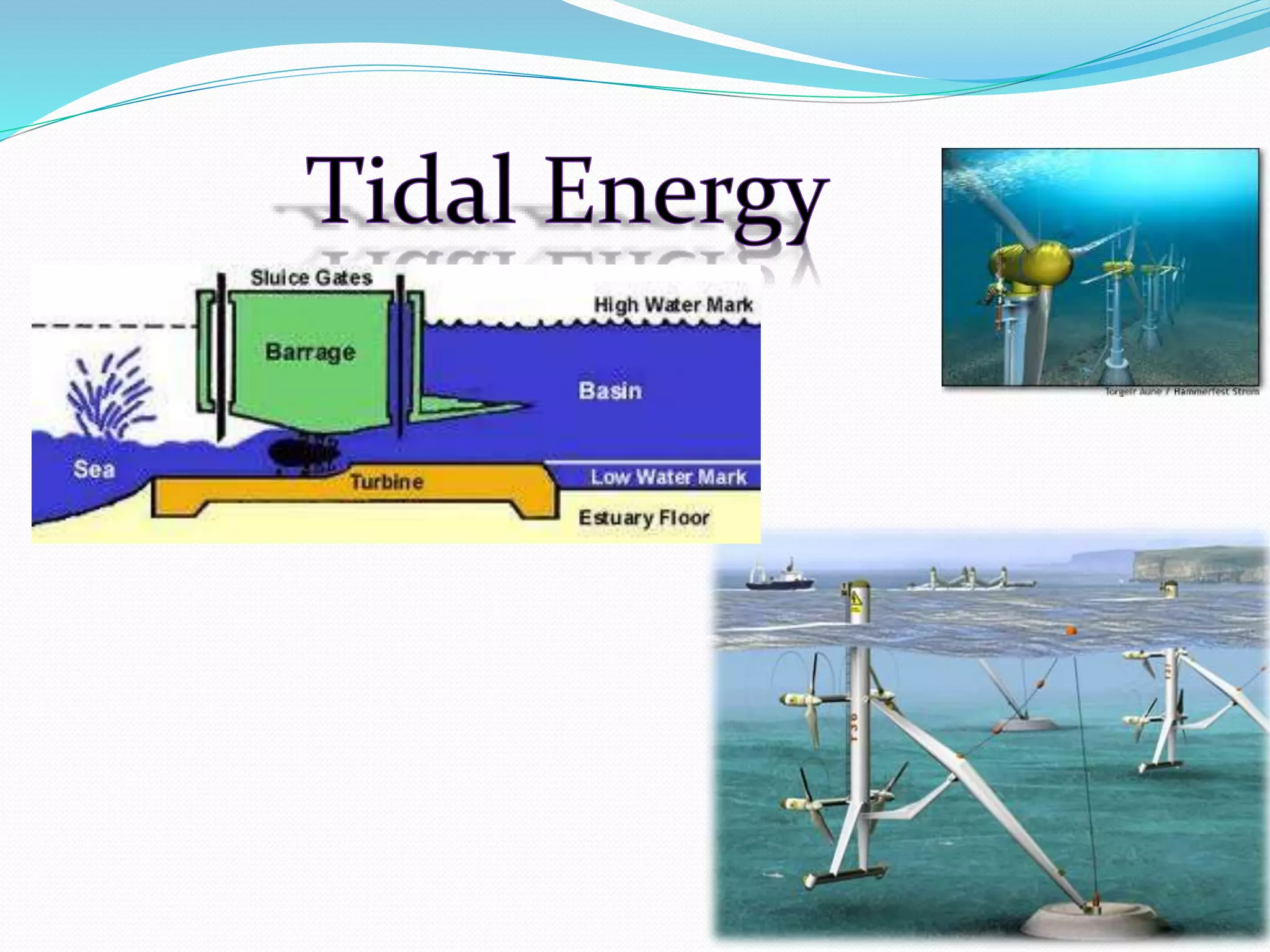
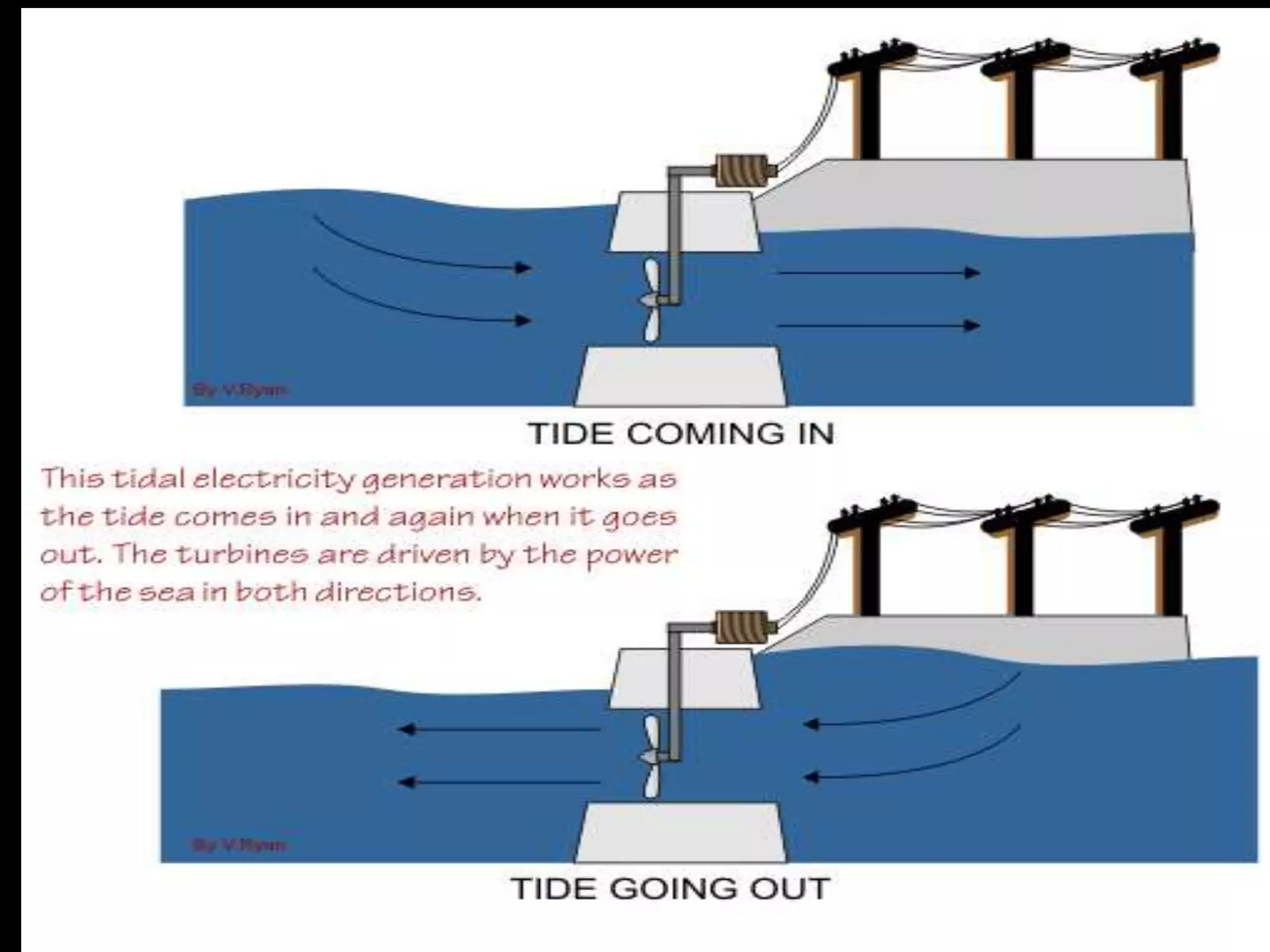
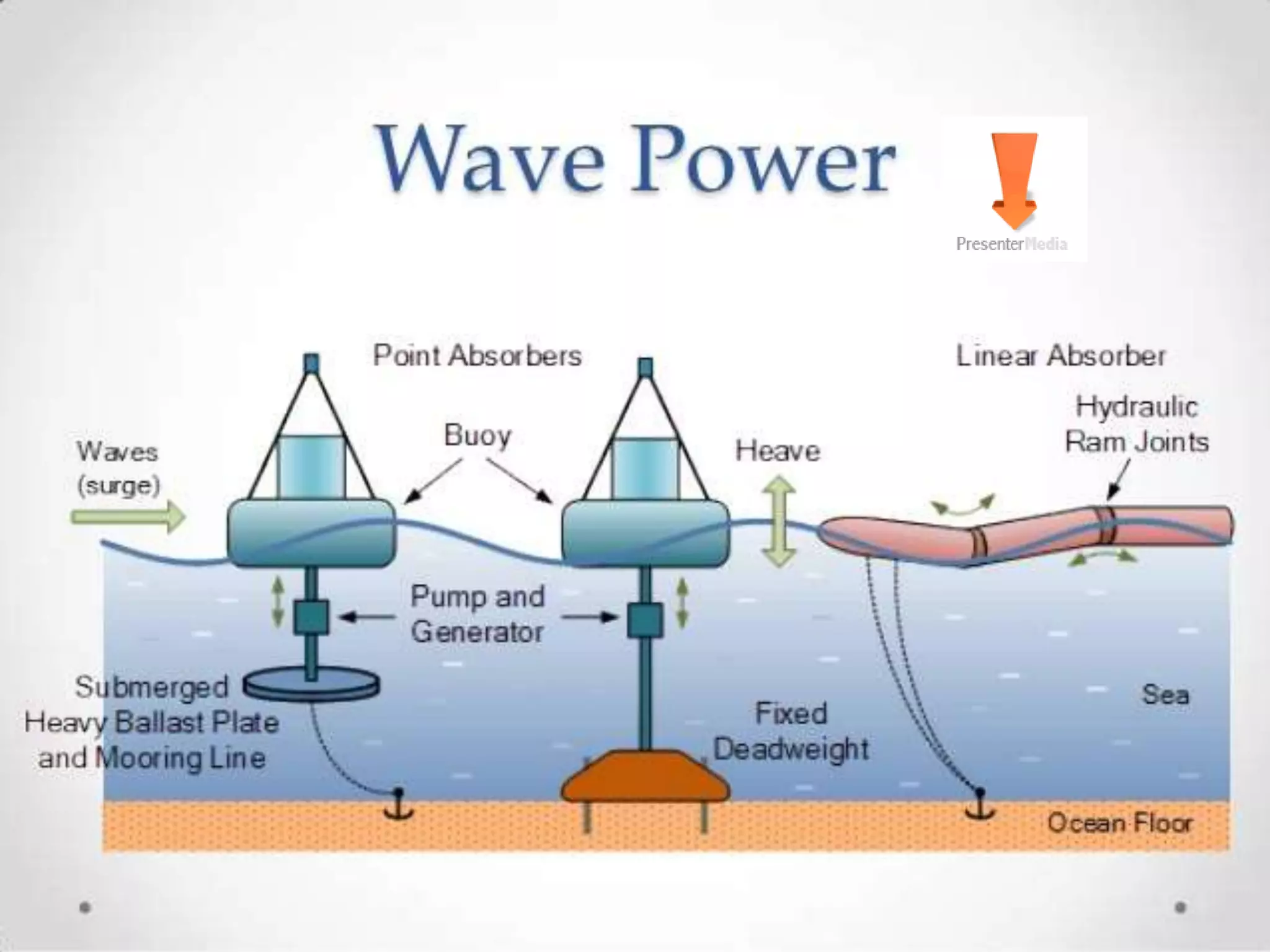
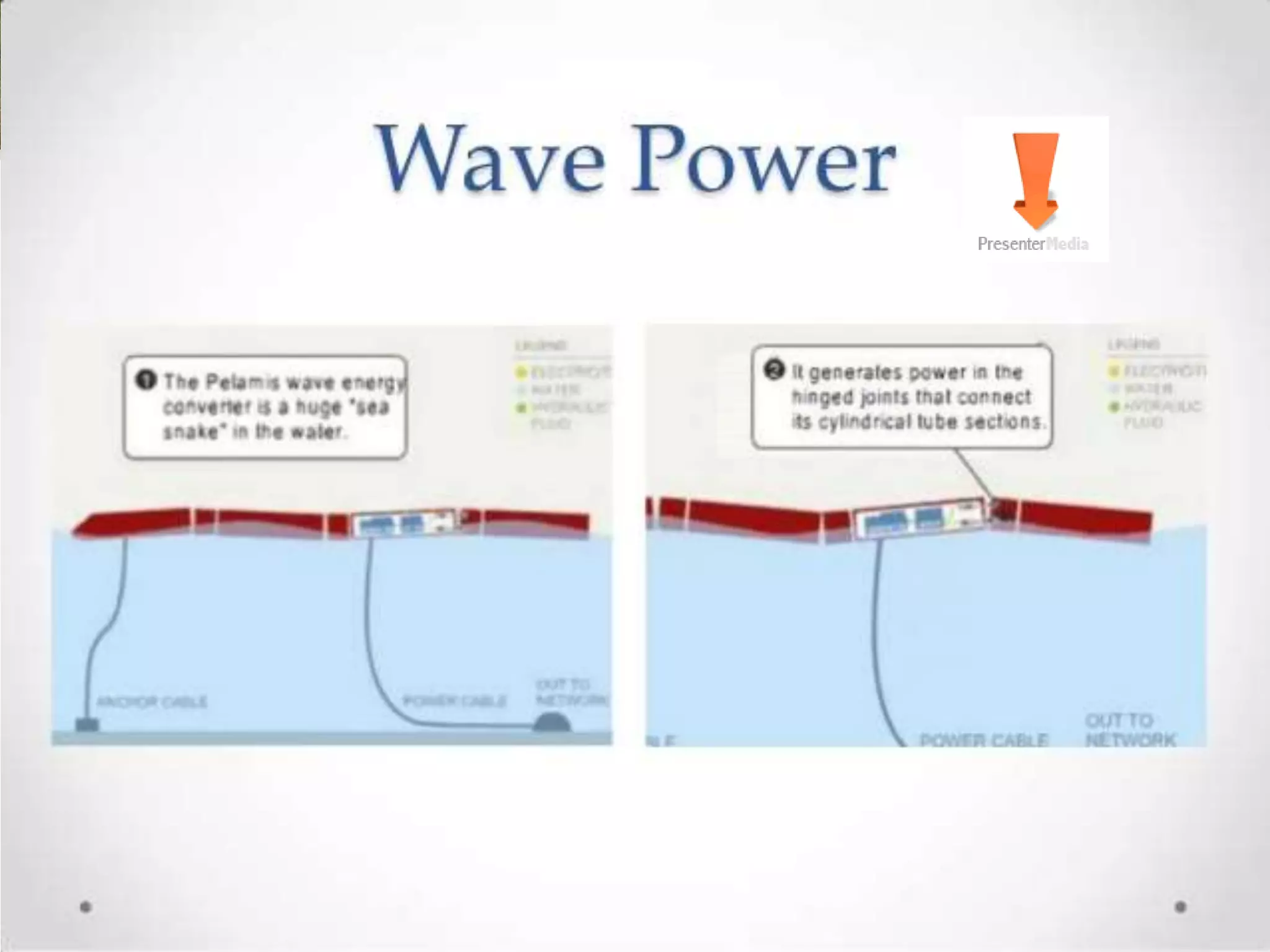
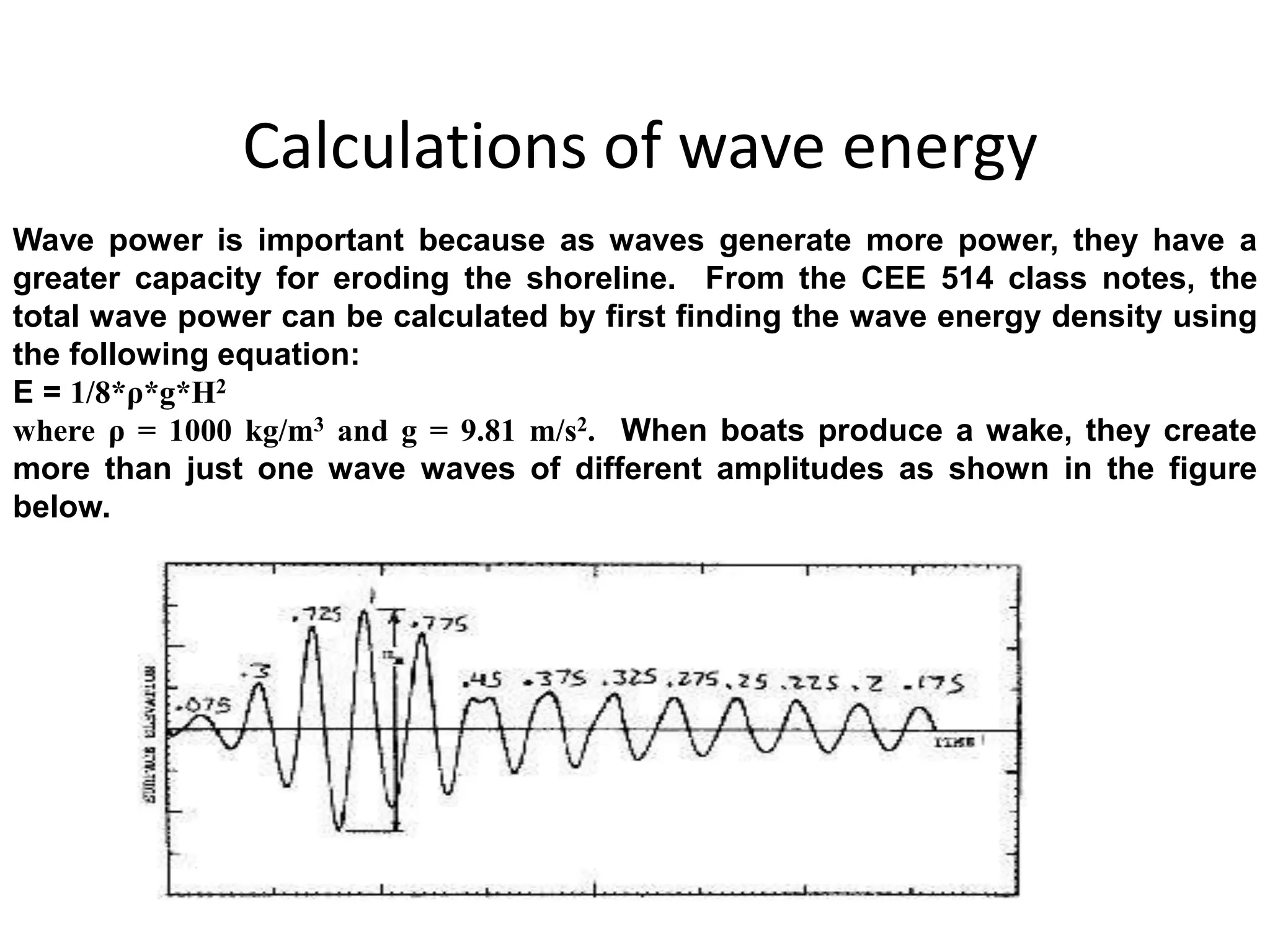
This document discusses various renewable energy sources including tidal energy, wind energy, hydro power, nuclear energy, and wave energy. It provides details on calculating tidal and wave energy. The document acknowledges those who helped with the project and discusses the importance of energy conservation. It describes different methods of tidal power generation such as tidal stream generators, tidal barrages, and dynamic tidal power. Overall, the document serves as a reference on renewable energy sources with a focus on tidal energy technologies.



![Acknowledgement
• For the successful completion of the project, I would like
to thank first to our teachers [Mrs. Rama mam,
Mrs.Gavathri mam, Mr.Jaiswal sir, Mrs.Jesna mam, Mrs.
Alka mam] who introduced me to this project and
incepted me with the idea of how to proceed with the
project. This project definitely would have not been a
successful project without his assistance and vigilance.
There are many other people whom I would like to
thank. First I would like to thank our parents for helping
me in the project with their own ideas and suggestions.
Again, I would like to thank the above mentioned people.
Without them, this project could not have been the way it
is.
• I hope you'd enjoy the project.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/energyoftarunsppt3-141026042616-conversion-gate02/75/non-conventional-sources-of-energy-4-2048.jpg)