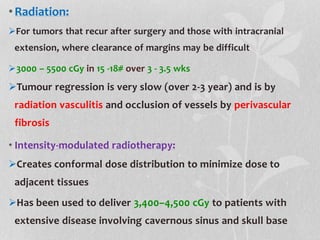
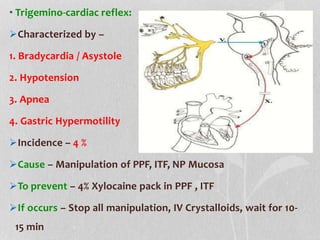
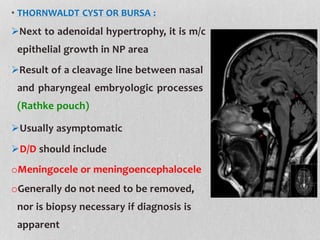
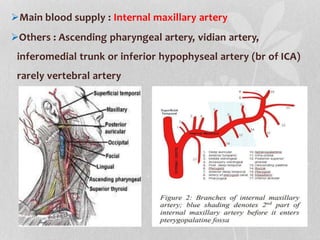
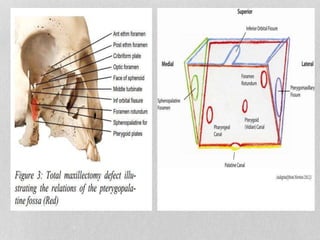
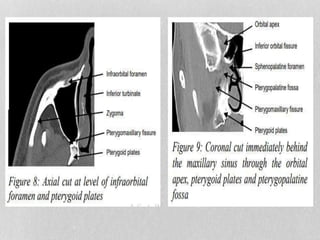
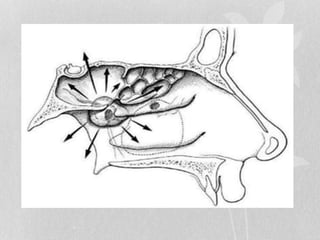
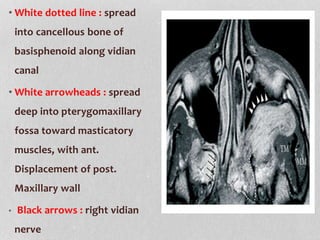
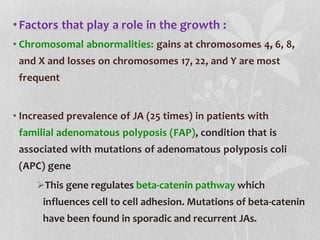
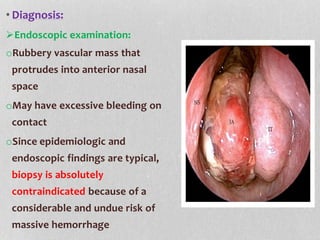
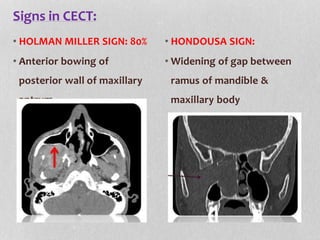
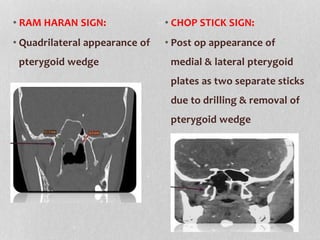
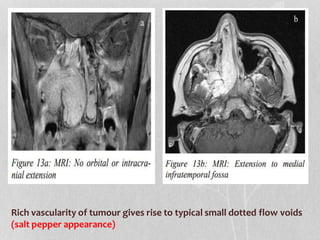
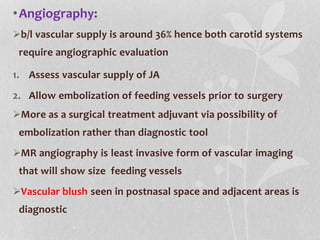
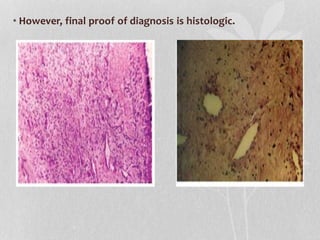
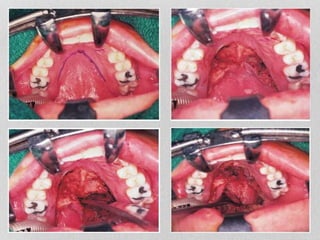
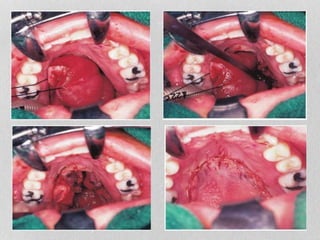
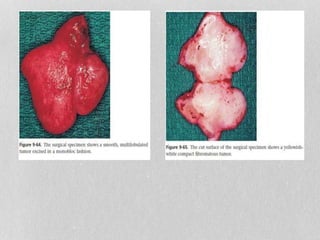
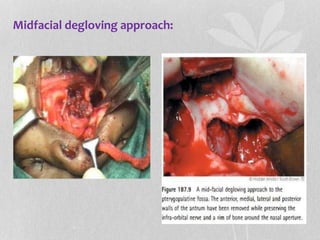
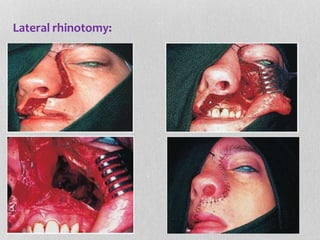
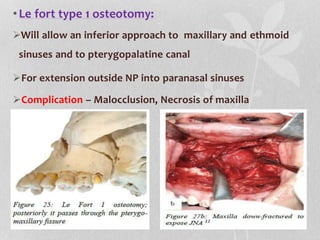
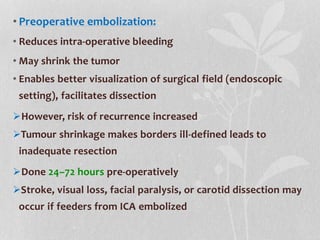
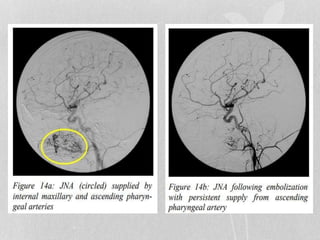
This document provides information on juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma (JNA), a benign but locally invasive vascular tumor that most commonly occurs in adolescent boys. It discusses the presentation, diagnostic approach, pathology, theories of pathogenesis, surgical techniques for resection including endoscopic and open approaches, preoperative embolization, and hormonal therapies for JNA. Imaging studies such as CT and MRI are useful for diagnosis by identifying the vascular tumor's site of origin and patterns of growth. Complete surgical resection is the main treatment, with the approach depending on tumor size, location and prior embolization.





























![•Hormonal Therapy:
Tumor enlargement with administration of testosterone and
shrinkage with estrogen therapy
Flutamide (2-methyl-n-[4-nitro-3{trifluoromethyl}phenyl]
propanamide), orally active non-steroidal androgen
antagonist
Gates et al. tumor reduction of 44% in 4 of 5 cases
receiving 6 week treatment course
Labra et al. tumor reduction of only 11.1% in 6 cases
receiving 3 week treatment course
Current recommendation 6 week course of flutamide as
adjuvant therapy in post-pubertal patient](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jna-230617194417-350354bc/85/JNA-pptx-57-320.jpg)