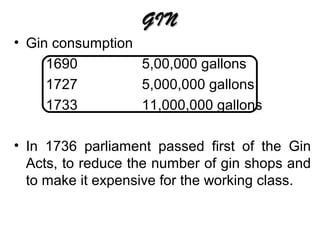
Gin originated in the 16th century when English soldiers brought it from the Netherlands. It grew rapidly in popularity in England during the 17th-18th centuries until acts of Parliament in the 1730s-1750s taxed and regulated gin production and sales. Gin is produced by infusing juniper and other botanicals into a neutral grain spirit. Common botanicals include coriander, angelica, cassia bark, orris root, and citrus peels. Gin can be flavored through either a head or cold mix method before aging. Popular gin brands include Gordon's, Tanqueray, and Bombay Sapphire. Plymouth gin uses local soft water in its production process. Flavored varieties