This document reviews scheduling algorithms for workflow applications in cloud computing. It discusses characteristics of cloud computing, deployment and service models, and the importance of scheduling in cloud computing. The document analyzes several scheduling algorithms proposed in literature that consider parameters like makespan, cost, load balancing, and priority. It finds that algorithms like Max-Min, Min-Min, and HEFT perform better than traditional algorithms in optimizing these parameters for workflow scheduling in cloud environments.


![04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 3
Cloud computing is an emerging technology for enabling
convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of
configurable computing resources that can be rapidly
provisioned and released with minimal management effort or
service provider interaction[1]
Uses pay-per-use model](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-3-2048.jpg)

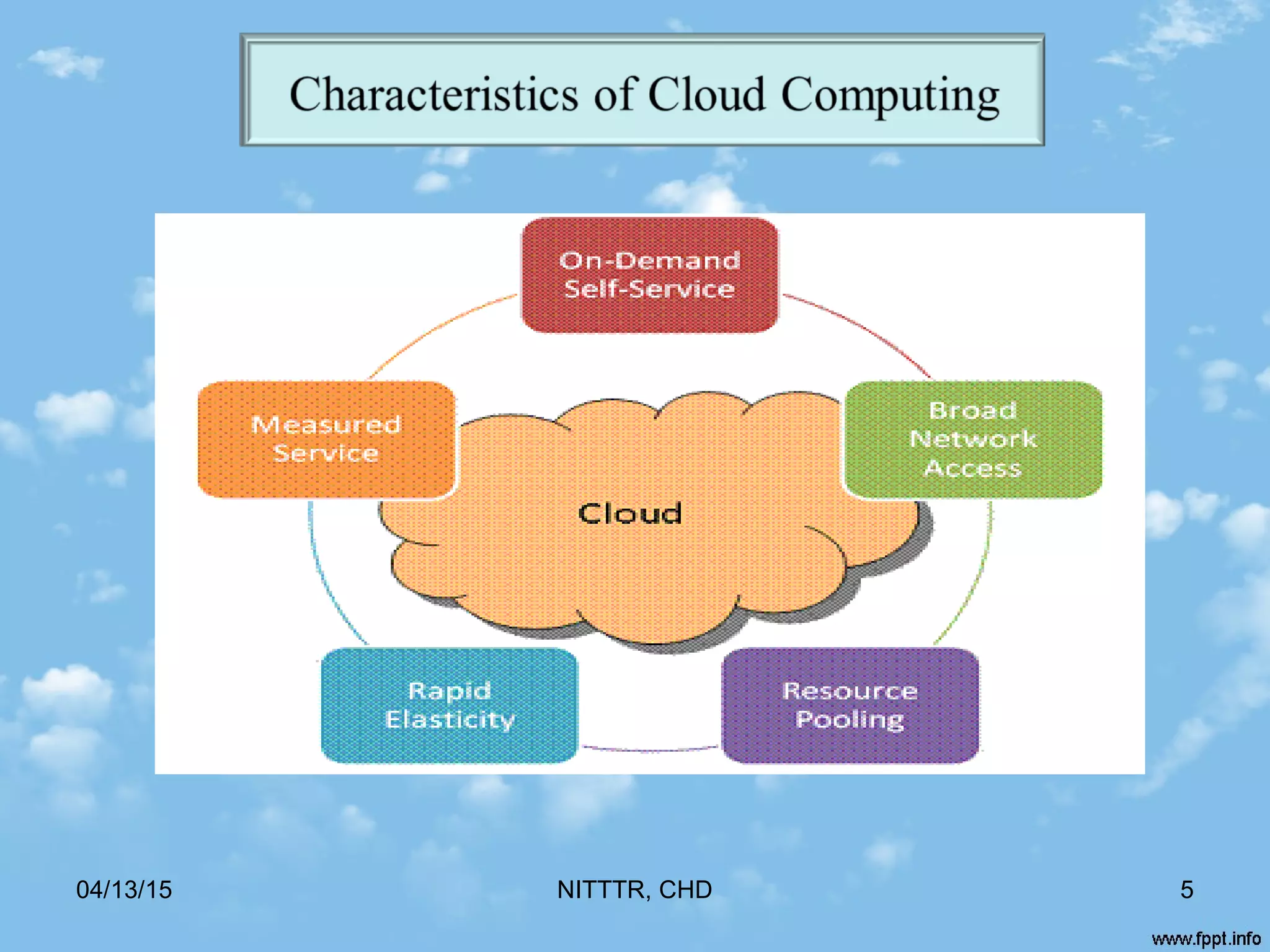
![ On-demand self-Service
* Cloud service provider provides huge services to the users on
their request [2]
Broad Network Access
* Computing resources are delivered over the network (e.g
Internet)
