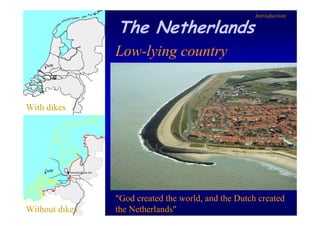
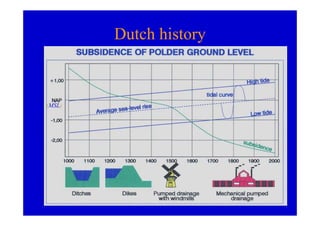
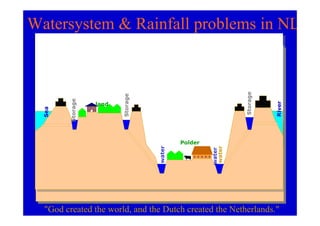
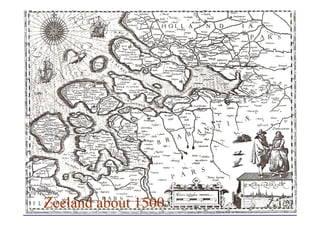
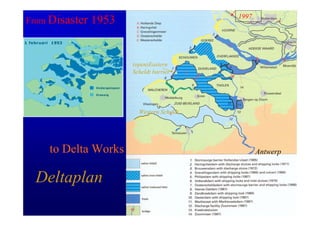
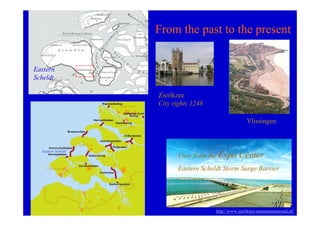
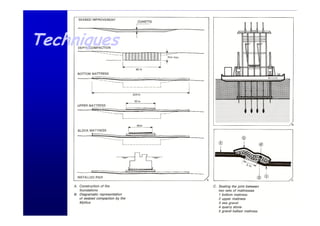
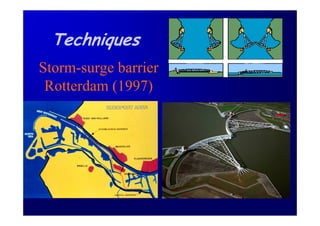
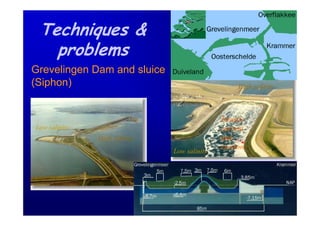
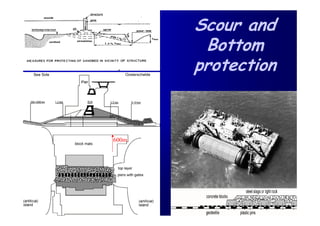
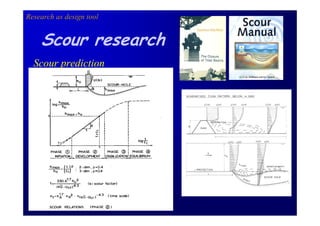
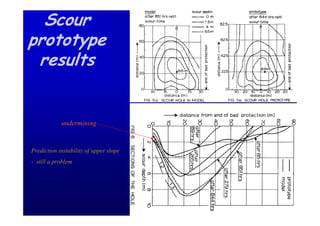
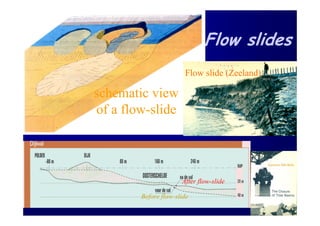
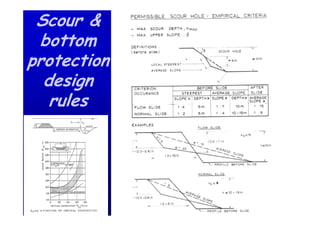
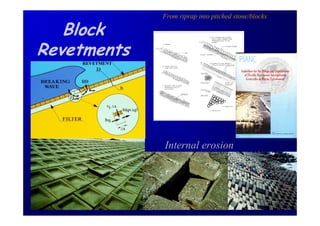
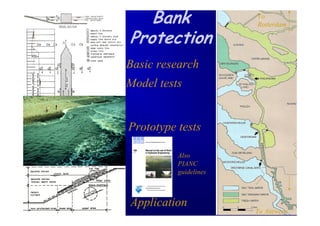
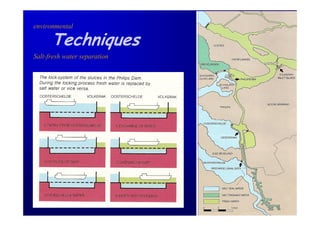
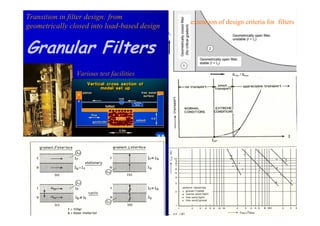
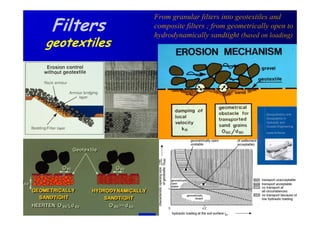
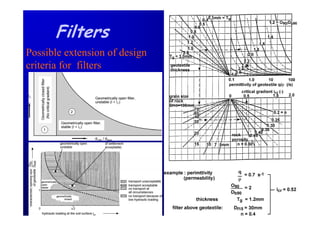
The document discusses the impact of the Delta Works project in the Netherlands on recent developments in hydraulic engineering. The Delta Works project involved large-scale flood protection works completed in the 1970s, including storm surge barriers and coastal defenses. This project stimulated new research and innovation, leading to transitions in techniques such as the use of geotextiles and composite filters, load-based filter design, block revetments, and consideration of environmental impacts in project design. The Delta Works had a significant influence on advancing knowledge and practice in hydraulic engineering.