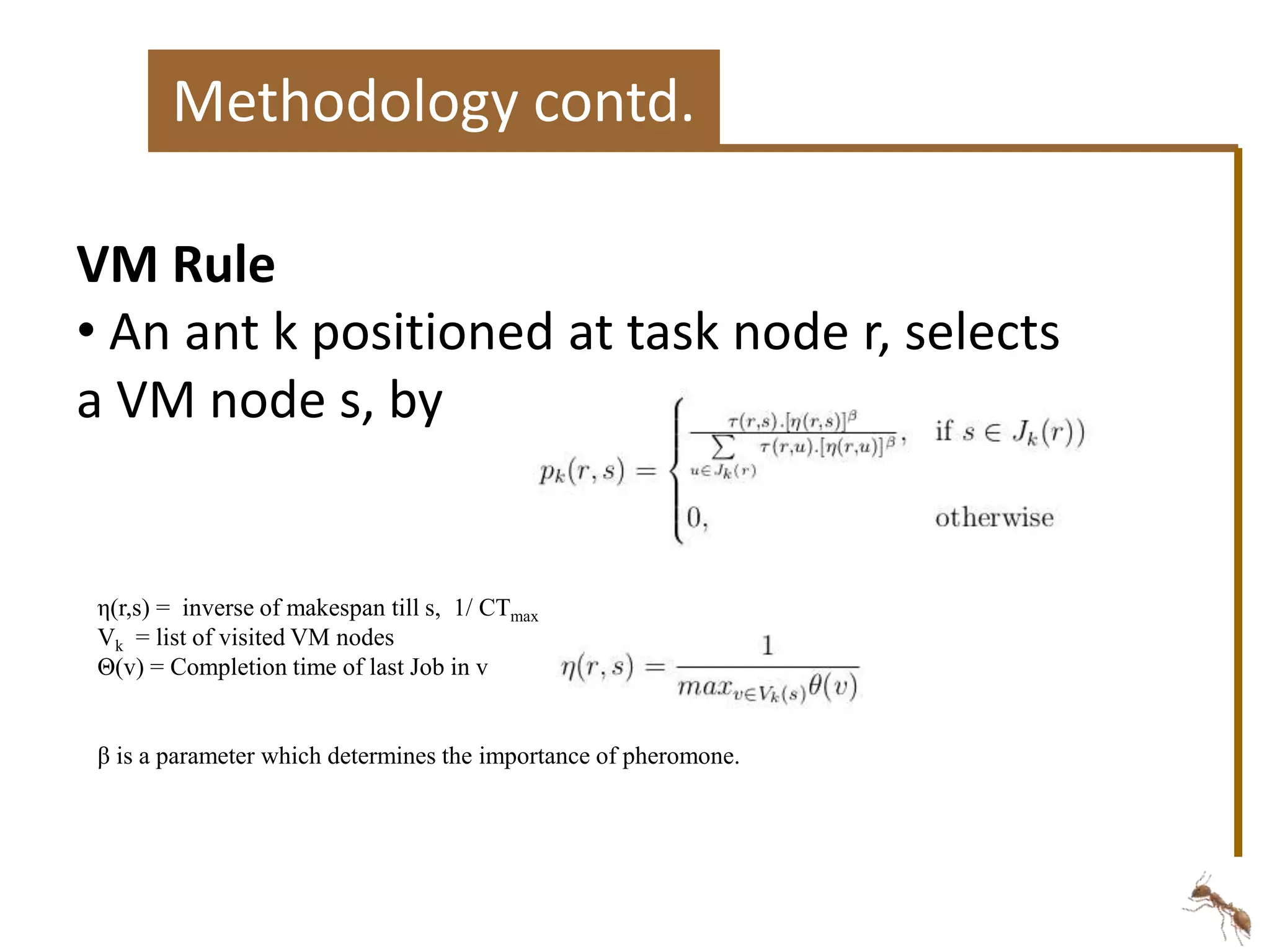
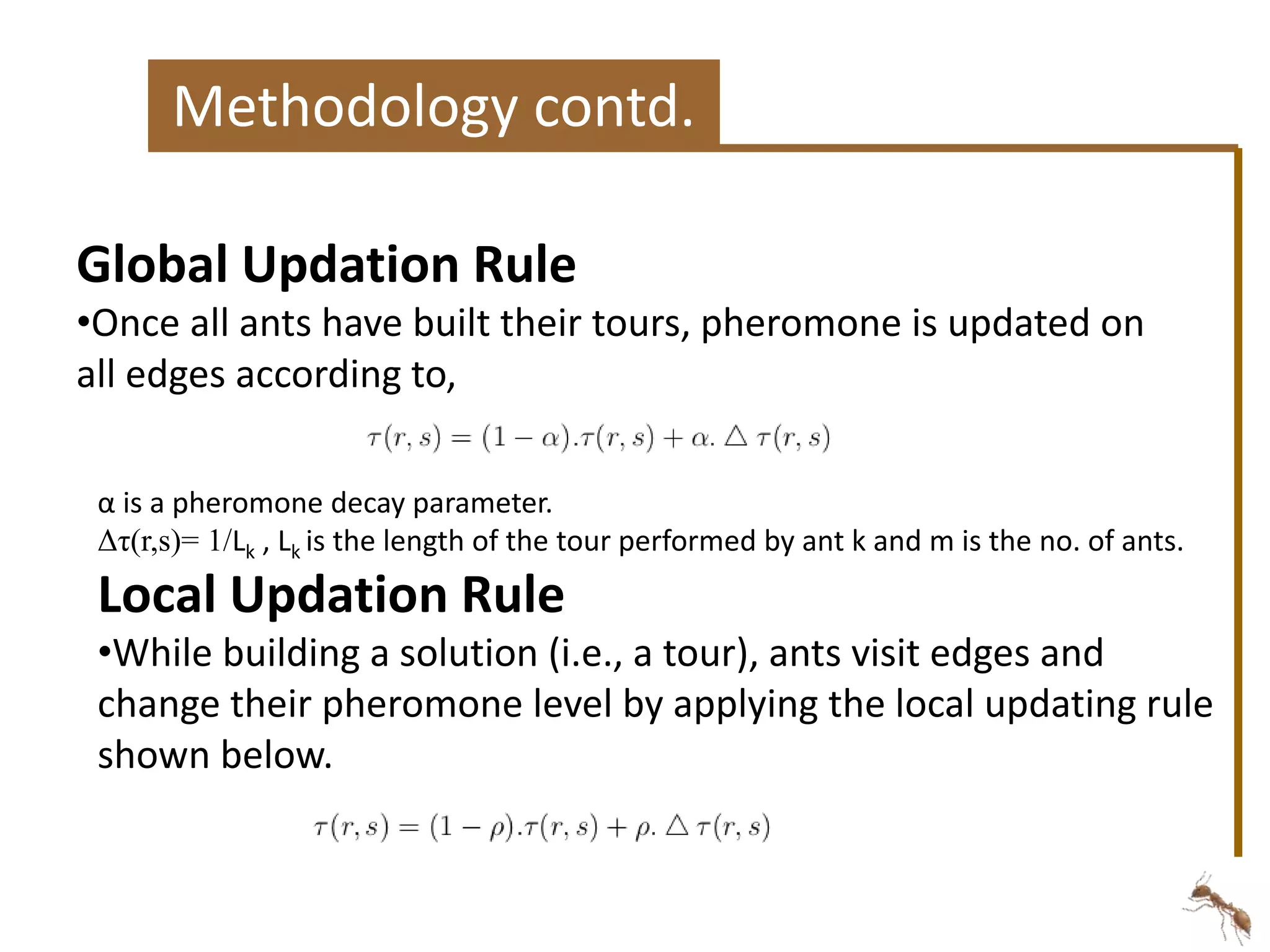
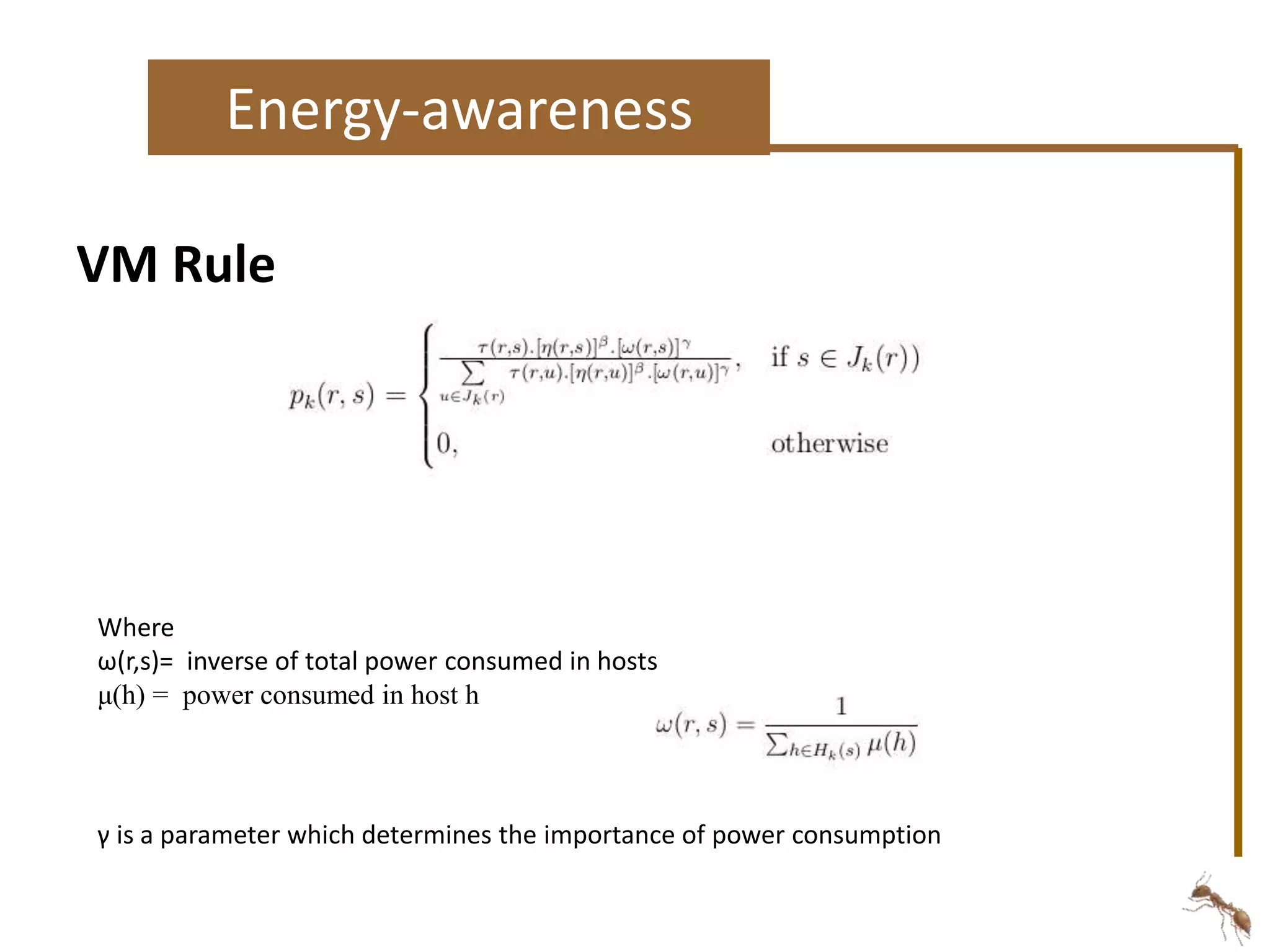
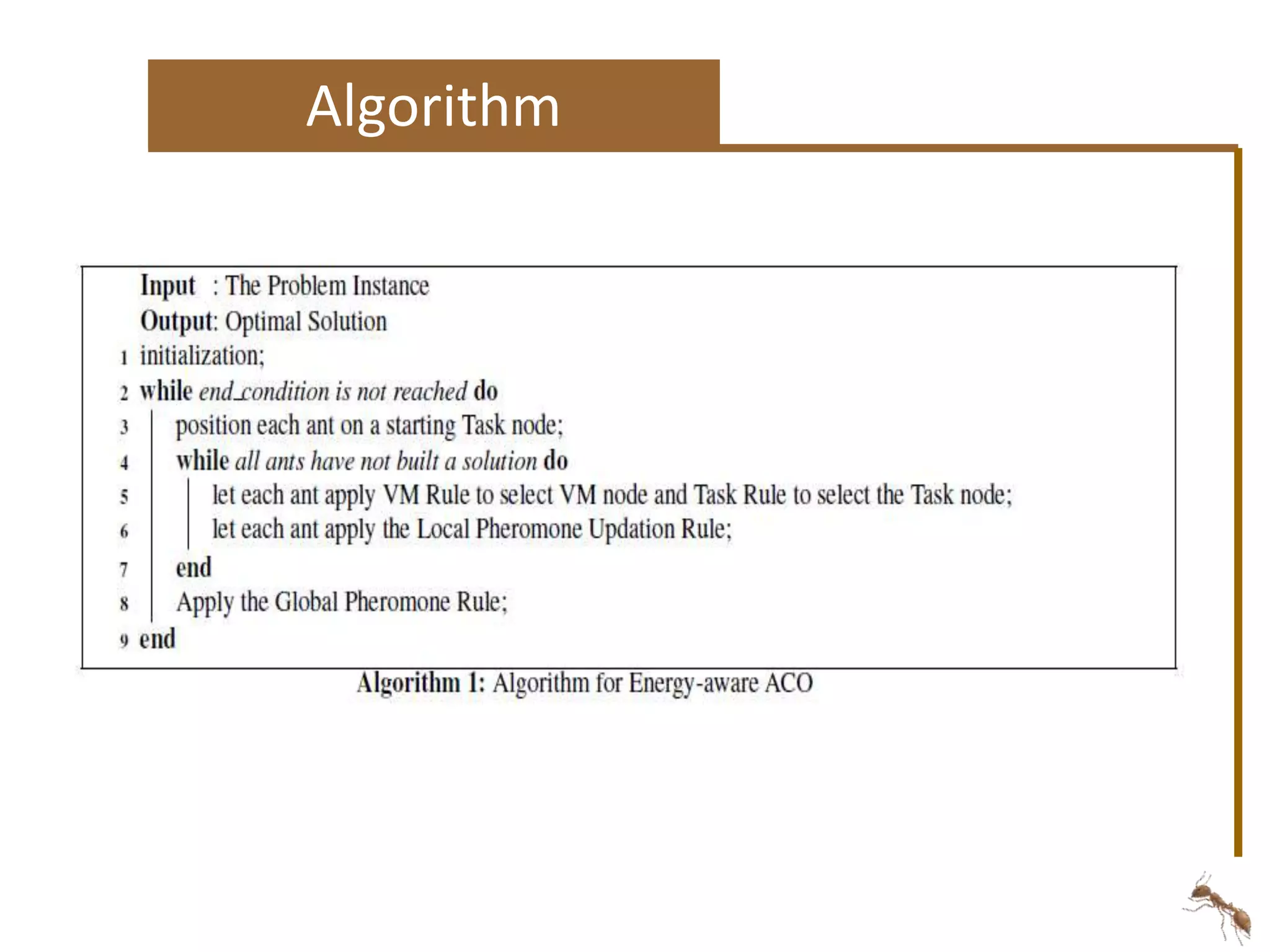
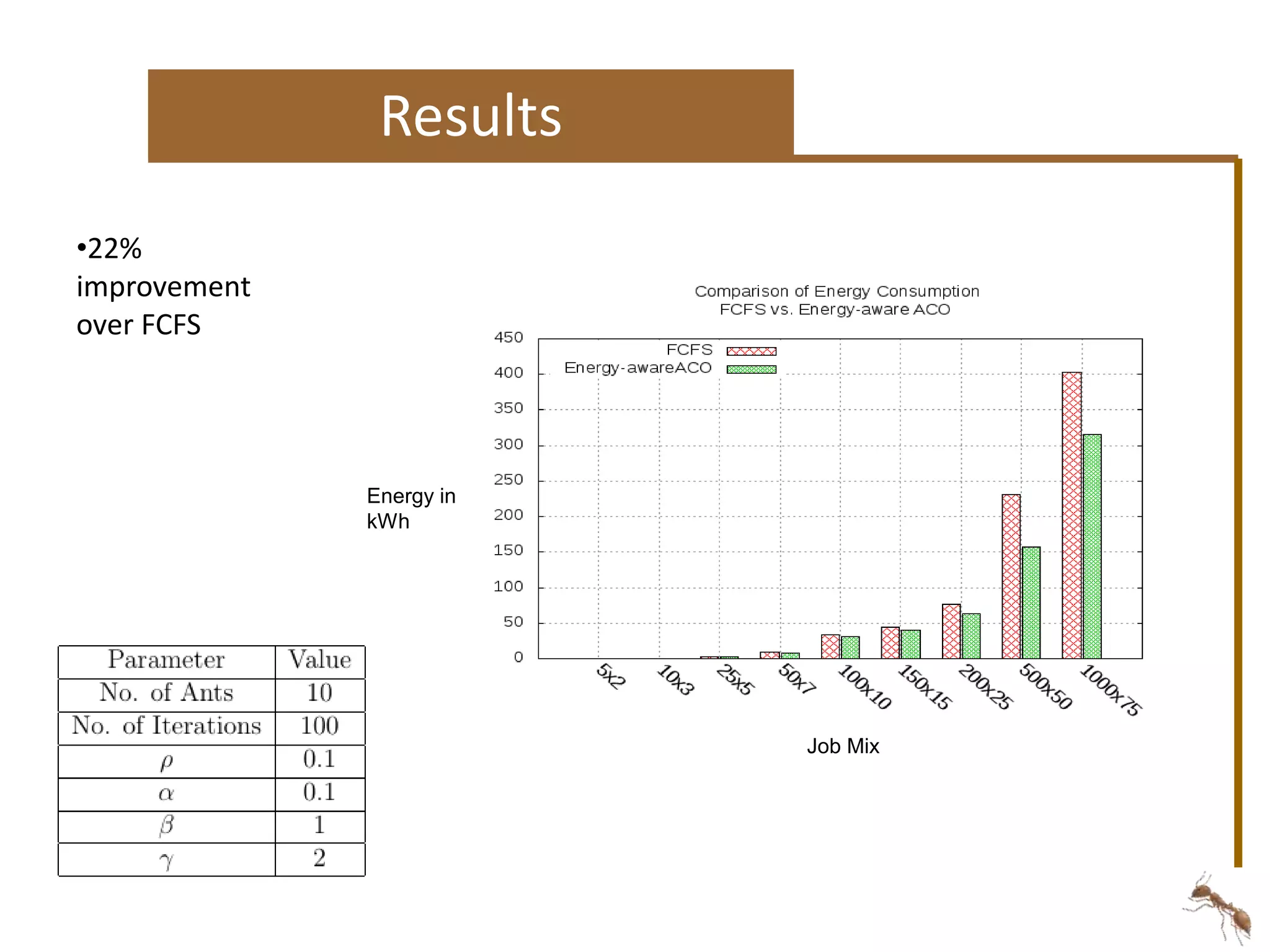
The document proposes an energy-aware task scheduling algorithm using ant colony optimization for cloud computing. It aims to minimize energy consumption in datacenters