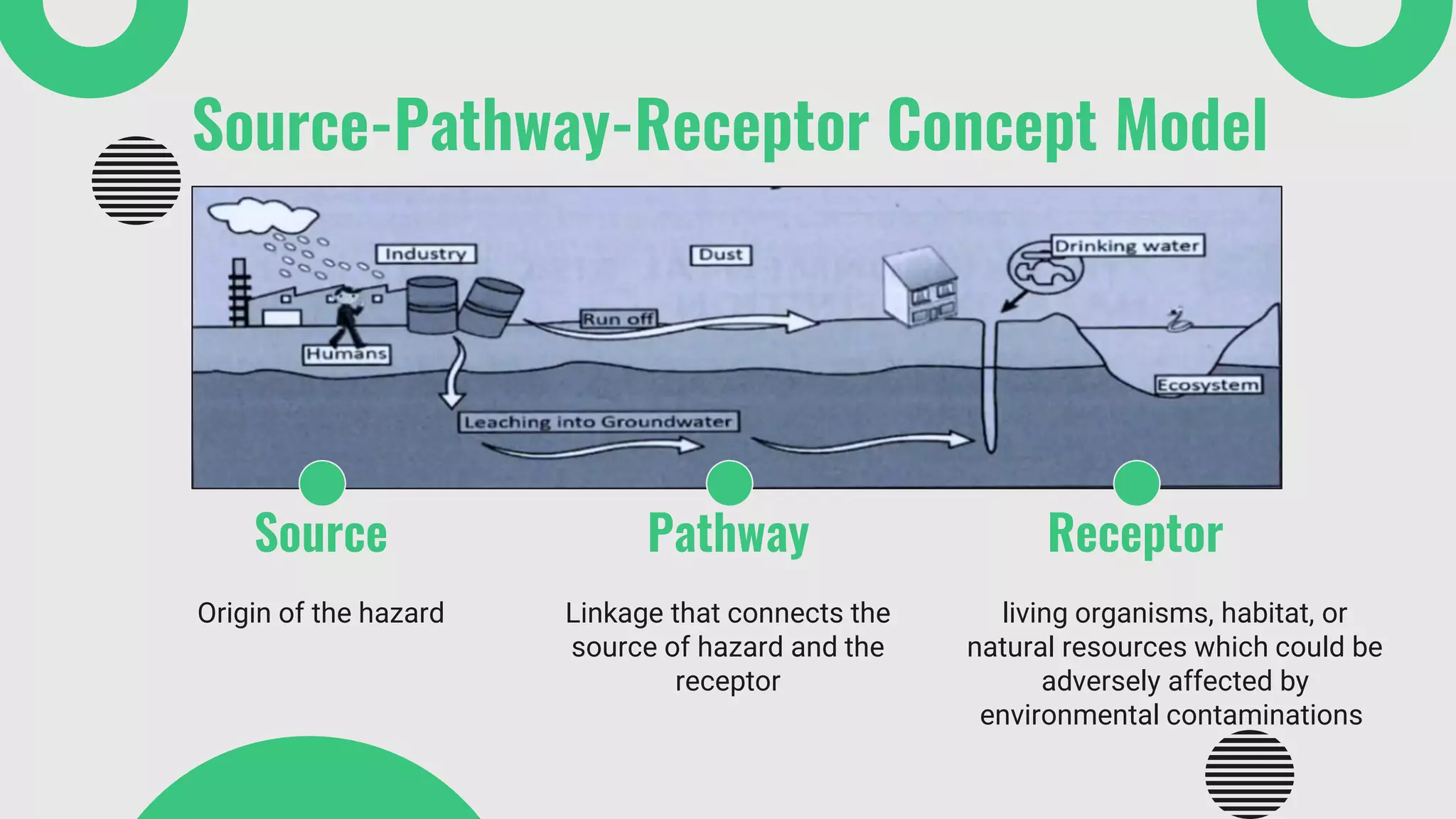
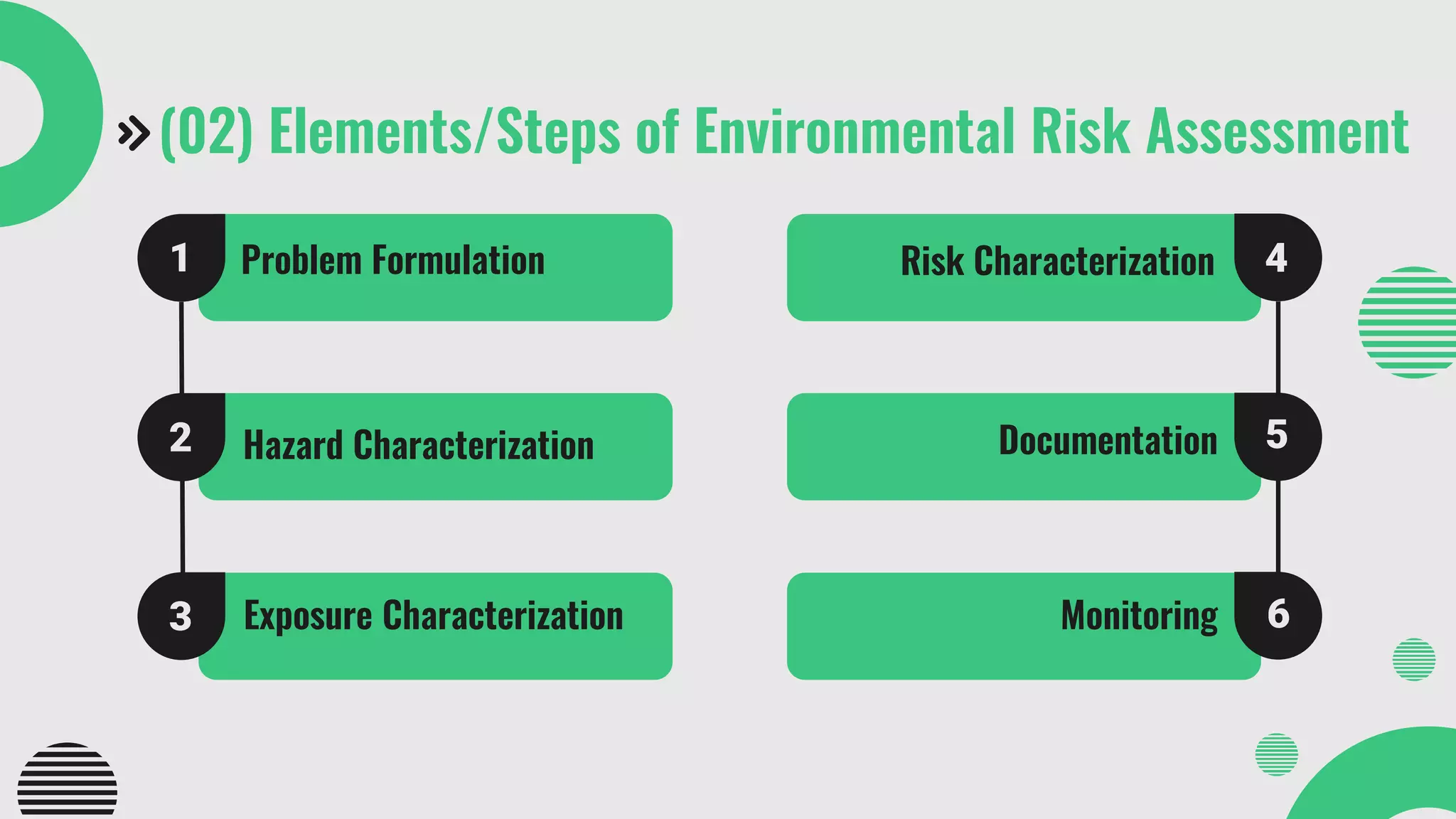
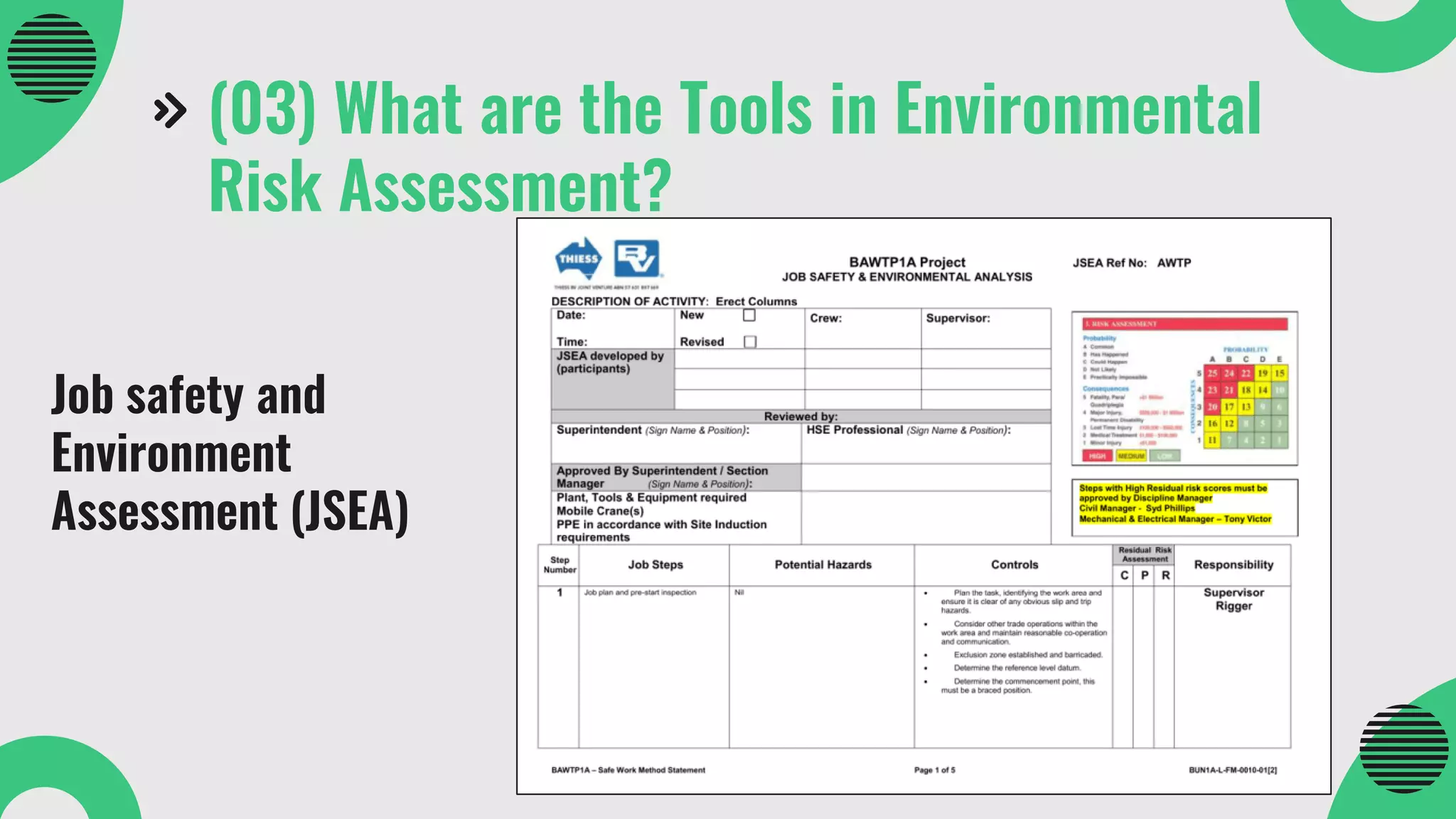
