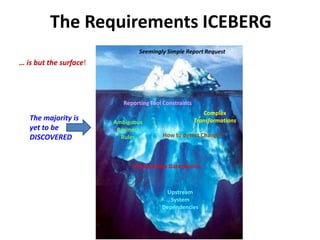
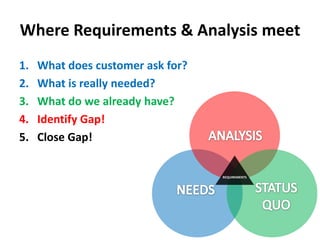
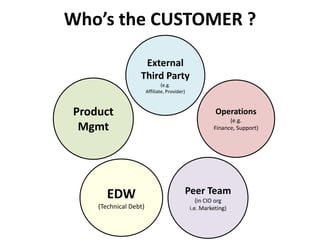
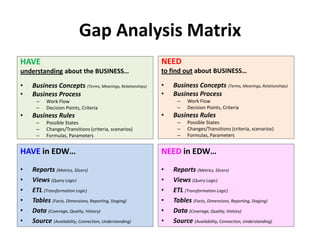
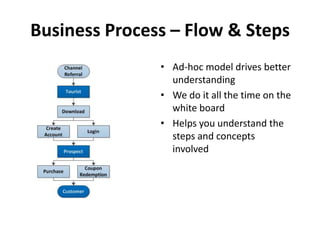
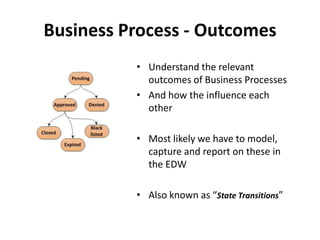
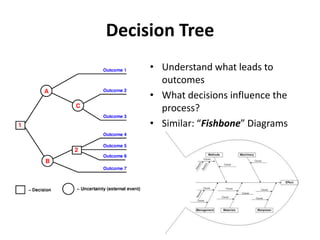
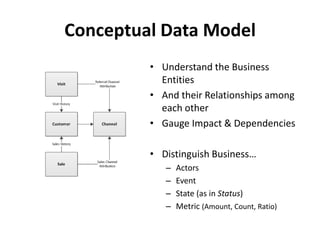
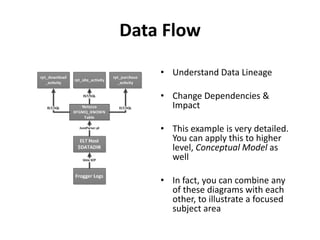
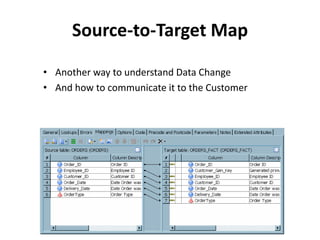
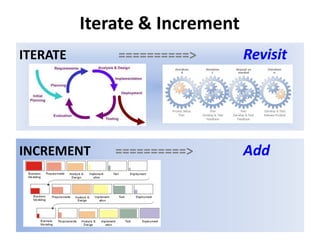
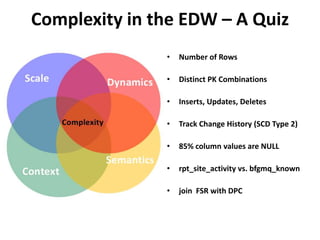
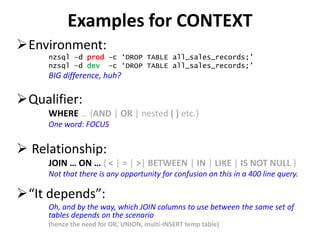
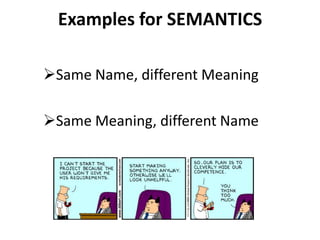
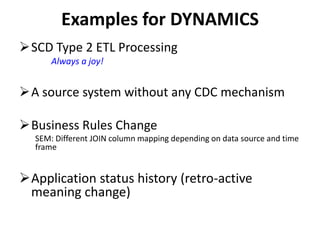
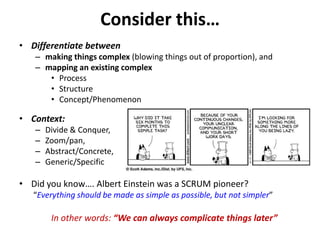
The document discusses requirements analysis and provides guidance on conducting an agile approach. It introduces the "Requirements Iceberg" concept and identifies relevant aspects of analysis. It emphasizes identifying customer needs rather than just the initial request, and provides examples of diagrams and models that can help uncover additional requirements, such as business process flows and conceptual data models. The document recommends iterating the analysis to incrementally build understanding and avoid getting stuck in analysis paralysis.