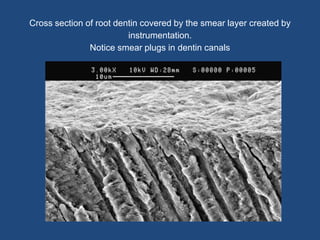
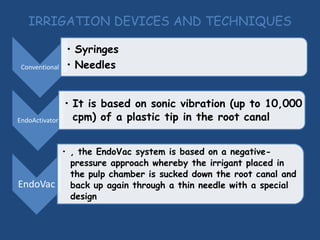
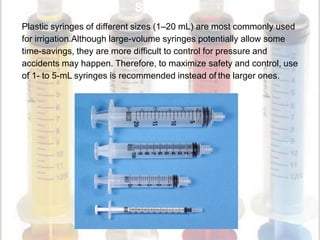
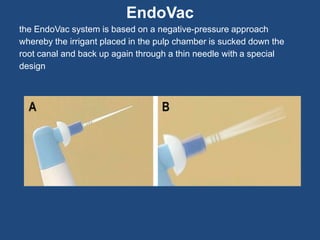
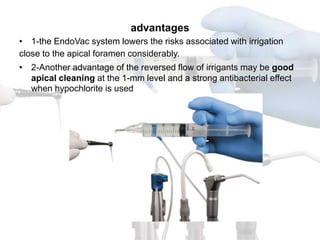
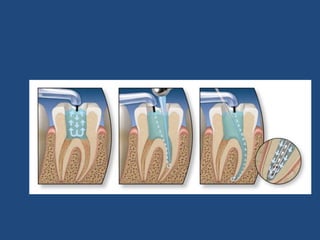
This document discusses endodontic irrigants and irrigation techniques. It describes the desired functions of irrigating solutions such as washing away debris, lubricating instruments, dissolving tissues, and killing bacteria. Sodium hypochlorite is the most commonly used irrigant due to its ability to dissolve organic material and kill bacteria, though it does not remove the smear layer. EDTA is often used along with sodium hypochlorite to remove the smear layer. Chlorhexidine has antimicrobial properties but does not dissolve tissues. Various irrigation devices and techniques are also discussed such as syringes, needles, sonic activation with EndoActivator, and negative pressure irrigation with EndoVac. Interactions