* Used by various client applications with different platforms
(such as laptops and mobile phones) [2]
Resource Pooling
* Cloud provider provide pool of resource that can be
dynamically assigned to multiple consumers [3]
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-6-2048.jpg)
![ Rapid Elasticity
* Cloud resources can be dynamically provisioned and released
automatically with user demand [2]
Measured Service
* Cloud systems automatically control and manage the resources
depending on the needs of users [3]
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-7-2048.jpg)
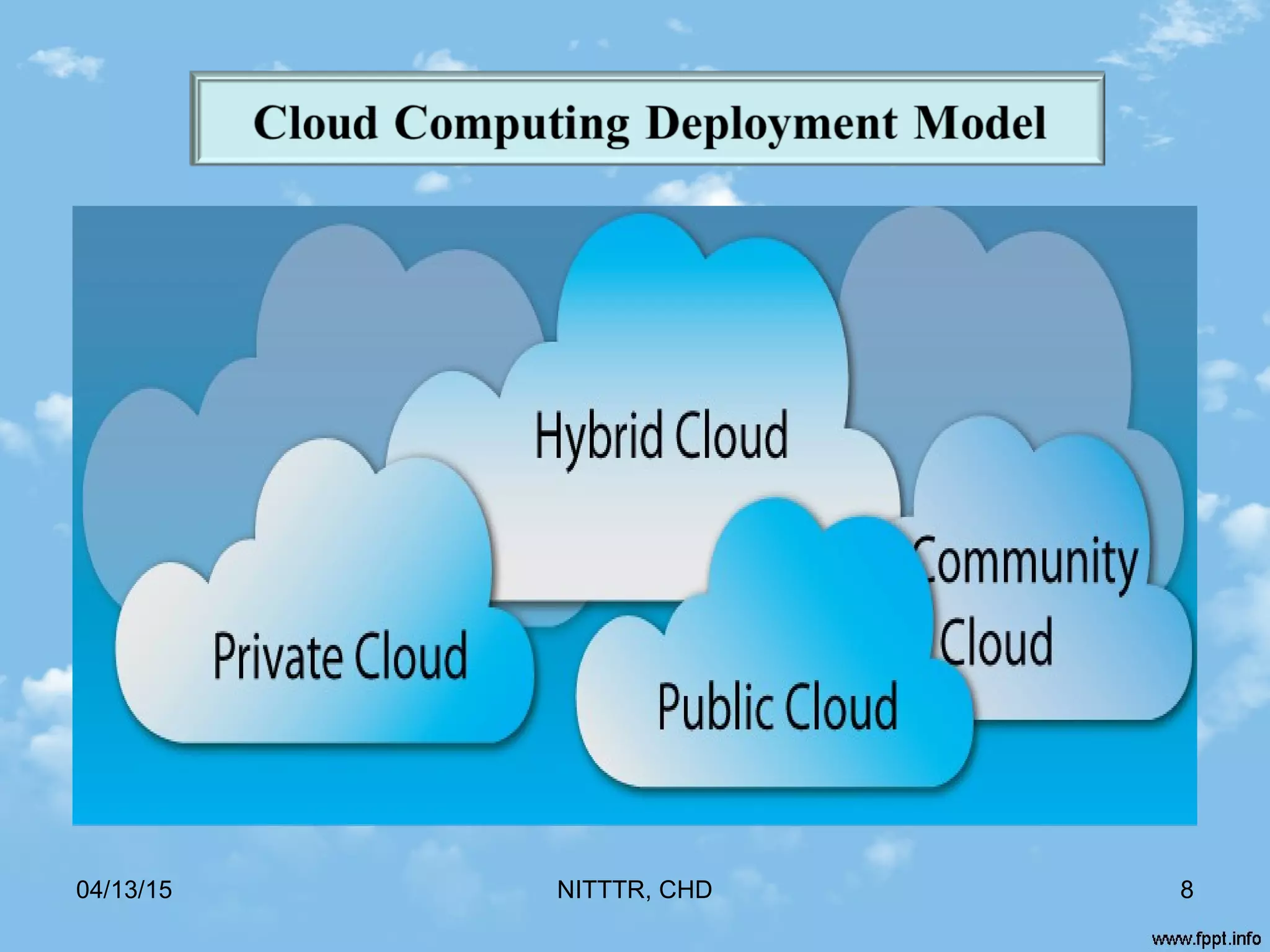
![ Private Cloud
* Used by the IT industry’s to provide the more security of data and
application [3]
Public Cloud
* Elasticity
* Reducing operation cost of IT Infrastructure [4]
Community Cloud
* Infrastructure shared by several organizations
Hybrid Cloud
* Combination of two or more deployment models [4]
04/13/15 9NITTTR, CHD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-9-2048.jpg)
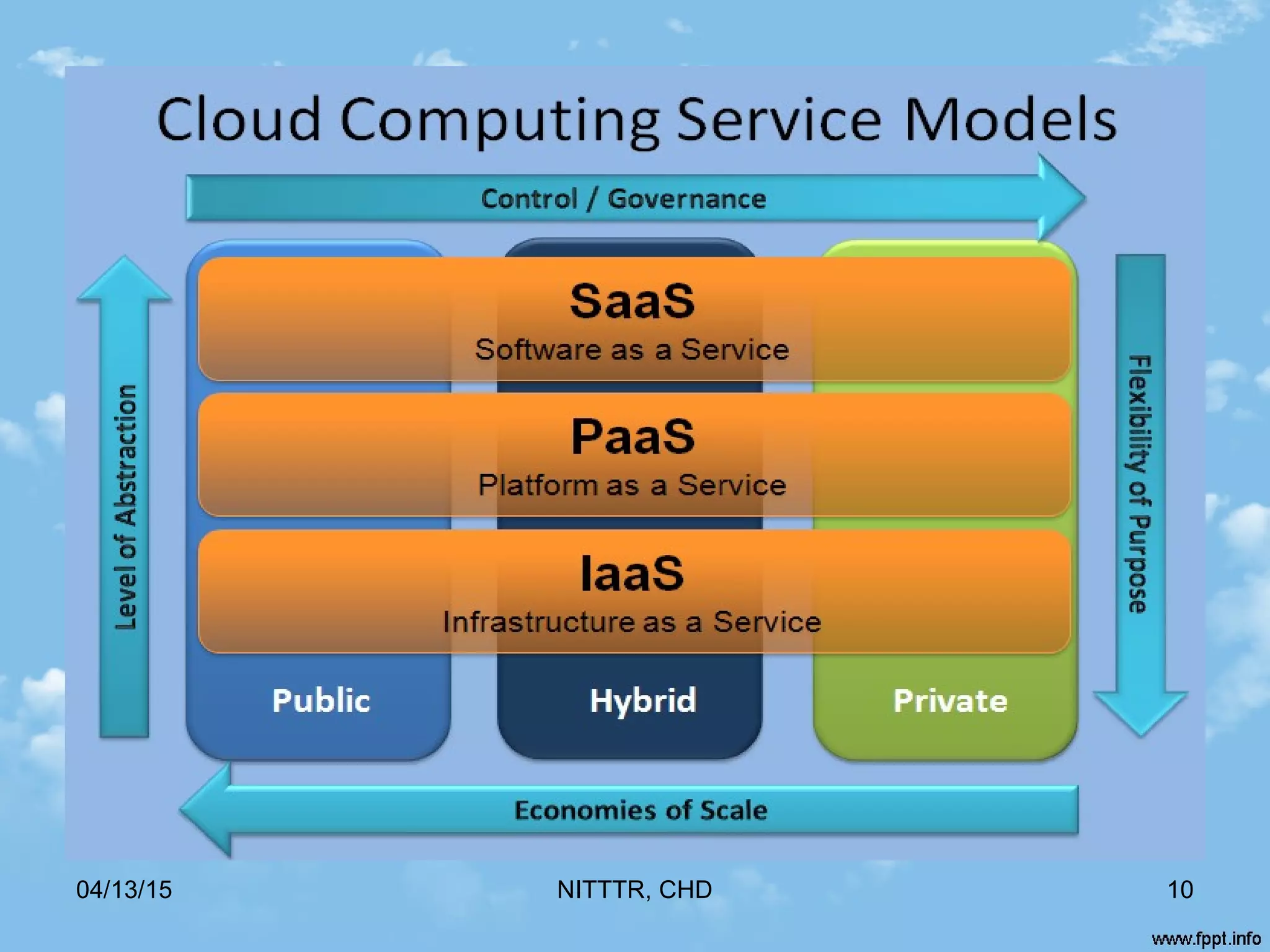
![ SaaS (Software as a Service)
* Application is hosted on the cloud as a service to the customers [3]
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
