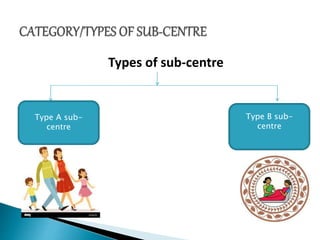
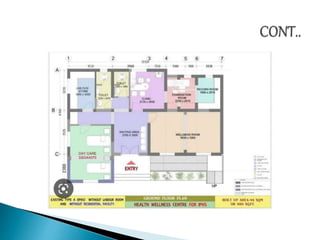
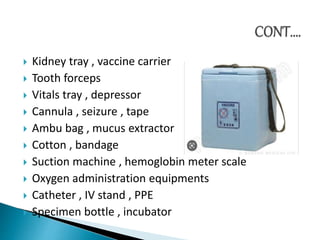
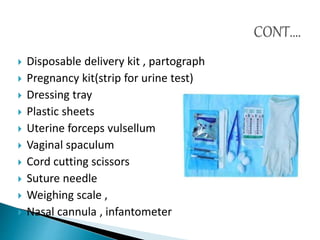
The document outlines the role and structure of sub-centres, now known as Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs), serving as the primary contact point for health services in rural India, catering to populations of 5,000 in plain areas and 3,000 in hilly areas. It discusses their objectives, types, infrastructure requirements, essential equipment, and services provided, including maternal and child health, family planning, and immunization. Additionally, the document highlights budgetary provisions and monitoring mechanisms to ensure quality health care and proper waste management in these centres.