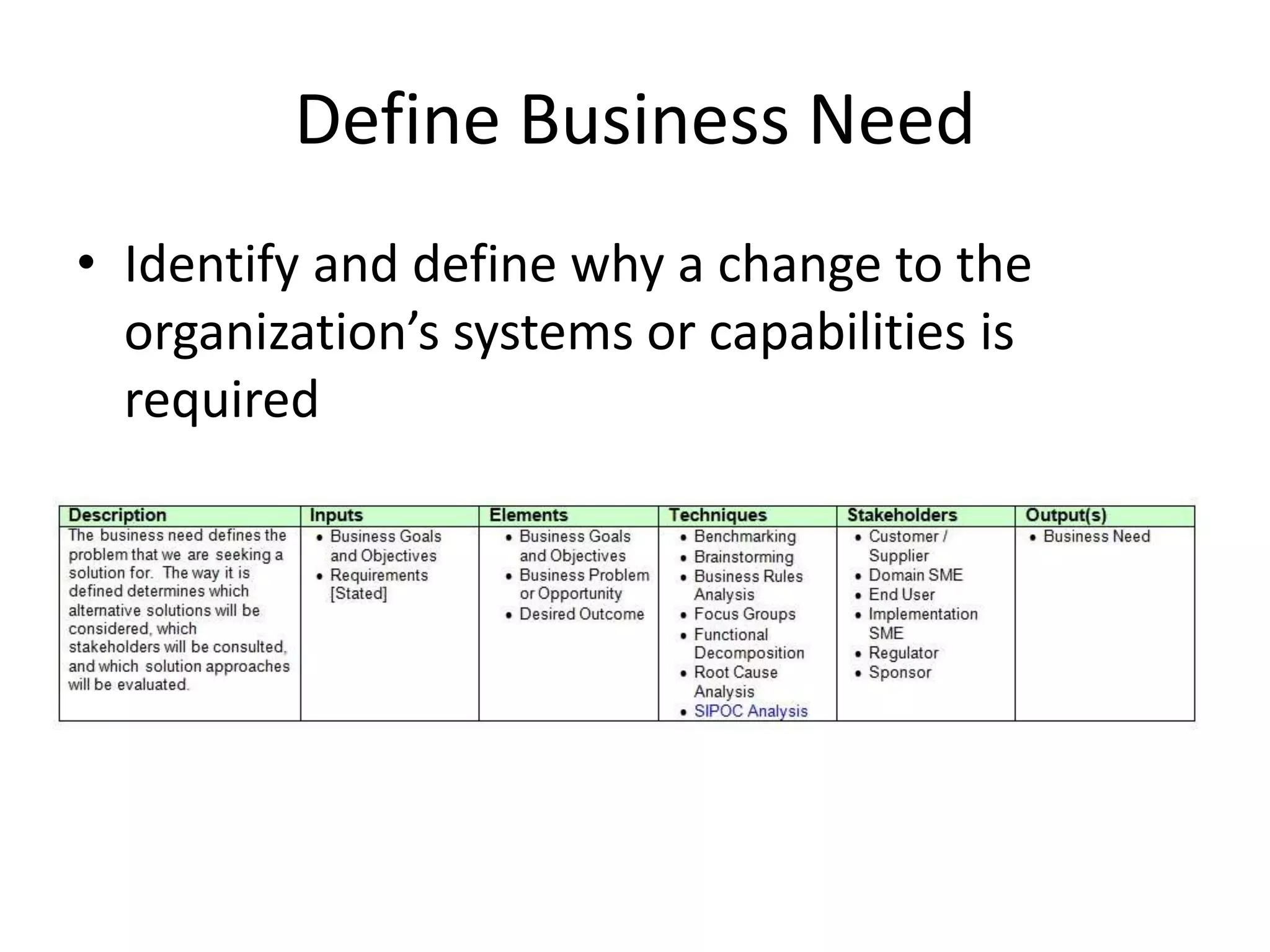
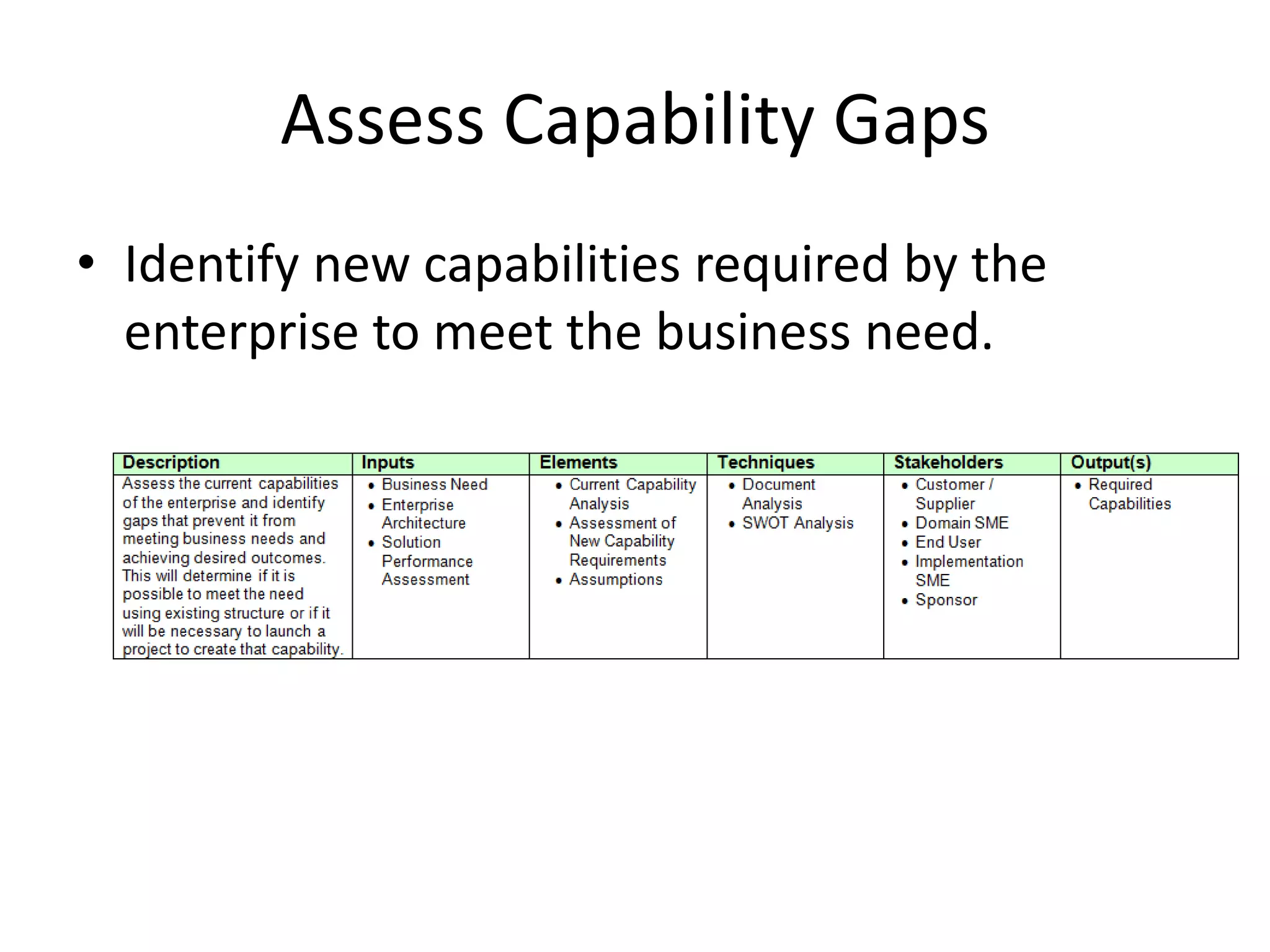
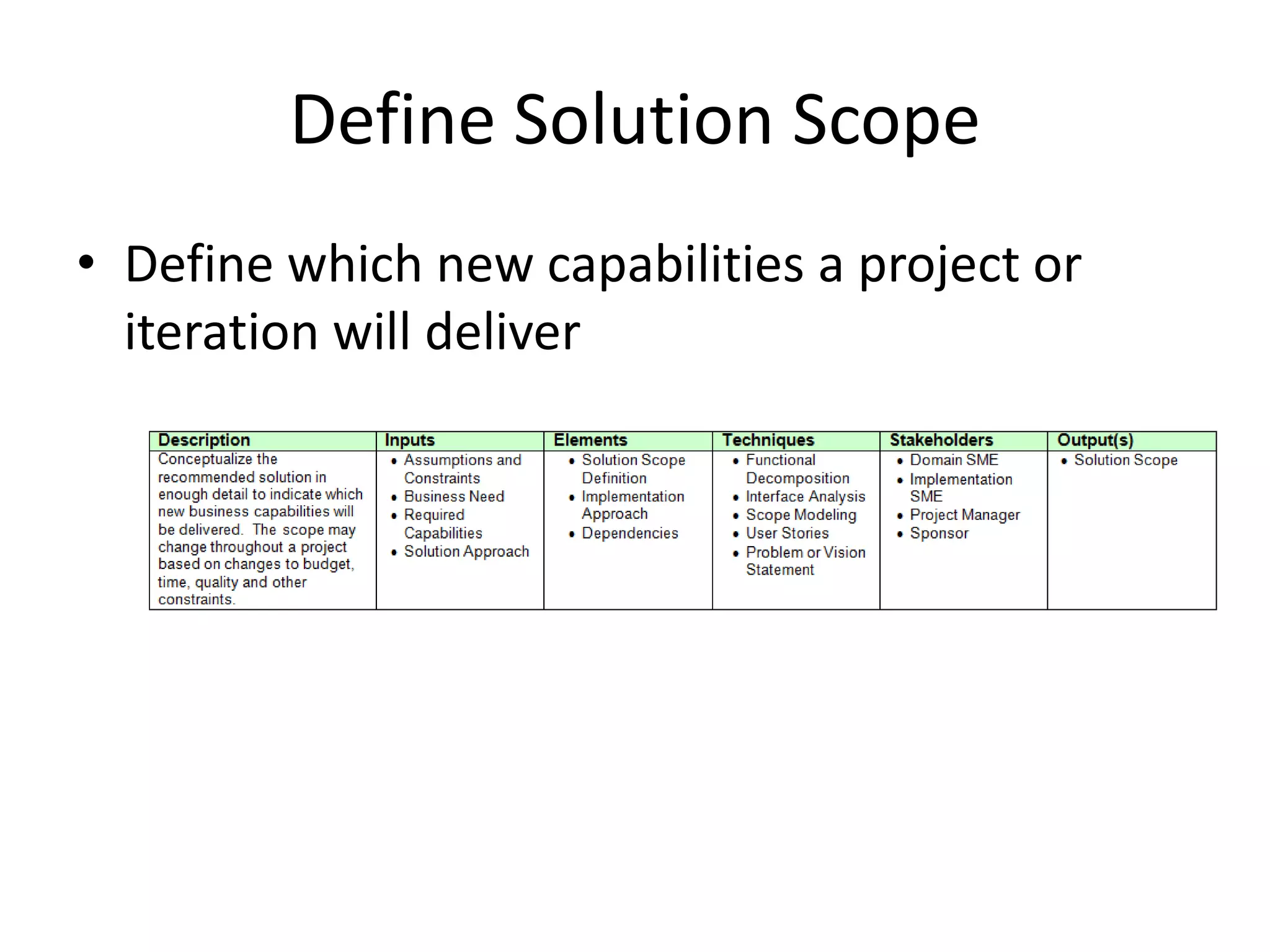
This document discusses enterprise analysis, which identifies business needs, assesses the impacts of changes, and determines feasible solution approaches. The key deliverables of enterprise analysis include a feasibility study, business case, business need assessment, and risk assessment. It outlines the steps of enterprise analysis as defining the business need, assessing capability gaps, determining a solution approach, defining the solution scope, and defining the business case.