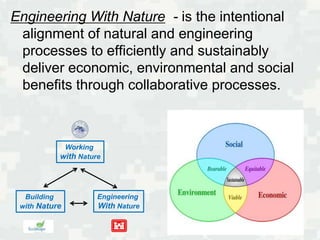
This document discusses the US Army Corps of Engineers' (USACE) initiative called "Engineering With Nature" (EWN), which aims to intentionally align natural and engineering processes to deliver both economic and environmental benefits. It provides the example of "Green Breakwaters," which modifies existing breakwater infrastructure to incorporate fish habitat features. The document summarizes a pilot project modifying breakwater toe blocks in Cleveland Harbor and proposes a similar project enhancing breakwaters in Ashtabula, Ohio. It outlines next steps to advance the EWN approach within USACE projects and research.