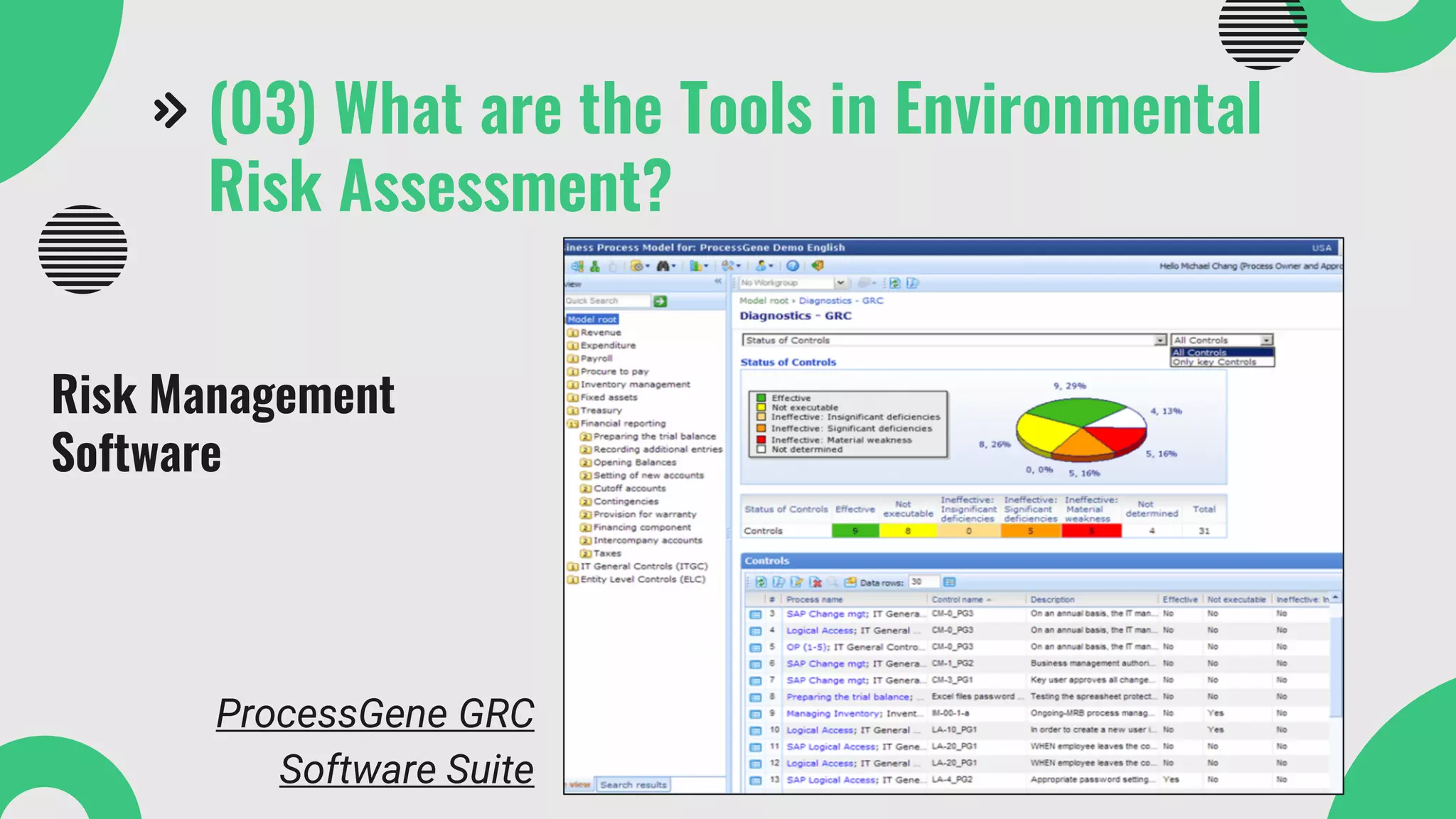
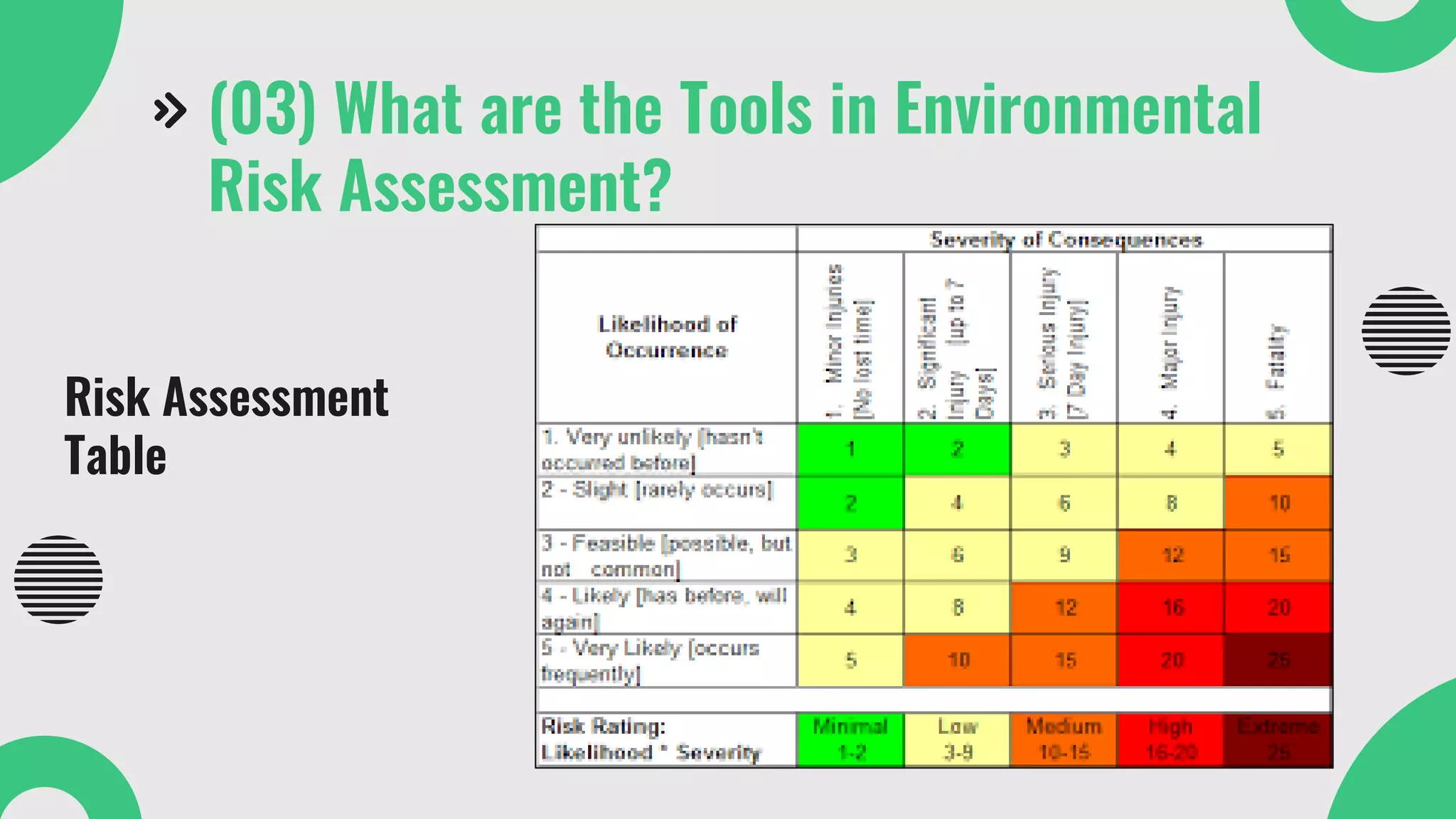
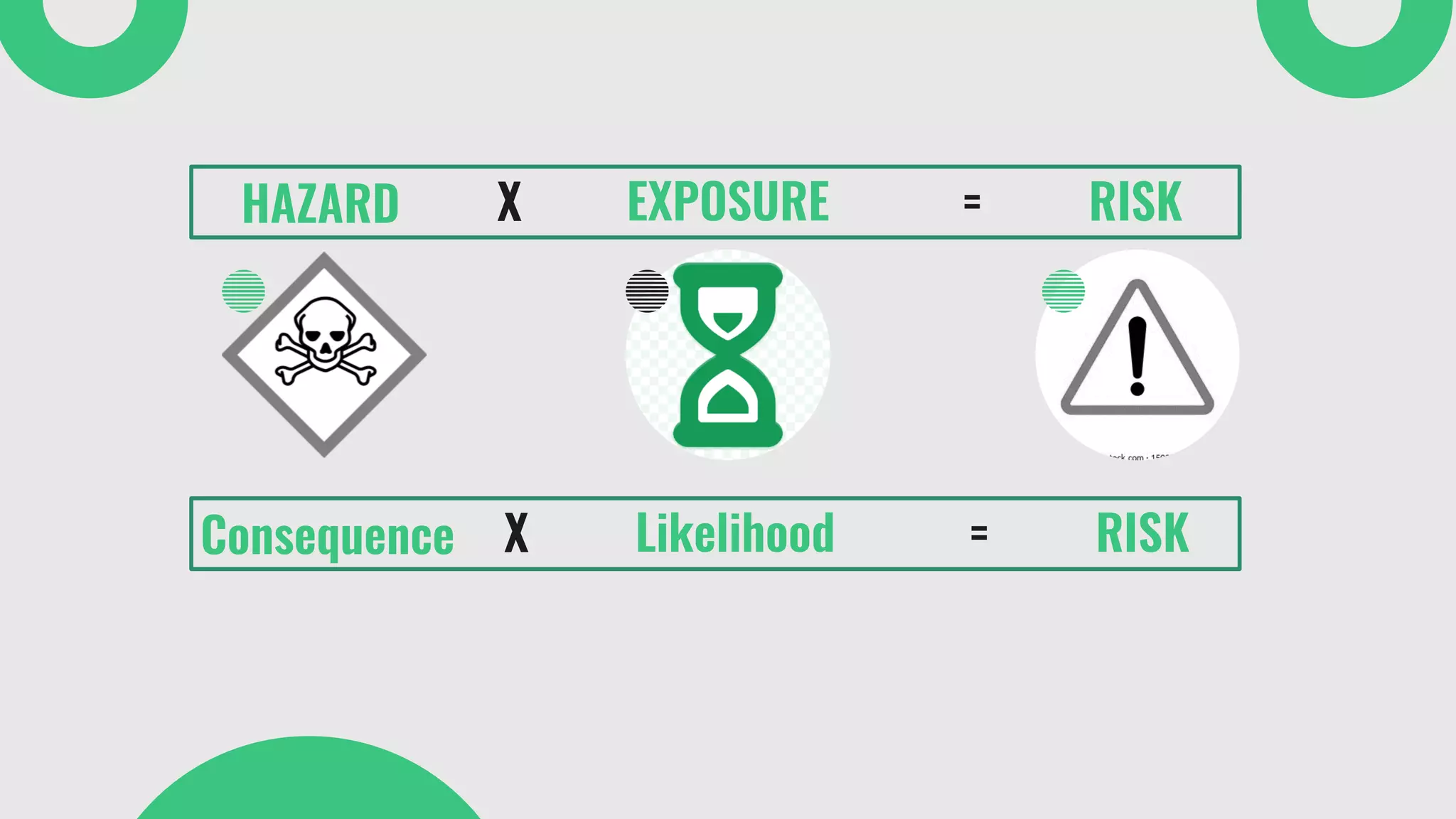
