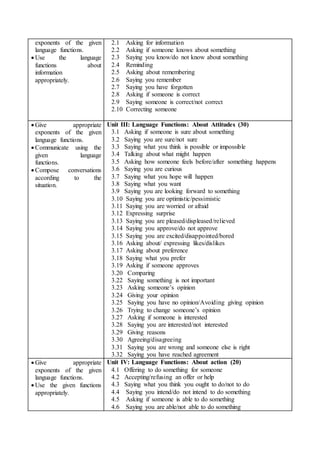
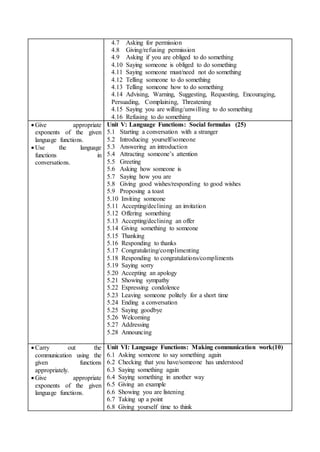
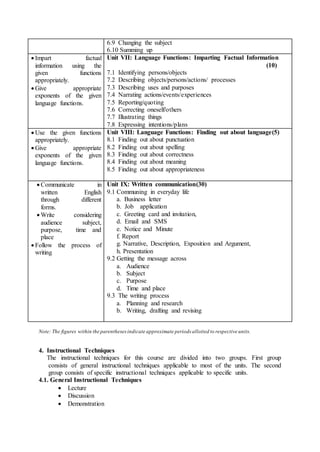
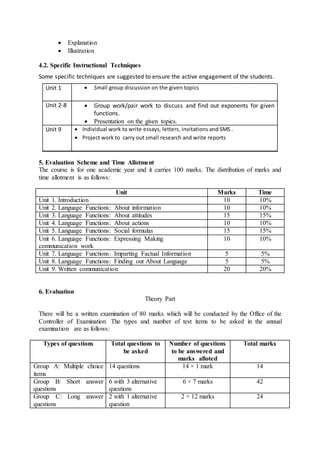
This document outlines an English communication course for B.Ed students. The course aims to develop students' functional English skills through 9 units covering various language functions. It will assess students with an 80-mark written exam and 20-mark practical exam testing their communicative skills. The written exam contains multiple choice, short answer, and long answer questions. Throughout the course, students will practice language functions through group activities, presentations and individual writing assignments like letters and reports.