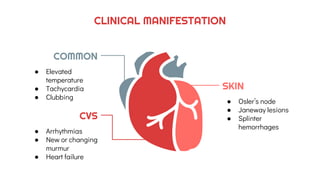
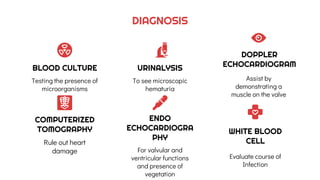
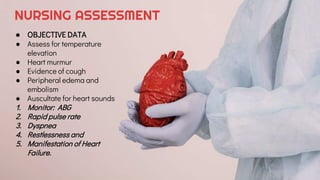
The document provides an overview of endocarditis, including its definition, pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and nursing management. It emphasizes the role of nursing assessments and interventions to address complications such as decreased cardiac output and ineffective breathing patterns. Key management strategies include administering oxygen therapy, antibiotics, and patient education.