* Provides and manages programming languages, libraries, services,
programming frameworks and inbuilt tools [4]
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
* Provide, manage and control the underlying infrastructure
including data storage, network resources and computing servers
[4]
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-11-2048.jpg)
![ Maps and manages execution of inter-dependent tasks on
distributed resources [5]
Types
Independent Task Scheduling
Workflow Scheduling
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-13-2048.jpg)
![ Many users are competing for the shared resources on the cloud
Scheduler has no control over the resources
Workflow applications are either computation-intensive or data-
intensive. These applications required large data transferred between
the multiple sites [5]
Different resources have different processing power
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-14-2048.jpg)

![Author Scheduling
Parameters
Tools Findings
Xiao Li Fang et
al.
( 2014)
[6]
• Makespan
• Resource
Utilization
CloudSim Minimize
makespan &
implement load
balancing
N. chopra and
S. Singh(2013)
[7]
• Deadline
• Cost
WorkflowSim Complete workflow
within deadline and
reduce cost
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-16-2048.jpg)
![Author Scheduling
Parameters
Tools Findings
T Amudha, T T
Dhivyaprabha
(2011) [8]
• Utilization
rate
• Makespan
• Priority
CloudSim Solve load balancing
problem and reduce
makespan as compare to
WMTM, Min-Min
Yifei Zhang
Yan-e Mao
(2010) [9]
• Makespan GridSim Generate 14% less
makespan than
generic algorithms
Qi Cao et al.
(2009) [10]
• Cost CloudSim Measure cost more
accurate and performance
of the activities
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-17-2048.jpg)
![Author Scheduling
Parameters
Tools Findings
Mustafizur
Rahman,
RajKumar
Buyya(2007)
[11]
• Priority
• Makespan
GridSim Generate better schedule
and perform better than
HEFT, Min-Min &
Max-Min
Sakellariou
Rizos, et al.
(2004)[12]
• Priority
• Time
CloudSim Perform better than
Min-Min and Max-Min
He Xiao
Shan, et al.
(2003) [13]
• Makespan
• Bandwidth
Grid
Environment
Outperform than
traditional Min-Min
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-18-2048.jpg)

![[1] Zhang Qi, Lu Cheng and Raouf Boutaba, “Cloud computing: state-
of-the-art and research Challenges,” Journal of Internet Services and
Applications, Vol.1, Issue No.1, pp.7-18, 2010.
