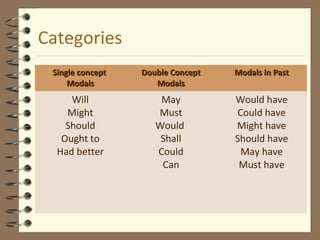
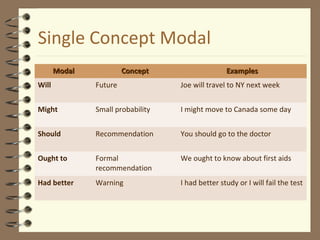
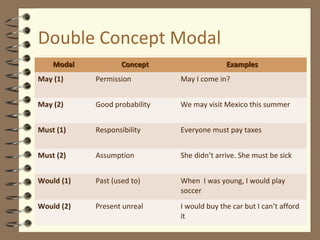
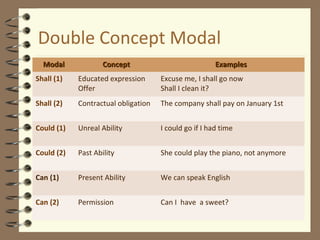
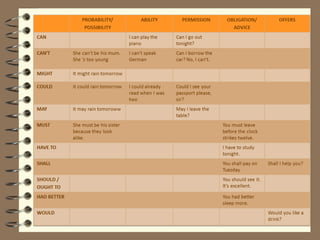
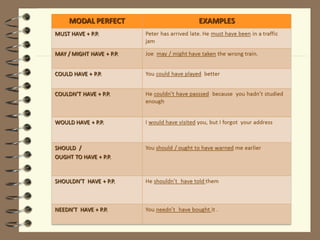
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that provide additional meaning to the main verb of a sentence. There are three categories of modal verbs: single concept modals that have one meaning, double concept modals that have two meanings depending on context, and modals used in the past tense. Modal verbs do not conjugate or take infinitives, and are followed by the bare infinitive form of the main verb. Their meaning depends on whether they express concepts like permission, obligation, possibility, or past habitual actions.