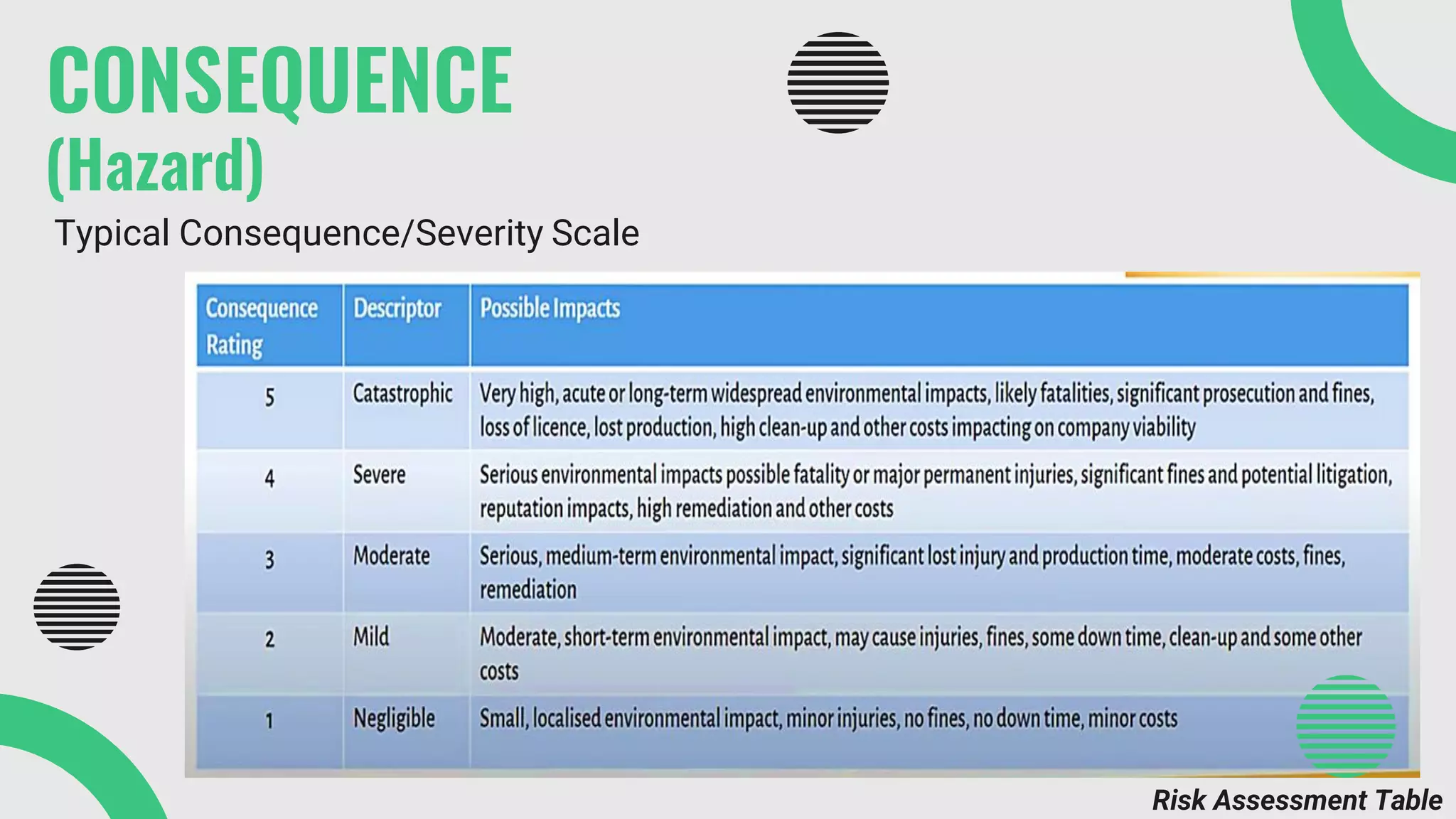
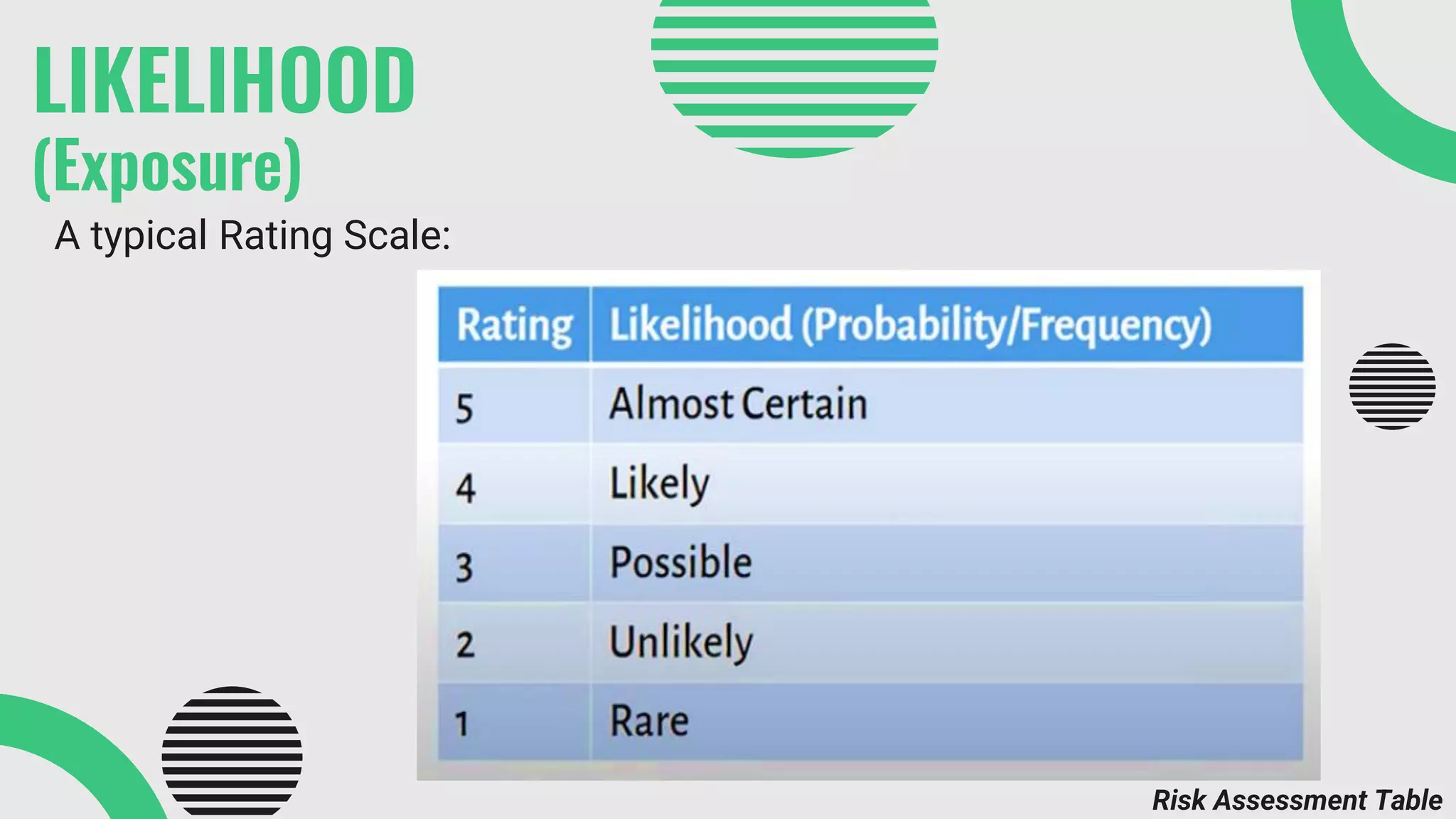
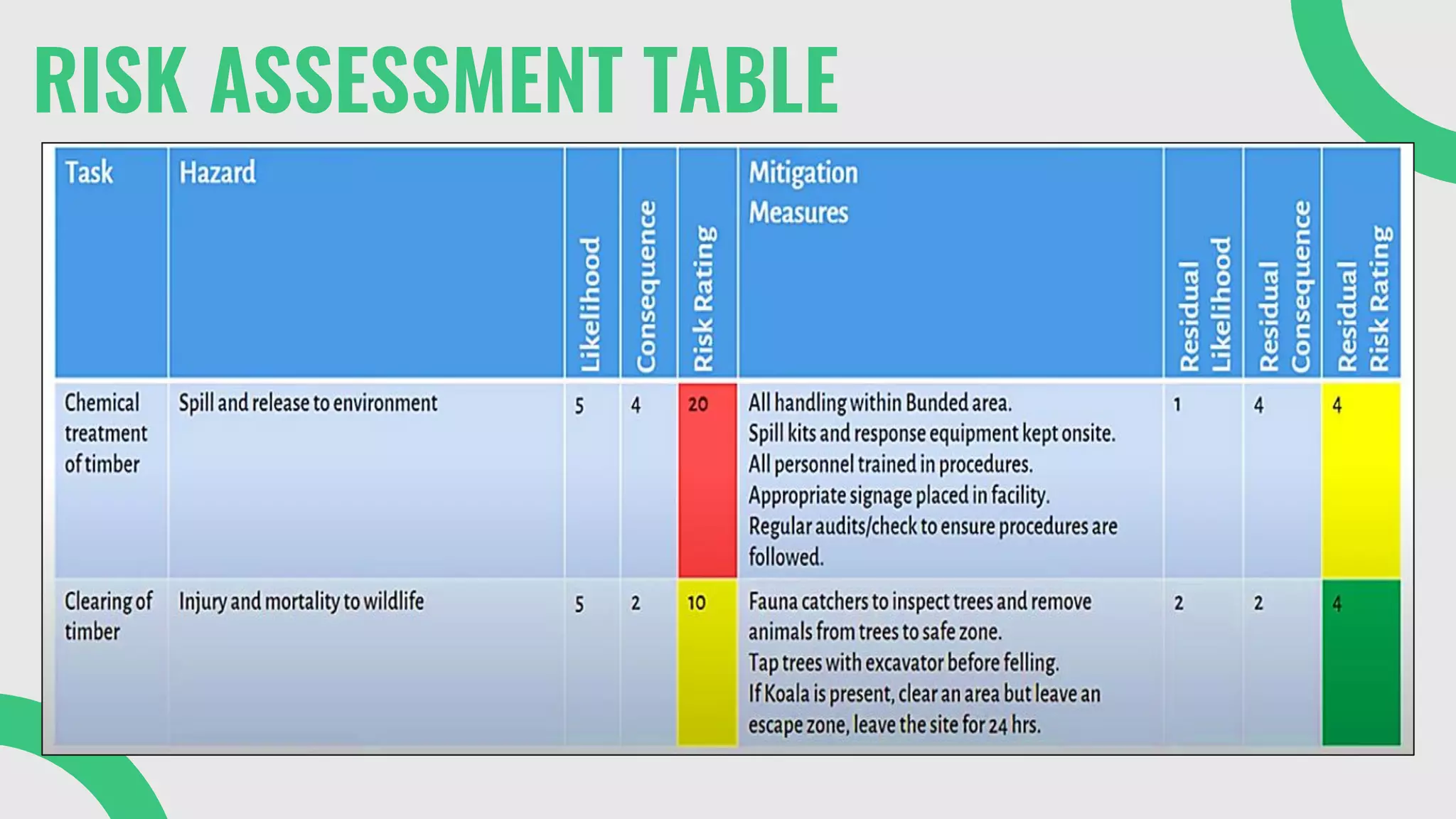
The document provides a comprehensive overview of environmental risk assessment (ERA) and management (ERM), detailing the steps involved in ERA, such as hazard characterization and exposure assessment, as well as the tools used in these processes. It emphasizes the importance of identifying hazards, assessing risks, and implementing management strategies to mitigate environmental impacts on human health and ecosystems. Key players in the process include risk managers, assessors, environmental scientists, and stakeholders, all of whom contribute to creating awareness and ensuring adherence to legal requirements.