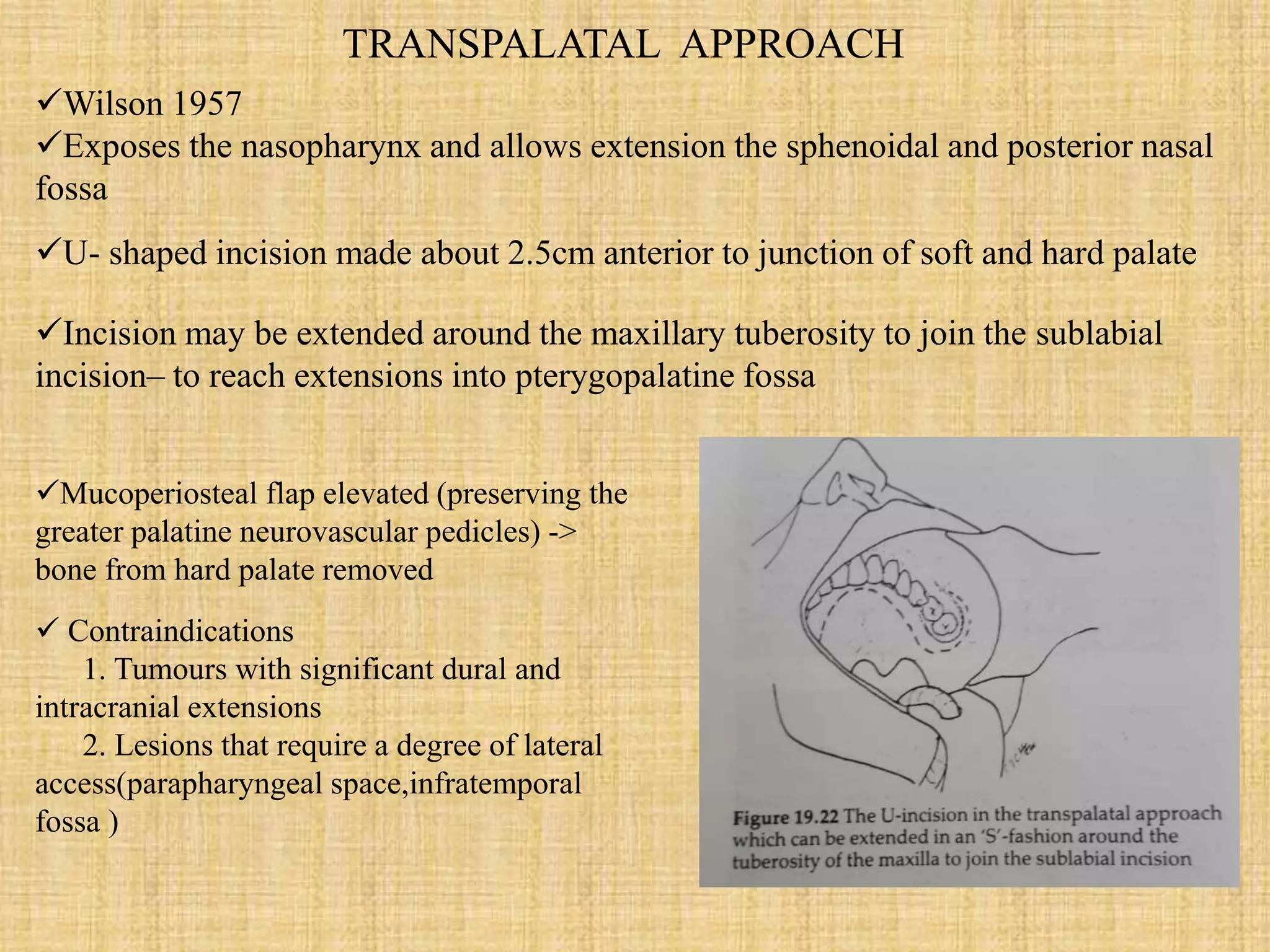
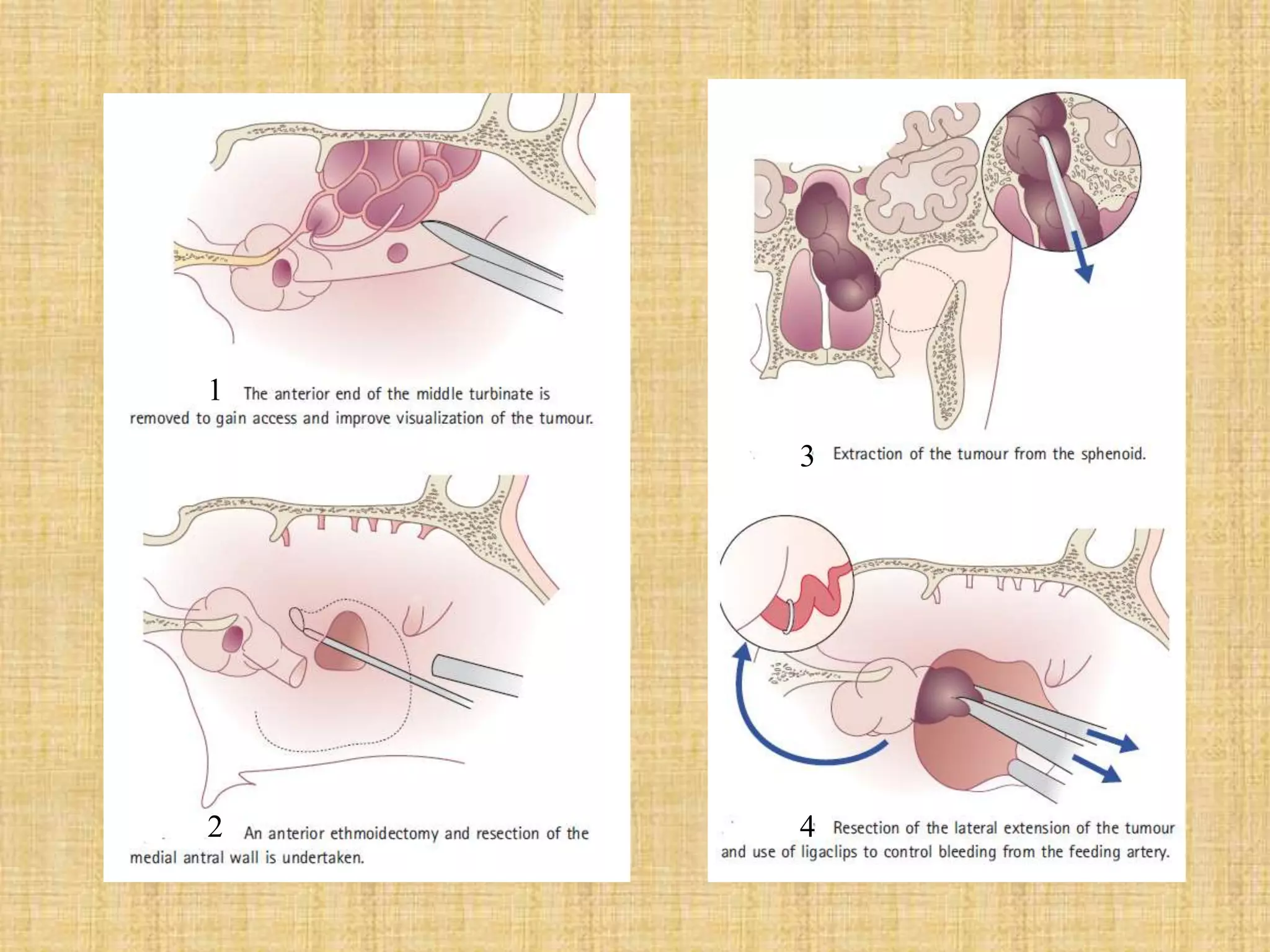
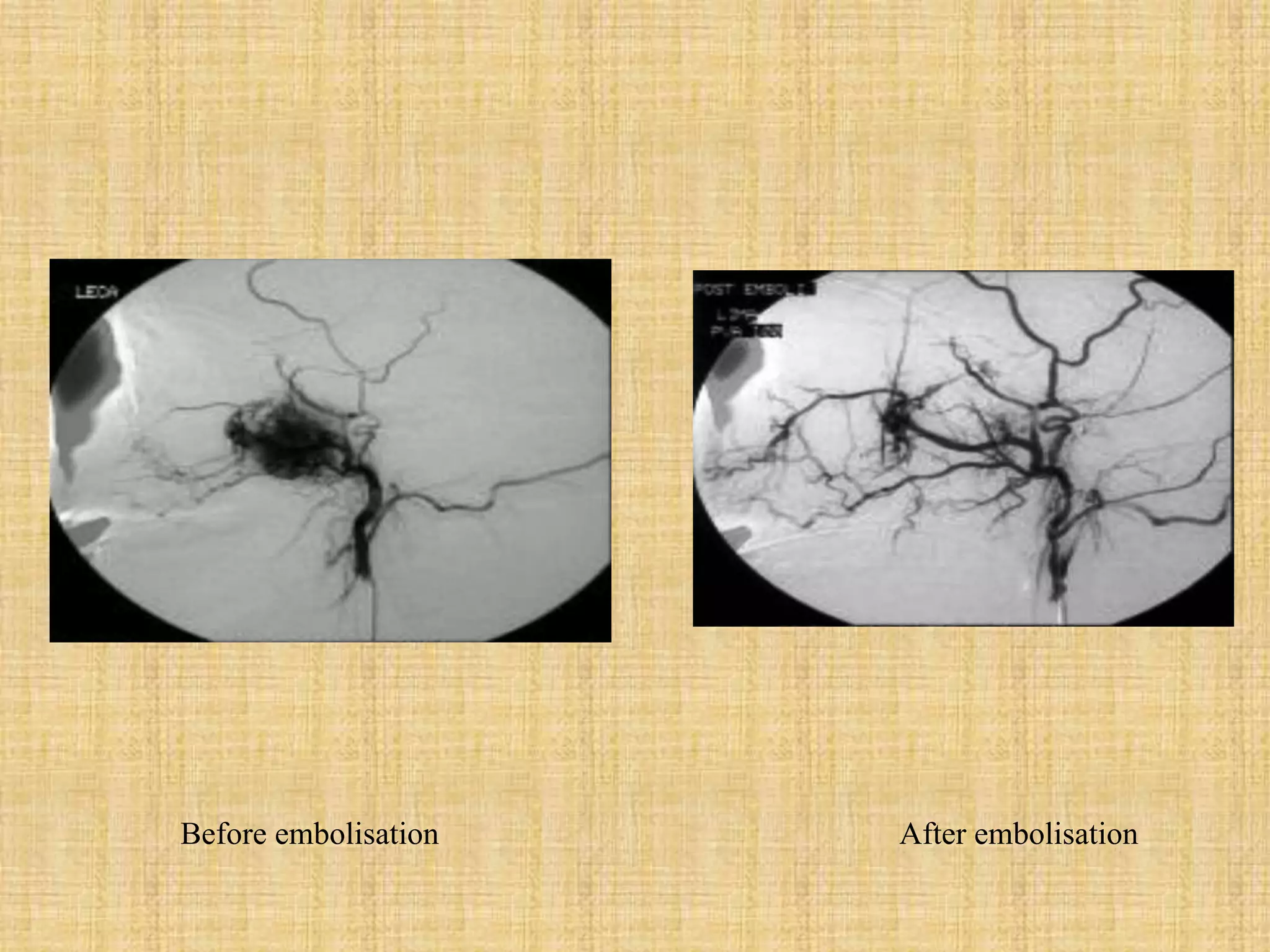
The document provides information on Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA), a rare benign tumor that most commonly affects adolescent males. It discusses the tumor's etiology, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation including imaging, and various treatment modalities. The current primary treatments are surgical resection via various open or endoscopic approaches, with the goal of complete removal while minimizing complications and risk of recurrence. Future areas of research include investigating the role of hormones and growth factors in tumor development to identify potential non-surgical therapies.










![SITE OF ORIGIN
• Broad base
• Originate from the sphenopalatine foramen
• Some authors also suggest that they may arise from
the nasopharyngeal vault or choana.
• A recent study by Lloyd et al(1999); suggests that
angiofibroma takes origin in the pterygopalatine fossa
at the aperture of the pterygoid canal. [1]
[1] Lloyd, G, Howard, D, Phelps, P, and Cheesman, A. Juvenile angiofibroma: the lessons of 20 years of modern imaging.
J Laryngol Otol. 1999; 113(2): 127-34.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jnajuvenilenasopharyngealangiofibromacurrenttreatmentmodalitiesand-171001161253/75/Jna-juvenile-nasopharyngeal-angiofibroma-current-treatment-modalities-11-2048.jpg)