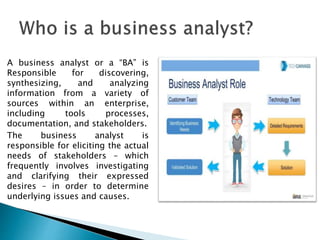
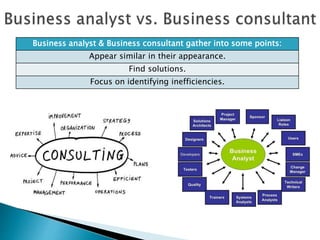
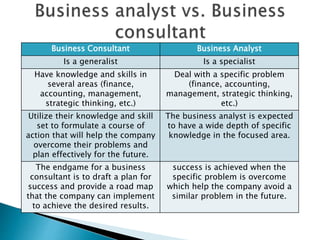
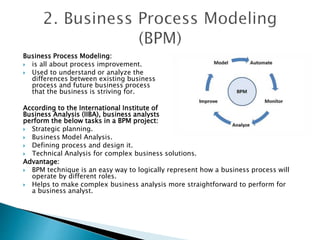
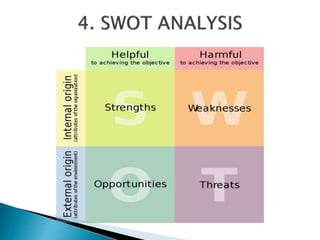
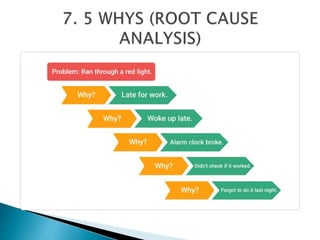
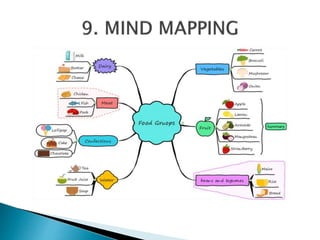
The document outlines the role and responsibilities of a business analyst, defining business analysis as the practice of enabling change by identifying needs and recommending solutions. It covers essential skills, job titles, and common techniques like SWOT, PESTLE, and business process modeling, emphasizing the importance of stakeholder communication. Additionally, it distinguishes the business analyst's function from that of a business consultant, highlighting the knowledge areas necessary for effective analysis and planning in organizations.