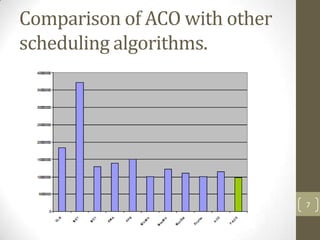
This document discusses using machine learning algorithms for job scheduling in a grid computing environment. It aims to minimize makespan, the total time to complete all tasks, by learning from past scheduling experiences. It proposes using ant colony optimization, where artificial ants probabilistically choose task-machine pairs to incrementally find optimal schedules. The algorithm is compared to other scheduling methods and extended to online scheduling by classifying jobs with attributes to appropriate machines. A feasibility study demonstrates classification and scheduling of test jobs using machine learning tools.


![Alternative solutions
• Grid scheduling algorithms such as
Opportunistic load balancing (OLB)
Maximum Standard deviation heuristic
• ANT COLONY OPTIMIZATION(ACO)
[1]
• ACO is a population based search optimization technique
developed in the year 1997
• This algorithm simulates a colony of artificial ants that behave
as cooperative agents where they are allowed to search and
reinforce pathways (solutions) in order to find the optimal
ones.
• This approach which is population based has been successfully
applied to many NP-hard optimization problems.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cse12007casestudy-131223010350-phpapp01/85/JOB-SCHEDULING-USING-ANT-COLONY-OPTIMIZATION-ALGORITHM-4-320.jpg)





![References
• [1].Ant Colony System: A Cooperative Learning Approach to the
Salesman Problem , Marco Dorigo,IEEE 1997
Traveling
• [2].An Improved Ant Algorithm for Grid Scheduling Problem,
Bagherzadeh, Mojtaba MadadyarAdeh,IEEE 2009
Jamshid
• [3].Task Scheduling with Load Balancing using Multiple Ant Colonies Optimization
in Grid Computing, Liang Bai, Yan-Li Hu, Song-Yang Lao, Wei-Ming Zhang,2010
IEEE
• [4].A Task scheduling for grid scheduling using Ant colony Optimization,Jun
Mao,IEEE 2011
• [5].Evaluating Scheduling Algorithms on Distributed
Ryan J. Wisnesky
Computational Grids,
• [6] Improved job grouping based PSO algorithm for task scheduling in grid
computing,Sudha sadhasivam,IJEST 2010
• [7] Wikipedia-Particle Swarm optimization.
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cse12007casestudy-131223010350-phpapp01/85/JOB-SCHEDULING-USING-ANT-COLONY-OPTIMIZATION-ALGORITHM-11-320.jpg)