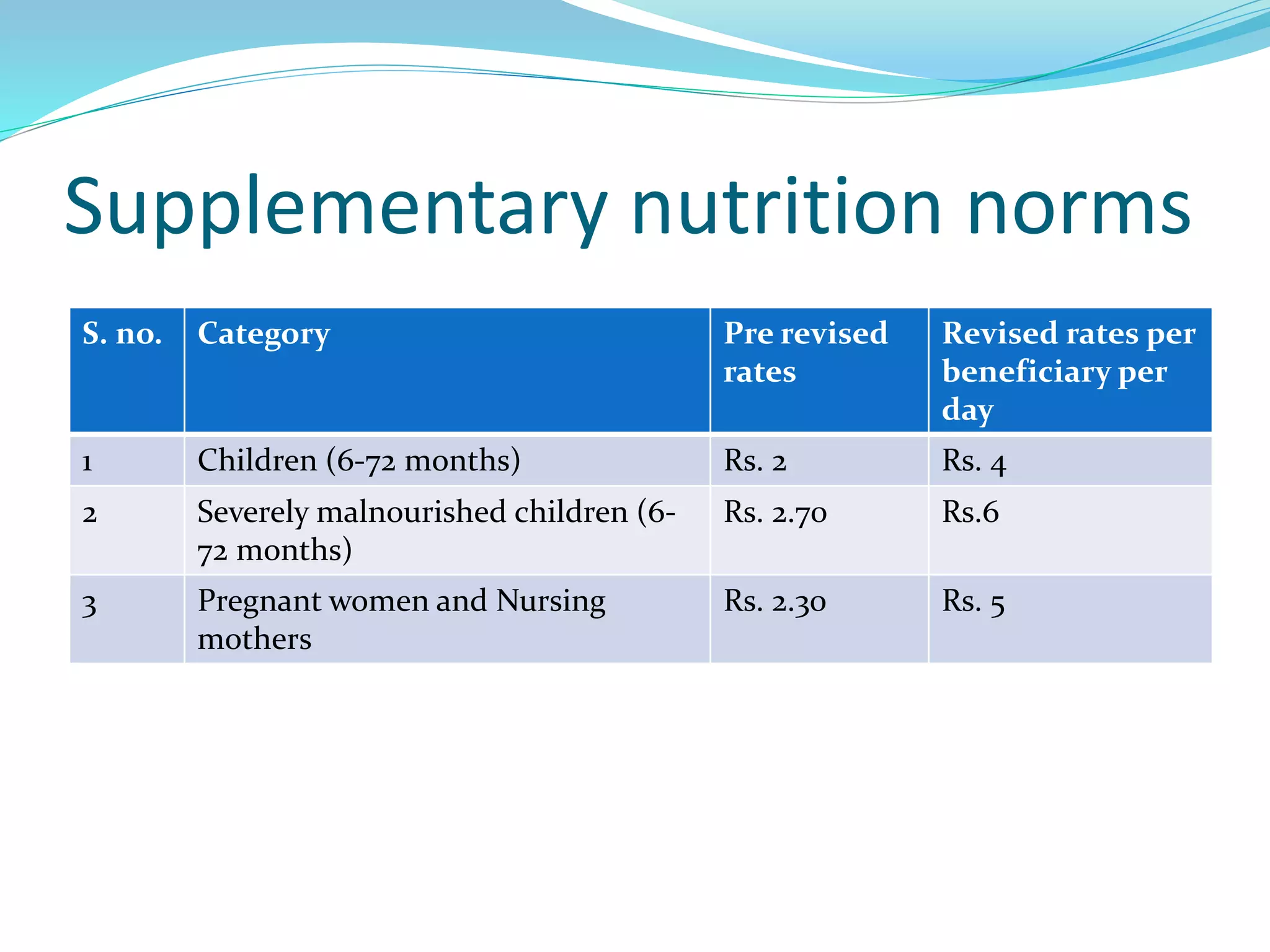
The ICDS Scheme provides services to promote early childhood development, with a focus on children under 6 years old, pregnant and lactating mothers, and adolescent girls. It aims to improve nutrition, reduce mortality and morbidity, and support education. Services include health checkups, immunizations, supplementary nutrition, non-formal preschool education, and community participation through Anganwadi centers. The program is funded jointly by central and state governments in India.