[2] Peeyush Mathur and Nikhil Nishchal , “ Cloud Computing: New
Challenge to the entire computer Industry,” International
Conference on Parallel, Distributed and Grid Compuitng, pp.223-
228,2010.
[3] Bhaskar Prasad Rimal, Eunmi Choi, “A taxonomy and survey of
cloud computing systems,” International Joint Conference on INC,
IMS and IDC, pp.44-51, 2009.
04/13/15 20NITTTR, CHD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-20-2048.jpg)
![04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 21
[4] Yashpalsinh Jadej, Kriti Modi, “Cloud Computing –Concepts,
Architecture and Challenges ,”International Conference on
Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technologies, pp. 887-890,
2012.
[5] Bittencourt, Luiz Femando and Edmundo Roberto Mauro Madeira,
“HCOC: a cost optimization algorithm for workflow scheduling in
hybrid clouds,” Journal of Internet Services and Applications, Vol.
2, Issue No. 3, pp. 207-227, 2011.
[6] Xiao Fang Li, Yingchi Mao, Xianjian Xiao and Yanbin Zhuang,
“An Improved Max-Min Task-Scheduling Algorithm for Elastic
Cloud,” International Symposium on Computer, pp.340-343, 2014.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-21-2048.jpg)
![04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 22
[7]Nitish Chopra, Sarbjeet Singh, “HEFT based Workflow Scheduling
Algorithm for Cost Optimization within Deadline in Hybrid
Clouds,” International Conference on Computing Communications
and Networking Technologies, pp.1-6, 2013.
[8] T Amudha, T T Dhivyaprabha, “QoS Priority Based Scheduling
and Proposed Framework for Task Scheduling in a Grid
environment,” International Conference on Recent Trends in
Information Technology, pp.650-655, 2011.
[9]Yifei Zhang,Yan-e Mao, “A SCP BASED Critical Path Scheduling
Strategy for Data-Intensive Workflows,” International Conference
on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, pp.1735-1739, 2010.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-22-2048.jpg)
![[10]Qi Cao, Zhi Bo Wei and Wen Mao Gong, “An optimized
Algorithm for Task Scheduling Based on Activity Based Costing in
Cloud Computing,” International Conference on Bioinformatics and
Biomedical Engineering, pp.1-3, 2009.
[11] Mustafizur Rahman, Srikumar Venugopal, Rajkumar Buyya,“A
Dynamic Critical Path Algorithm for Scheduling Scientific
Workflow Applications on Cloud Grids,” International Conference
on e-Science and Grid Computing, pp.35-42, 2007.
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-23-2048.jpg)
![[12] Sakellariou, Rizos, and Henan Zhao, “A hybrid heuristic for DAG
scheduling on heterogeneous systems,” Parallel and Distributed
Processing Symposium, pp.111-116, 2004.
[13] He XiaoShan, Sun XianH and Gregor von Laszewski, “QoS
Guided Min-Min Heuristic for Grid Task Scheduling ” Journal of
Computer Science and Technology, Vol.18, Issue No.4, pp.442-
451, 2003.
[14] S.Devipriya and C.Ramesh, “Improved Max_Min Heuristic Model
for Task Scheduling in Cloud, ”International Conference on Green
Computing, Communication and Conservation of Energy, pp.883-
888, 2013.
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-24-2048.jpg)
![[15] Zhcheng Cai, Xiaoping Li, Jatinder N.D. Gupta, “Critical Path-
Based Iterative Heuristic for Workflow Scheduling in Utility and
Cloud Computing,” International Conference on Service Oriented
Computing, pp.207-221, 2013.
[16] Juan J. Durillo, Hamid Mohammadi Fard, Radu Prodan, “
MOHEFT: A Multi-Objective List-based Method for Workflow
Scheduling,” International Conference on Cloud Computing
Technology and Science, pp.185-192, 2012.
.
04/13/15 NITTTR, CHD 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/schedulingpaper-150413111925-conversion-gate01/75/REVIEW-PAPER-on-Scheduling-in-Cloud-Computing-25-2048.jpg)