by scheduling tasks efficiently across virtual machines and physical hosts. The algorithm uses concepts from ant colony optimization to probabilistically determine good task-to-resource allocations. The results show that the proposed approach reduces energy consumption by 22% compared to a first-come, first-served scheduling approach.



![Task Scheduling
•Scheduling [3] the n tasks (T1, T2,…,Tn) to m
Virtual Machines (VM1, VM2,…,VMm) running
on p Physical hosts (P1, P2,…,Pp) in such a way
that maximum completion time or makespan of
these n tasks will be minimized.
•n>m>p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conference-final-140910011909-phpapp01/75/Energy-aware-Task-Scheduling-using-Ant-colony-Optimization-in-cloud-5-2048.jpg)

![System Model
•Cloudsim [16]
•CIS registry hold
information about the
resources
•Scheduler (or Broker)
is enhanced to be an
energy-aware
scheduler](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conference-final-140910011909-phpapp01/75/Energy-aware-Task-Scheduling-using-Ant-colony-Optimization-in-cloud-9-2048.jpg)
![System Model
•LP Model (Based on [13])
•ϕ = CPU Utilization
•Pidle = Power when
CPU is idle
•Pmax = Power when
CPU is fully utilized
•RT Model (Based on [12] )
•The Expected
Time to Compute is
given by
•Wi = Workload
•CCj = Computing
Capacity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conference-final-140910011909-phpapp01/75/Energy-aware-Task-Scheduling-using-Ant-colony-Optimization-in-cloud-10-2048.jpg)